Analysis: ISIS leader’s hideout in Turkish-controlled part of Syria raises questions
October 31, 2019 1 Comment
 In 2011, the discovery of Osama bin Laden’s hideout in Abbottabad raised questions about Pakistan’s knowledge of his whereabouts. Today it is hardly controversial to suggest that at least some elements in the Pakistani government must have been aware of bin Laden’s location. Last week’s discovery of Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi in a region of Syria controlled by Turkey inevitably raises similar questions about Ankara’s role in the Syrian conflict and its relationship with the Islamic State.
In 2011, the discovery of Osama bin Laden’s hideout in Abbottabad raised questions about Pakistan’s knowledge of his whereabouts. Today it is hardly controversial to suggest that at least some elements in the Pakistani government must have been aware of bin Laden’s location. Last week’s discovery of Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi in a region of Syria controlled by Turkey inevitably raises similar questions about Ankara’s role in the Syrian conflict and its relationship with the Islamic State.
The self-proclaimed caliph of the Islamic State was found hiding in Barisha, a village in the Syrian province of Idlib, which is located just two miles from the Turkish border. The region that surrounds Barisha is under the control of Turkey and can most accurately be described as a Turkish protectorate inside Syria. The area north of Barisha has been under Turkish control since August of 2016, when Ankara launched Operation Euphrates Shield, a cross-border operation conducted by the Turkish Armed Forces in cooperation with Turkish-baked militias in Syria. In early 2018, Turkish and pro-Turkish forces extended their territorial control further south, capturing Barisha and all surrounding regions. They remain in control of the area to this day.
Turkish-occupied northern Syria is often described as a “proto-state”. It is governed by a collection of local councils of Turkmens and Arabs, with some Kurds and Yazidis also present. These councils elect representatives to the self-proclaimed Syrian Interim Government, which was formed in Turkey by Turkish-backed Syrian exiles and is currently headquartered in Azaz, an Arab-majority city of 30,000 that is under direct Turkish military control. Azaz is also the headquarters of the Turkish-backed “Free Police”, a gendarmerie-style militia that is funded, trained and equipped by the Turkish government.
In addition to the Turkish troops, the region is controlled by the Turkish-funded Syrian National Army. The 25,000 troops of the SNA —which is jokingly referred to by the locals as the “Turkish Syrian National Army”— operate completely under Turkish command. A substantial portion of the SNA’s force consists of former Islamic State fighters who switched their allegiance to the SNA once they saw the writing on the wall. Others are former members of the group that used to call itself Jabhat al-Nusra, an al-Qaeda affiliate that has become the most powerful Salafi-jihadist force in Syria after the demise of the Islamic State.
Turkish-occupied northern Syria is also the base of Ahrar al-Sham, a Salafi-jihadist group consisting of over 20,000 fighters, which is not officially aligned with al-Qaeda, but has similar goals. Since at least 2017, Ahrar al-Sham has effectively operated as a Turkish proxy militia and is in charge of dozens of check points and observation posts throughout the region. Lastly, the area is home to Hurras al-Din, yet another Salafi-jihadist group that is affiliated with al-Qaeda —though its leaders deny it. The group is able to operate in Turkish-controlled areas of Syria with suspicious ease. It was this group, Hurras al-Din, that sheltered al-Baghdadi in Barisha in return for cash.
Given Turkey’s military and political control of Idlib province, the question arises of how the world’s most high-profile terrorist leader was able to enter the region and receive protection from a militia that operates there under the watchful eye of the Turkish military. The New York Times reports that al-Baghdadi had been living in Barisha for several months before last week’s raid, and that Washington had been aware of his hideout location since the summer. Was Turkish intelligence also aware of the Islamic State leader’s whereabouts? If not, how could that be? If yes, why did it take a Kurdish spy, handled by Syrian Kurdish intelligence, to locate him and provide information to the Untited States? More importantly, what exactly is the relationship between Turkey and the al-Qaeda-linked Islamists who seem to operate freely in Idlib and provide protection to senior Islamic State officials in exchange for cash?
