Iran spied on ISIS supporters through fake phone wallpaper app, say researchers
September 14, 2018 1 Comment
 Supporters of the Islamic State, most of them Persian speakers, were spied on by the government of Iran after they downloaded a fake smartphone application with wallpaper images, according to an online security firm. Iran is a major adversary of the radical Sunni group Islamic State. The latter considers Shiism (Iran’s state religion) as an abomination. Not surprisingly, therefore, the Islamic State, which is also known as the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS), relies largely on supporters from the Arabic-speaking regions of the Levant. But according to estimates, Sunnis constitute about 10 percent of Iran’s population, and ISIS has found some fertile ground among Iran’s 8 million-strong Sunni minority. As a result, the government in Tehran is highly mistrustful of Iranian Sunnis, many of whom are ethnic Kurds, Baluchis, Azeris or Turkomans, and systematically spies on them.
Supporters of the Islamic State, most of them Persian speakers, were spied on by the government of Iran after they downloaded a fake smartphone application with wallpaper images, according to an online security firm. Iran is a major adversary of the radical Sunni group Islamic State. The latter considers Shiism (Iran’s state religion) as an abomination. Not surprisingly, therefore, the Islamic State, which is also known as the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS), relies largely on supporters from the Arabic-speaking regions of the Levant. But according to estimates, Sunnis constitute about 10 percent of Iran’s population, and ISIS has found some fertile ground among Iran’s 8 million-strong Sunni minority. As a result, the government in Tehran is highly mistrustful of Iranian Sunnis, many of whom are ethnic Kurds, Baluchis, Azeris or Turkomans, and systematically spies on them.
According to the Israeli online security firm Check Point Software Technologies, one way in which Tehran has spied on Persian-speaking ISIS supporters is through fake smartphone applications. In an article published last week, the company said it had uncovered a state-sponsored surveillance operation that it had codenamed “Domestic Kitten”. The Check Point article said that the operation had gone on for more than two years, but had remained undetected “due to the artful deception of its attackers towards their targets”. The surveillance of targeted phones was carried out with the help of an application that featured pro-ISIS-themed wallpapers, which users could download on their devices. Yet another program linked to the same vendor was a fake version of the Firat News Agency mobile phone application. The Firat News Agency is a legitimate Iranian information service featuring news about Iran’s Kurdish minority. But both applications were in fact malware that gave a remote party full access to all text messages sent or received on the compromised phones. They also gave a remote party access to records of phone calls, Internet browser activity and bookmarks, and all files stored on the compromised phones. Additionally, the fake applications gave away the geo-location of compromised devices, and used their built-in cameras and microphones as surveillance devices.
Check Point said that the majority of compromised phones belonged to Persian-speaking members of Iran’s Kurdish and Turkoman minorities. The company stressed that it was not able to confirm the identity of the sponsoring party with absolute accuracy. However, the nature of the fake applications, the infrastructure of the surveillance operation, as well as the identities of those targeted, posed a strong possibility that “Domestic Kitten” was sponsored by the government of Iran, it concluded. Last July, the American cyber security firm Symantec said that it had uncovered a new cyber espionage group called “Leafminer”, which was allegedly sponsored by the Iranian state. The group had reportedly launched attacks on more than 800 agencies and organizations in in countries such as Israel, Egypt, Bahrain, Qatar, Kuwait, the United Arab Emirates, Afghanistan and Azerbaijan.
