Opinion: Fumbling Russian spies fail to stop ISIS-K attack, despite warnings from U.S.
March 25, 2024 7 Comments
 NO COUNTRY HAS BETTER intelligence on the Islamic State-Khorasan Province (known as ISIS-K) than the United States. American forces have faced ISIS-K almost from the moment the group was founded in 2015 in Pakistan, just a few miles from the Afghan border. It was there that a group of disaffected members of the Tehreek-e-Taliban-e-Pakistan (TTP, commonly referred to as the Pakistani Taliban) began turning their backs on al-Qaeda, which they saw as a failing brand, and joined the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS).
NO COUNTRY HAS BETTER intelligence on the Islamic State-Khorasan Province (known as ISIS-K) than the United States. American forces have faced ISIS-K almost from the moment the group was founded in 2015 in Pakistan, just a few miles from the Afghan border. It was there that a group of disaffected members of the Tehreek-e-Taliban-e-Pakistan (TTP, commonly referred to as the Pakistani Taliban) began turning their backs on al-Qaeda, which they saw as a failing brand, and joined the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS).
By 2017, ISIS-K had begun to draw to its ranks hundreds of fighters from central and south Asia, who were inspired by the group’s goal of establishing an Islamic caliphate in the lands of the greater Khorasan. The term refers to a historical region that extends from eastern Iran and Turkmenistan, to the mountains of Kyrgyzstan, containing all of present-day Afghanistan, most of Uzbekistan, and even some parts of the Russian Caucasus. Like the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS) during its heyday, ISIS-K aspires to establish control over a territorially unified entity and then use perpetual war to expand its influence in central Asia and beyond.
Until 2021, the biggest obstacle to ISIS-K’s plan for regional domination was the U.S. By some accounts, American forces and Western-trained Afghan commando units had managed to eliminate more than half of ISIS-K’s 4,000-strong base in northeastern Afghanistan. Since the hurried U.S. withdrawal from the country in 2021 (which was marred by an ISIS-K suicide bombing that killed nearly 200 people, including 13 U.S. troops), ISIS-K has expanded its reach beyond all prior measure. The group has since claimed responsibility for attacks in Afghanistan, Pakistan, Iran, and now Russia, that have killed over 600 people and injured thousands.
A primary reason for the proliferation of ISIS-K’s terrorist activity is that the U.S., which has more intelligence than anyone on the group, issues warnings that are  not being taken into consideration by the group’s primary targets, namely Afghanistan, Iran, and Russia. Indeed, despite the Washington’s best efforts, its warnings about pending ISIS-K attacks have been ignored by the group’s primary targets. A few days after an ISIS-K attack killed nearly 100 people in Kerman, Iran, The Wall Street Journal claimed the U.S. government had provided Tehran with “a private warning” of an imminent terrorist threat from ISIS-K. If that is true, then the Iranians clearly did not heed Washington’s warning.
not being taken into consideration by the group’s primary targets, namely Afghanistan, Iran, and Russia. Indeed, despite the Washington’s best efforts, its warnings about pending ISIS-K attacks have been ignored by the group’s primary targets. A few days after an ISIS-K attack killed nearly 100 people in Kerman, Iran, The Wall Street Journal claimed the U.S. government had provided Tehran with “a private warning” of an imminent terrorist threat from ISIS-K. If that is true, then the Iranians clearly did not heed Washington’s warning.