There are clearly more questions than answers here. If the United States is serious about combating Islamist extremism in the Middle East, it must press Ankara on these questions as a matter of urgency.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 31 October 2019 | Permalink
 American defense officials with knowledge of Special Operations Forces activities in Syria are concerned that their secrets may fall into the hands of the Russians, as the Kurds switch their allegiance to the Moscow-backed Syrian government. Members of the United States Special Operations Forces and the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) have had a presence in Kurdish-dominated northern Syria since
American defense officials with knowledge of Special Operations Forces activities in Syria are concerned that their secrets may fall into the hands of the Russians, as the Kurds switch their allegiance to the Moscow-backed Syrian government. Members of the United States Special Operations Forces and the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) have had a presence in Kurdish-dominated northern Syria since  Senior White House officials close to United States President Donald Trump believed that Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan was bluffing when he threatened to invade northern Syria, according to sources. For over two years, most of northern Syria has been controlled by American-supported Kurdish militias, who were instrumental in helping Washington defeat the Islamic State. But the growing strength of the Kurdish forces alarmed Turkey, which views Kurdish nationalism as a bigger threat than the Islamic State.
Senior White House officials close to United States President Donald Trump believed that Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan was bluffing when he threatened to invade northern Syria, according to sources. For over two years, most of northern Syria has been controlled by American-supported Kurdish militias, who were instrumental in helping Washington defeat the Islamic State. But the growing strength of the Kurdish forces alarmed Turkey, which views Kurdish nationalism as a bigger threat than the Islamic State. Officials in the United States, Europe and the Middle East have warned that thousands of jailed members of the Islamic State could escape from Kurdish-controlled prisons in northern Syria if Turkey invades the region. For more than two years, the area has been controlled by American-supported Kurdish militias, who were instrumental in helping Washington defeat the Islamic State —also known as Islamic State of Iraq and Syria, or ISIS. But the growing strength of the Kurdish forces has alarmed Turkey, which views Kurdish nationalism in the region as a bigger threat than Salafi jihadism. Ankara has repeatedly threatened to invade northern Syria and disarm the Kurdish groups, which it sees as terrorist.
Officials in the United States, Europe and the Middle East have warned that thousands of jailed members of the Islamic State could escape from Kurdish-controlled prisons in northern Syria if Turkey invades the region. For more than two years, the area has been controlled by American-supported Kurdish militias, who were instrumental in helping Washington defeat the Islamic State —also known as Islamic State of Iraq and Syria, or ISIS. But the growing strength of the Kurdish forces has alarmed Turkey, which views Kurdish nationalism in the region as a bigger threat than Salafi jihadism. Ankara has repeatedly threatened to invade northern Syria and disarm the Kurdish groups, which it sees as terrorist. In an effort to remain relevant, al-Qaeda has shifted its strategic focus from Yemen to Syria but continues to pursue a globalist agenda by seeking ways to attack Western targets, according to an expert report. Following the meteoric rise of the Islamic State in 2014, al-Qaeda found it difficult to retain its title as the main representative of the worldwide Sunni insurgency. But in an
In an effort to remain relevant, al-Qaeda has shifted its strategic focus from Yemen to Syria but continues to pursue a globalist agenda by seeking ways to attack Western targets, according to an expert report. Following the meteoric rise of the Islamic State in 2014, al-Qaeda found it difficult to retain its title as the main representative of the worldwide Sunni insurgency. But in an  The Islamic State is capable of make a sudden comeback in the Middle East that could be “faster and even more devastating” than 2014, when the group quickly conquered territory the size of Britain, according to a new report from the Institute for the Study of War (ISW). The Washington-based think-tank’s report is based on the most recent data about the presence in the Middle East of the militant Islamist group, which is also known as the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria. The 76-page
The Islamic State is capable of make a sudden comeback in the Middle East that could be “faster and even more devastating” than 2014, when the group quickly conquered territory the size of Britain, according to a new report from the Institute for the Study of War (ISW). The Washington-based think-tank’s report is based on the most recent data about the presence in the Middle East of the militant Islamist group, which is also known as the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria. The 76-page  Intelligence officials warn that Iraq’s fragile stability may be at risk, following reports that as many as a thousand armed Islamic State fighters have entered Iraq from Syria in recent weeks. The organization calling itself the Islamic State (known also as the Islamic State of Iraq an Syria, or ISIS) is on its last legs in Baghouz, a Syrian village located on the banks of the Euphrates River near the Syrian-Iraqi border. Its fighters are
Intelligence officials warn that Iraq’s fragile stability may be at risk, following reports that as many as a thousand armed Islamic State fighters have entered Iraq from Syria in recent weeks. The organization calling itself the Islamic State (known also as the Islamic State of Iraq an Syria, or ISIS) is on its last legs in Baghouz, a Syrian village located on the banks of the Euphrates River near the Syrian-Iraqi border. Its fighters are  The role of women inside the Islamic State is growing, as the Sunni militant group is transmuting into an underground organization, according to a Harvard University terrorism expert. Since its meteoric rise in Iraq and Syria, the Islamic State has been known for advocating for strict segregation between men and women. In the early stages of the group’s emergence, combat roles were exclusively performed by men, while women’s roles were limited to childbearing and housework. But according to Vera Mironova, Visiting Scholar in the Economics Department at Harvard University, and former Associate of the International Security Program at Harvard’s Belfer Center, the Islamic State’s policy on gender roles is shifting rapidly.