► Author: Ian Allen | Date: 14 September 2018 | Permalink
 An online fundraising campaign is seeking to secure the release of over 4,000 pages of documents relating to a controversial mind control program developed by the United States Central Intelligence Agency. The project, referred to as MKNAOMI/MKULTRA in US government files, was a joint effort by the CIA and the US Department of Defense to study the effects of substances such as heroin and LSD on the human brain. It began in 1953 and over the years involved the work of hundreds of scientists, many of whom were not aware they were working on a CIA project. But it was hurriedly shut down in 1976, once post-Watergate investigations by the US Congress revealed that it led to the
An online fundraising campaign is seeking to secure the release of over 4,000 pages of documents relating to a controversial mind control program developed by the United States Central Intelligence Agency. The project, referred to as MKNAOMI/MKULTRA in US government files, was a joint effort by the CIA and the US Department of Defense to study the effects of substances such as heroin and LSD on the human brain. It began in 1953 and over the years involved the work of hundreds of scientists, many of whom were not aware they were working on a CIA project. But it was hurriedly shut down in 1976, once post-Watergate investigations by the US Congress revealed that it led to the 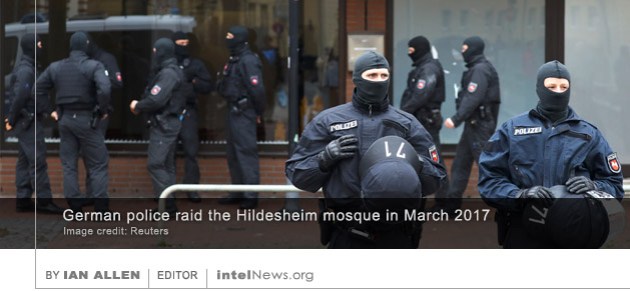 Authorities in Germany announced yesterday the arrest of a German national who is accused of spying on a central German mosque on behalf of Jordan, according to media reports. The man was reportedly arrested on Tuesday at an unknown location by officers of Germany’s domestic intelligence agency, the Federal Office for the Protection of the Constitution (BfV). In a press statement, the agency said the man is a 33-year-old German national named “Alexander B.”. German privacy rules forbid the public identification of crime suspects prior to their conviction in a court of law.
Authorities in Germany announced yesterday the arrest of a German national who is accused of spying on a central German mosque on behalf of Jordan, according to media reports. The man was reportedly arrested on Tuesday at an unknown location by officers of Germany’s domestic intelligence agency, the Federal Office for the Protection of the Constitution (BfV). In a press statement, the agency said the man is a 33-year-old German national named “Alexander B.”. German privacy rules forbid the public identification of crime suspects prior to their conviction in a court of law.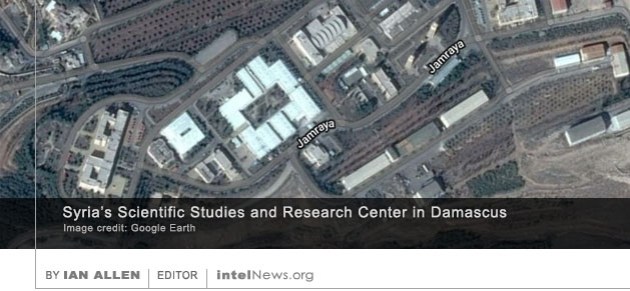 One of Syria’s leading pro-government newspapers has said that Israel was behind a bomb blast in Hama province that killed a senior scientist working for the country’s missile program. Aziz Azbar was reportedly a senior research director at the Syrian Scientific Studies and Research Center, known as CERS. The Damascus-based agency is thought to be at the center of the Syrian government’s formidable chemical weapons program. Last year, the United States Department of the Treasury imposed economic sanctions on nearly 300 CERS employees, after Washington accused them of being directly responsible for the Syrian government’s repeated use of chemical weapons against rebels and civilians. The European Union, as well as the French and British governments, also imposed sanctions on CERS and its staff.
