Russian-Iranian alliance over Syria is not as strong as some believe
November 18, 2015 Leave a comment
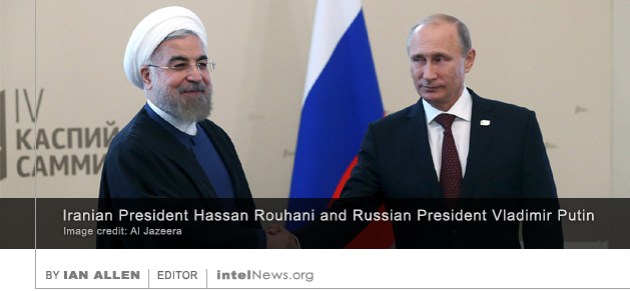 The governments of Russia and the Islamic Republic of Iran are arguably the two most important allies of Syrian President Bashar al-Assad. But the Russian-Iranian alliance over Syria is not as solid —and may not be as durable— as some believe. On Monday, Iranian news agency ISNA reported that Iran’s minister for intelligence condemned Russia’s increased military involvement in Syria and said it would weaken Iran’s security. The minister, Mahmoud Alavi, opined at a press conference in Tehran that the intensification of Russia’s military operations in Syria would backfire against Iran, because it would prompt the Islamic State to “redouble its efforts to destabilize Iran’s security”.
The governments of Russia and the Islamic Republic of Iran are arguably the two most important allies of Syrian President Bashar al-Assad. But the Russian-Iranian alliance over Syria is not as solid —and may not be as durable— as some believe. On Monday, Iranian news agency ISNA reported that Iran’s minister for intelligence condemned Russia’s increased military involvement in Syria and said it would weaken Iran’s security. The minister, Mahmoud Alavi, opined at a press conference in Tehran that the intensification of Russia’s military operations in Syria would backfire against Iran, because it would prompt the Islamic State to “redouble its efforts to destabilize Iran’s security”.
Alavi’s comments came two weeks after Major General Mohammad Ali Jafari, the head of Iran’s Revolutionary Guards Corps said that Iran cared about the stability of al-Assad’s regime in Syria more than Russia did. Jafari was responding to earlier comments made by Maria Zakharova, spokeswoman for the Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs, who said that Moscow would not insist in keeping al-Assad in power in Damascus as a matter of principle. When asked to comment on Zakharova’s comments, Jafari said Iran had to accept that Russia “may not care if al-Assad stays in power as we do”. The difference between Tehran and Moscow, said Jafari, was that “we don’t know any better person to replace him”.
So does that spell changes in the dynamics of the Russian-Iranian alliance over Syria? Such an eventuality should not be discounted, says Sergey Aleksashenko, nonresident senior fellow at the Brookings Institution. He explains that, although both the Russians and the Iranians have aided al-Assad, their reasons for doing so are very different. Russia’s interests in Syria center on maintaining access to its naval base in Tartus, and on retaining a geopolitical presence in the Middle East. Iran’s support for Assad aims to prevent Tehran’s traditional foes, namely Saudi Arabia and the Gulf States, from turning Syria into their protectorate. Additionally, says Aleksashenko, Iran appears much more willing to deploy ground troops in the fight against ISIS than Russia. The Islamic Republic is also much more willing to go against the wishes of other regional powers, like Saudi Arabia and Turkey, which Moscow tends to court.
Ultimately, says Aleksashenko, “although Russia has strategic interests in Syria, it has no intention to keep a military presence in the Middle East forever”. The Iranians, however, have no choice but to dwell in one of the world’s most unstable regions. Al-Assad’s removal would add significantly to that instability, and that is not something that Tehran is willing to permit.
► Author: Ian Allen | Date: 18 November 2015 | Permalink
 The recent attacks by Islamic State militants in Paris continue to dominate the world’s headlines. But the double suicide blasts that struck Beirut three days earlier are far more significant for the future of the Syrian Civil War. The outpouring of grief that followed the attacks of November 15 in the French capital prompted
The recent attacks by Islamic State militants in Paris continue to dominate the world’s headlines. But the double suicide blasts that struck Beirut three days earlier are far more significant for the future of the Syrian Civil War. The outpouring of grief that followed the attacks of November 15 in the French capital prompted  there, and even the Mossad, Israel’s feared spy service, rarely ventures in the Hezbollah-controlled neighborhoods.
there, and even the Mossad, Israel’s feared spy service, rarely ventures in the Hezbollah-controlled neighborhoods. After issuing successive denials earlier in the week, United States officials have now
After issuing successive denials earlier in the week, United States officials have now 






In change of policy, Russia and US begin sharing intelligence with France
November 19, 2015 by Joseph Fitsanakis Leave a comment
French officials described that development as a “change in the US position”. IntelNews readers will recall that the United States and France limited their intelligence cooperation last summer, after it emerged that the US had spied on the communications of three French presidents, from 1995 to 2012. Paris scaled back drastically its intelligence cooperation with Washington following subsequent revelations that the National Security Agency had targeted the personal cell phone of Francois Hollande, France’s current head of state.
Also on Wednesday, Russian President Vladimir Putin instructed the Russian Armed Forces stationed in Syria to treat their French counterparts “as allies”. Putin reportedly told the leadership of the Russian military in Syria that they “must establish direct contact with the French and work with them as with allies”. This is a significant development, given that Russia is one of the few countries that continues to maintain an active intelligence-collection program on the ground in Syria. Unlike the US, France, and most other Western states, Russia has not closed its embassy in Damascus and is thus able to run networks of human sources throughout the country. The news of increased Russian intelligence-sharing with France came as Moscow announced//announced// on Wednesday that it was stepping up intelligence-gathering throughout the Middle East, according to Andrei Kartapolov, a senior official in the Russian Army’s General Staff.
Meanwhile, an unnamed Moroccan security official told Reuters on Wednesday that intelligence shared by the Moroccan intelligence services with their French counterparts led to a raid in an apartment in Paris in connection with the November 13 attacks there. Two people were shot dead or committed suicide and seven others were arrested during Wednesday’s dramatic raid in the Paris suburb of St. Denis.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 19 November 2015 | Permalink
Filed under Expert news and commentary on intelligence, espionage, spies and spying Tagged with Andrei Kartapolov, France, intelligence cooperation, Jean-Yves Le Drian, Morocco, News, Peter Cook, Russia, Syrian Civil War, United States