The role of women inside the Islamic State is growing, as the Sunni militant group is transmuting into an underground organization, according to a Harvard University terrorism expert. Since its meteoric rise in Iraq and Syria, the Islamic State has been known for advocating for strict segregation between men and women. In the early stages of the group’s emergence, combat roles were exclusively performed by men, while women’s roles were limited to childbearing and housework. But according to Vera Mironova, Visiting Scholar in the Economics Department at Harvard University, and former Associate of the International Security Program at Harvard’s Belfer Center, the Islamic State’s policy on gender roles is shifting rapidly. The “illusion of safety” has been blamed for the death of four American service members in northern Syria last week, after a suicide bomber attacked a restaurant, killing at least 19 people and wounding countless others. The deadly attack happened in Manbij, a small Kurdish-majority town near the Syrian-Turkish border, which American forces previously viewed as an oasis of security in the war-torn country. American troops fought alongside a coalition of Kurdish and Arab fighters who in 2016 took control of Manbij from the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS). Since then, American forces have remained in the area —mostly to prevent a military invasion by Washington’s ally Turkey, which views the Kurds as terrorists and has threatened to destroy their armed forces.
The “illusion of safety” has been blamed for the death of four American service members in northern Syria last week, after a suicide bomber attacked a restaurant, killing at least 19 people and wounding countless others. The deadly attack happened in Manbij, a small Kurdish-majority town near the Syrian-Turkish border, which American forces previously viewed as an oasis of security in the war-torn country. American troops fought alongside a coalition of Kurdish and Arab fighters who in 2016 took control of Manbij from the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS). Since then, American forces have remained in the area —mostly to prevent a military invasion by Washington’s ally Turkey, which views the Kurds as terrorists and has threatened to destroy their armed forces. A report from the United States Department of Defense warns that the Islamic State is swiftly returning to its insurgent roots, as observers in Iraq and Syria caution that the group is witnessing a revival. It has been four years since the Islamic State —known then as the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria, or ISIS— conquered much of eastern Syria and more than a third of Iraq’s territory. But by the end of 2017, virtually the entirety of ISIS’ self-styled ‘caliphate’ had been obliterated by an ‘unholy alliance’ of US-backed Iraqi government forces, Iranian-supported Shiite militias, Kurdish guerillas and Western airpower.
A report from the United States Department of Defense warns that the Islamic State is swiftly returning to its insurgent roots, as observers in Iraq and Syria caution that the group is witnessing a revival. It has been four years since the Islamic State —known then as the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria, or ISIS— conquered much of eastern Syria and more than a third of Iraq’s territory. But by the end of 2017, virtually the entirety of ISIS’ self-styled ‘caliphate’ had been obliterated by an ‘unholy alliance’ of US-backed Iraqi government forces, Iranian-supported Shiite militias, Kurdish guerillas and Western airpower. A delegation of senior American government officials met secretly with Syria’s spy chiefs in an effort to lay out the terms of a possible deal between Washington and Damascus, according to a Lebanese newspaper. Relations between the United States and Syria have been strained since the late 1950s, when Damascus blamed Washington for a failed coup and expelled America’s ambassador there. In 2012, the US shut down its embassy in the Syrian capital in response to the government’s violent suppression of protests. Since then, Washington has carried out missile strikes on Syrian soil at least twice, while openly supporting armed groups that are opposed to the government of President Bashar al-Assad.