One of Syria’s leading pro-government newspapers has said that Israel was behind a bomb blast in Hama province that killed a senior scientist working for the country’s missile program. Aziz Azbar was reportedly a senior research director at the Syrian Scientific Studies and Research Center, known as CERS. The Damascus-based agency is thought to be at the center of the Syrian government’s formidable chemical weapons program. Last year, the United States Department of the Treasury imposed economic sanctions on nearly 300 CERS employees, after Washington accused them of being directly responsible for the Syrian government’s repeated use of chemical weapons against rebels and civilians. The European Union, as well as the French and British governments, also imposed sanctions on CERS and its staff.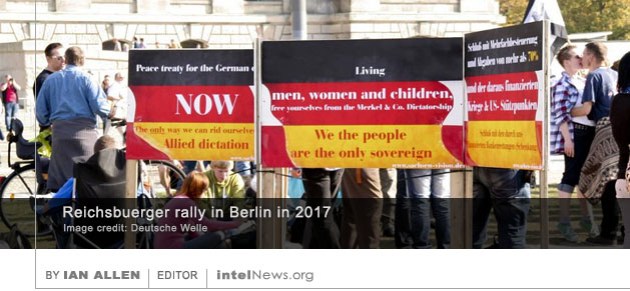 Adherents of a bizarre far-right movement in Germany, who claim to be citizens of Prussia, are arming themselves and pose a growing security threat, says a new report by the country’s domestic spy service. The members of the movement call themselves Reichsbuerger (“citizens of the Reich”) and reject the legitimacy of the Federal Republic of Germany. Instead of the modern-day German state, which emerged in 1990 from the union of East and West Germany, Reichsbuergers swear allegiance to the Deutsches Reich (German Reich), the Nazi German state that existed between 1933 and 1945. They also claim that the Deutsches Reich, which they occasionally refer to as Prussia, continues to exist in its pre-1945 state and is still governed by a provisional government in exile.
Adherents of a bizarre far-right movement in Germany, who claim to be citizens of Prussia, are arming themselves and pose a growing security threat, says a new report by the country’s domestic spy service. The members of the movement call themselves Reichsbuerger (“citizens of the Reich”) and reject the legitimacy of the Federal Republic of Germany. Instead of the modern-day German state, which emerged in 1990 from the union of East and West Germany, Reichsbuergers swear allegiance to the Deutsches Reich (German Reich), the Nazi German state that existed between 1933 and 1945. They also claim that the Deutsches Reich, which they occasionally refer to as Prussia, continues to exist in its pre-1945 state and is still governed by a provisional government in exile. Intelligence directors from Russia, China, Iran and Pakistan met on Tuesday to discuss regional cooperation with particular reference to combating the Islamic State in Afghanistan. Information about the high-level meeting was
Intelligence directors from Russia, China, Iran and Pakistan met on Tuesday to discuss regional cooperation with particular reference to combating the Islamic State in Afghanistan. Information about the high-level meeting was  Dozens of Dutch security officers, legal experts, diplomats and other civil servants were systematically spied on by Ukrainian and Russian intelligence services while probing the aftermath of the MH17 disaster, according to a report on Dutch television. Malaysia Airlines Flight 17, a scheduled passenger flight from Amsterdam to Kuala Lumpur, was
Dozens of Dutch security officers, legal experts, diplomats and other civil servants were systematically spied on by Ukrainian and Russian intelligence services while probing the aftermath of the MH17 disaster, according to a report on Dutch television. Malaysia Airlines Flight 17, a scheduled passenger flight from Amsterdam to Kuala Lumpur, was  Singaporean officials have dismissed reports that a promotional item given away for free during the June 12 summit between the leaders of the United States and North Korea contained an espionage device. Over 2500 reporters from nearly every country covered the meeting between US President Donald Trump and North Korean Supreme Leader Kim Jong-un. Upon arriving in Singapore’s Sentosa Island, where the summit took place, journalists were given a free promotional packet that included novelty items such as pens, notepads, a water bottle, and a USB fan. The USB fan consisted of blades connected to a miniature electric motor, which was in turn connected to a USB cable. The cable allowed the device to be powered by a computer or other electronic device with a built-in USB port.