It now appears that, once again, Washington had considerable intelligence insight into ISIS-K’s plans to strike inside Russia. On March 7, the U.S. embassy in Russia warned on its website that “extremists have imminent plans to target large gatherings in Moscow, to include concerts”. The warning provided no specifics. However, seeing how U.S. authorities issued private warnings to Iran, a country with which the U.S. has no diplomatic relations, then it is highly likely they provided similar information to Russia, which at least hosts American diplomats and intelligence officers on its soil. Yet, not only did the Russians ignore these warnings, but they openly dismissed them. Read more of this post

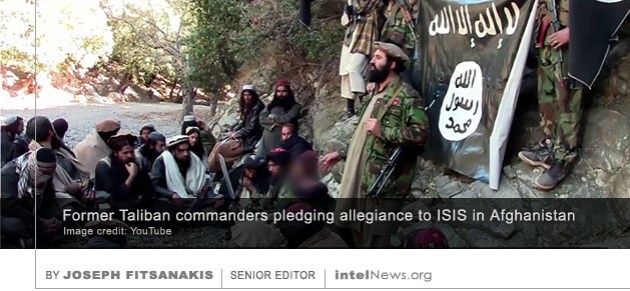 The Islamic State group in Afghanistan is now more threatening than the Taliban to both Afghan and Western interests, according to some experts, who warn that many of its fighters are moving there from the Middle East. It was in late 2014 when the Islamic State, known formerly as the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS), made its initial appearance in Afghanistan. Soon an official Islamic State affiliate emerged in Afghanistan, calling itself Islamic State – Khorasan Province. Security observers estimated the group’s strength to below 150 armed fighters, most of them Pakistani Taliban who had sought refuge in Afghanistan, or small cadres of Afghan Taliban who pursued a more globalized Salafist agenda. Aided by the growing worldwide notoriety of its parent organization in Iraq and Syria, the Islamic State – Khorasan Province grew in size in 2015 and 2016. Its armed cadres were joined by Salafist-jihadists from Central Asia and the Indian subcontinent, as well as by radical Muslims from China’s northwestern Xinjiang Province. In 2016, as the Islamic State began retreating in the Middle East, fighters from there gradually began to make their way to Afghanistan, adding to the numerical strength of the organization’s Khorasan Province branch.
The Islamic State group in Afghanistan is now more threatening than the Taliban to both Afghan and Western interests, according to some experts, who warn that many of its fighters are moving there from the Middle East. It was in late 2014 when the Islamic State, known formerly as the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS), made its initial appearance in Afghanistan. Soon an official Islamic State affiliate emerged in Afghanistan, calling itself Islamic State – Khorasan Province. Security observers estimated the group’s strength to below 150 armed fighters, most of them Pakistani Taliban who had sought refuge in Afghanistan, or small cadres of Afghan Taliban who pursued a more globalized Salafist agenda. Aided by the growing worldwide notoriety of its parent organization in Iraq and Syria, the Islamic State – Khorasan Province grew in size in 2015 and 2016. Its armed cadres were joined by Salafist-jihadists from Central Asia and the Indian subcontinent, as well as by radical Muslims from China’s northwestern Xinjiang Province. In 2016, as the Islamic State began retreating in the Middle East, fighters from there gradually began to make their way to Afghanistan, adding to the numerical strength of the organization’s Khorasan Province branch.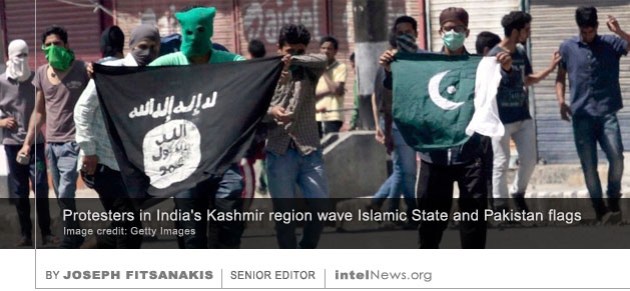 The group calling itself the Islamic State has announced the establishment of a new overseas province in Pakistan, just days after proclaiming another new overseas province in northern India. Until recently, the Islamic State’s operations in Asia were conducted under the banner of the Islamic State – Khorasan Province, or IS-KP. The shadowy group was founded in early 2015 and was led by former Taliban warlords who pledged allegiance to Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, the spiritual leader and self-proclaimed emir of the Islamic State. Since that time, at least two of IS-KP’s leaders have been killed by United States forces, while the group has been engaged in a war against rival militant groups in Afghanistan and Pakistan, notably the Taliban.
The group calling itself the Islamic State has announced the establishment of a new overseas province in Pakistan, just days after proclaiming another new overseas province in northern India. Until recently, the Islamic State’s operations in Asia were conducted under the banner of the Islamic State – Khorasan Province, or IS-KP. The shadowy group was founded in early 2015 and was led by former Taliban warlords who pledged allegiance to Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, the spiritual leader and self-proclaimed emir of the Islamic State. Since that time, at least two of IS-KP’s leaders have been killed by United States forces, while the group has been engaged in a war against rival militant groups in Afghanistan and Pakistan, notably the Taliban.