A delegation of senior American government officials met secretly with Syria’s spy chiefs in an effort to lay out the terms of a possible deal between Washington and Damascus, according to a Lebanese newspaper. Relations between the United States and Syria have been strained since the late 1950s, when Damascus blamed Washington for a failed coup and expelled America’s ambassador there. In 2012, the US shut down its embassy in the Syrian capital in response to the government’s violent suppression of protests. Since then, Washington has carried out missile strikes on Syrian soil at least twice, while openly supporting armed groups that are opposed to the government of President Bashar al-Assad.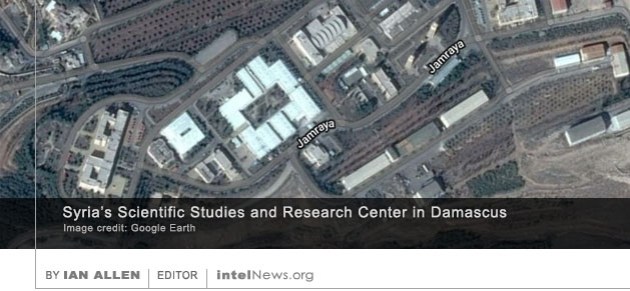 One of Syria’s leading pro-government newspapers has said that Israel was behind a bomb blast in Hama province that killed a senior scientist working for the country’s missile program. Aziz Azbar was reportedly a senior research director at the Syrian Scientific Studies and Research Center, known as CERS. The Damascus-based agency is thought to be at the center of the Syrian government’s formidable chemical weapons program. Last year, the United States Department of the Treasury imposed economic sanctions on nearly 300 CERS employees, after Washington accused them of being directly responsible for the Syrian government’s repeated use of chemical weapons against rebels and civilians. The European Union, as well as the French and British governments, also imposed sanctions on CERS and its staff.
One of Syria’s leading pro-government newspapers has said that Israel was behind a bomb blast in Hama province that killed a senior scientist working for the country’s missile program. Aziz Azbar was reportedly a senior research director at the Syrian Scientific Studies and Research Center, known as CERS. The Damascus-based agency is thought to be at the center of the Syrian government’s formidable chemical weapons program. Last year, the United States Department of the Treasury imposed economic sanctions on nearly 300 CERS employees, after Washington accused them of being directly responsible for the Syrian government’s repeated use of chemical weapons against rebels and civilians. The European Union, as well as the French and British governments, also imposed sanctions on CERS and its staff. A United States federal judge ruled on Monday that a tweet by President Donald Trump did not inadvertently disclose a top-secret program by the Central Intelligence Agency to aid rebel groups in Syria. The lawsuit, brought by The New York Times, centered on news reports published in 2017 by
A United States federal judge ruled on Monday that a tweet by President Donald Trump did not inadvertently disclose a top-secret program by the Central Intelligence Agency to aid rebel groups in Syria. The lawsuit, brought by The New York Times, centered on news reports published in 2017 by 






Turkey’s arrest of al-Baghdadi’s sister is ‘intelligence goldmine’ says official
November 6, 2019 by Joseph Fitsanakis 1 Comment
Awad was arrested during a raid by the Turkish-backed Free Syrian Army at a makeshift refugee camp in the suburbs of Azaz, a city of 30,000 located approximately 20 miles northwest of Aleppo. The Aleppo province in northwestern Syria has been under Turkish military control since 2016. Since then, the Turkish military command has relied on the Ankara-backed Free Syrian Army and a selection of smaller pro-Turkish militia to control the region.
The Associated Press reported that Awad was detained along with her family, including her husband, her daughter-in-law, and her five children. Five other adults were arrested in the vicinity of the refugee camp, all of them Iraqi citizens, but there is no word yet on whether they are in any way connected with the Islamic State. Turkish officials told the Associated Press yesterday that Awad, her husband and her daughter-in-law were being interrogated.
The news agency quoted one Turkish government official as saying that Awad’s capture was “an intelligence goldmine. What she knows about [the Islamic State] can significantly expand our understanding of the group and help us catch more bad guys”, the official is reported to have told the Associated Press.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 06 November 2019 | Permalink
Filed under Expert news and commentary on intelligence, espionage, spies and spying Tagged with Aleppo (Syria), Azaz (Syria), Islamic State, News, Rasmiya Awad, Syria, Turkey