Previously obscure N. Korean hacker group is now stronger than ever, say experts
February 21, 2018 Leave a comment
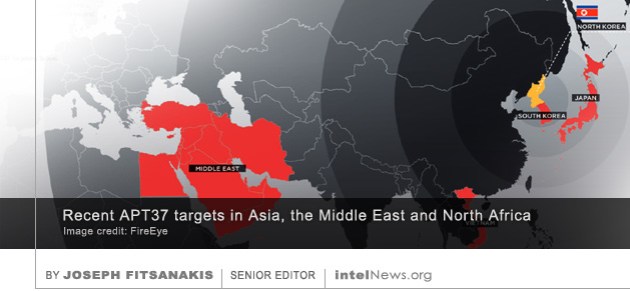 A little-known North Korean cyber espionage group has widened its scope and increased its sophistication in the past year, and now threatens targets worldwide, according to a new report by a leading cyber security firm. Since 2010, most cyber-attacks by North Korean hackers have been attributed to a group dubbed “Lazarus” by cyber security specialists. The Lazarus Group is thought to have perpetrated the infamous Sony Pictures attacks in 2014, and the worldwide wave or ransomware attacks dubbed WannaCry by experts in 2017. It is widely believed that the Lazarus Group operates on behalf of the government of North Korea. Most of its operations constitute destructive attacks —mostly cyber sabotage— and financial criminal activity.
A little-known North Korean cyber espionage group has widened its scope and increased its sophistication in the past year, and now threatens targets worldwide, according to a new report by a leading cyber security firm. Since 2010, most cyber-attacks by North Korean hackers have been attributed to a group dubbed “Lazarus” by cyber security specialists. The Lazarus Group is thought to have perpetrated the infamous Sony Pictures attacks in 2014, and the worldwide wave or ransomware attacks dubbed WannaCry by experts in 2017. It is widely believed that the Lazarus Group operates on behalf of the government of North Korea. Most of its operations constitute destructive attacks —mostly cyber sabotage— and financial criminal activity.
For the past six years, a smaller hacker element within the Lazarus Group has engaged in intelligence collection and cyber espionage. Cyber security researchers have dubbed this sub-element “APT37”, “ScarCruft” or “Group123”. Historically, APT37 has focused on civilian and military targets with links to the South Korean government. The hacker group has also targeted human rights groups and individual North Korean defectors living in South Korea. However, a new report warns that APT37 has significantly expanded its activities in terms of both scope and sophistication in the past year. The report, published on Tuesday by the cyber security firm FireEye, suggests that APT37 has recently struck at targets in countries like Vietnam and Japan, and that its activities have disrupted telecommunications networks and commercial hubs in the Middle East.
According to the FireEye report, aerospace companies, financial institutions and telecom- munications service providers in at least three continents have been targeted by APT37 in recent months. What is even more worrying, says the report, is that the hacker group is now capable of exploiting so-called “zero-day” vulnerabilities. These are software bugs and glitches in commonly used software, which have not been detected by software providers and are therefore exploitable by malicious hackers. FireEye said in its report that the North Korean regime will be tempted to use APT37 increasingly often “in previously unfamiliar roles and regions”, as cyber security experts are catching up with some of Pyongyang’s more visible hacker groups, such as Lazarus.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 21 February 2018 | Permalink
 A group of cyber spies with close links to the Iranian government is becoming increasingly competent and adept, and could soon bring down entire computer networks, according to a leading cyber security firm. The California-based cyber security company FireEye said that it has been monitoring the operations of the mysterious group of cyber spies since 2013. The company, whose clients include Sony Pictures, JP Morgan Chase and Target, said that the Iranian group appears to be especially interested in gathering secrets from aviation, aerospace and petrochemical companies.
A group of cyber spies with close links to the Iranian government is becoming increasingly competent and adept, and could soon bring down entire computer networks, according to a leading cyber security firm. The California-based cyber security company FireEye said that it has been monitoring the operations of the mysterious group of cyber spies since 2013. The company, whose clients include Sony Pictures, JP Morgan Chase and Target, said that the Iranian group appears to be especially interested in gathering secrets from aviation, aerospace and petrochemical companies.







Massive hacker attack triggers US National Security Council emergency meeting
December 15, 2020 by Joseph Fitsanakis 2 Comments
Although it was only discovered last week, the cyberespionage campaign is believed to date to last spring, possibly as early as March. Sources called it a highly sophisticated operation that originated from a “top-tier” adversary –a term that refers to a handful of state actors that have access to the most elite cyber operatives and advanced technologies known to exist.
As of last night, US government officials had not publicly identified the state actor believed to be behind the cyberespionage campaign, which experts have coined the “2020 supply chain attack”. But several American and European news outlets pointed to Russia as the culprit, citing sources familiar with the investigation. The Washington Post said the Russian Foreign Intelligence Service, known as SVR, was behind the attack. The Russian government denied on Monday that its agencies had any role in the attacks.
The origins of the attack are believed to be in the private sector. It began when a sophisticated illicit cyber actor, known by the nickname Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) 29, or Cozy Bear, stole cyber tools used by two major government contractors, FireEye and SolarWinds. These cyber tools are used to detect and patch vulnerabilities in computer systems. These companies provide services to numerous US government customers, including the Departments of Defense, State, Treasury and Commerce. Other US government customers include the National Security Agency and the Office of the President, including the White House Situation Room. All of these entities have reportedly been affected by this cyber espionage operation.
By disguising their malicious software as software patches, the hackers were reportedly able to access and monitor, in real time, email traffic within and between government agencies. It is not known at this time whether US intelligence agencies, other than the National Security Agency, have been affected by this hack. All branches of the US military maintain intelligence components. Additionally, the Department of the Treasury operates the Office of Intelligence Analysis, while the Department of State is in charge of the Bureau of Intelligence and Research. The White House said yesterday that it had asked the Federal Bureau of Investigation and the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency to probe the attack and evaluate the extent of the damage caused to US government operations.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 15 December 2020 | Permalink
Filed under Expert news and commentary on intelligence, espionage, spies and spying Tagged with APT29, CISA, computer hacking, Cozy Bear, cyberespionage, cybersecurity, FireEye Inc., News, SolarWinds, United States