Singaporean officials have dismissed reports that a promotional item given away for free during the June 12 summit between the leaders of the United States and North Korea contained an espionage device. Over 2500 reporters from nearly every country covered the meeting between US President Donald Trump and North Korean Supreme Leader Kim Jong-un. Upon arriving in Singapore’s Sentosa Island, where the summit took place, journalists were given a free promotional packet that included novelty items such as pens, notepads, a water bottle, and a USB fan. The USB fan consisted of blades connected to a miniature electric motor, which was in turn connected to a USB cable. The cable allowed the device to be powered by a computer or other electronic device with a built-in USB port. The United States has for the first time imposed economic sanctions on a number of Russian companies, which it says helped the Kremlin spy on targets in North America and Western Europe. On Monday, the US Department of the Treasury said it would apply severe economic restrictions on a number of Russian firms that work closely with the Kremlin. One of the companies was
The United States has for the first time imposed economic sanctions on a number of Russian companies, which it says helped the Kremlin spy on targets in North America and Western Europe. On Monday, the US Department of the Treasury said it would apply severe economic restrictions on a number of Russian firms that work closely with the Kremlin. One of the companies was 
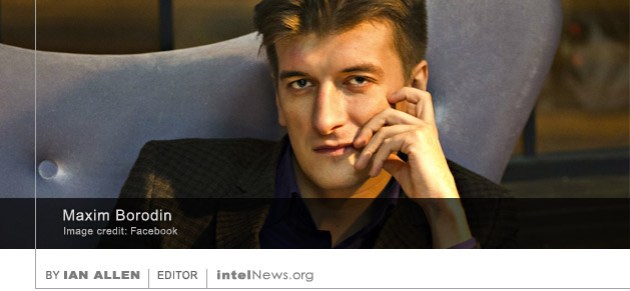 A Russian investigative journalist, who wrote a series of articles about Russian soldiers-for-hire in Syria, has died after falling from the balcony of his apartment in western Siberia. Some of his colleagues say they suspect foul play. Maxim Borodin wrote for Novy Den (New Day) an investigative online magazine. In the past few weeks, Novy Den published a series of probing articles by Borodin about the activities of Russian mercenaries working for the Syrian President Bashar al-Assad. Borodin was one of just a handful of Russian journalists who reported on claims that more than 200 Russian mercenaries were killed in Syria on February 7.
A Russian investigative journalist, who wrote a series of articles about Russian soldiers-for-hire in Syria, has died after falling from the balcony of his apartment in western Siberia. Some of his colleagues say they suspect foul play. Maxim Borodin wrote for Novy Den (New Day) an investigative online magazine. In the past few weeks, Novy Den published a series of probing articles by Borodin about the activities of Russian mercenaries working for the Syrian President Bashar al-Assad. Borodin was one of just a handful of Russian journalists who reported on claims that more than 200 Russian mercenaries were killed in Syria on February 7.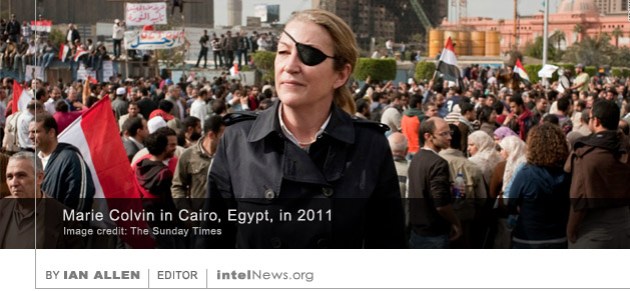 The Syrian government tracked down and killed American journalist Marie Colvin in order to stop her from reporting about the Syrian Civil War, according to a Syrian intelligence officer who has defected to Europe. Colvin was an experienced war correspondent who worked for The Sunday Times. The British newspaper sent her to Syria soon after the outbreak of the war. From there, she gave live interviews to media outlets such as CNN and the BBC. But on the morning of February 22, 2012, Colvin was killed along with French war photographer Remi Ochlik. Their death came when Syrian government forces repeatedly shelled a media center in the city of Homs, which housed the two reporters.
The Syrian government tracked down and killed American journalist Marie Colvin in order to stop her from reporting about the Syrian Civil War, according to a Syrian intelligence officer who has defected to Europe. Colvin was an experienced war correspondent who worked for The Sunday Times. The British newspaper sent her to Syria soon after the outbreak of the war. From there, she gave live interviews to media outlets such as CNN and the BBC. But on the morning of February 22, 2012, Colvin was killed along with French war photographer Remi Ochlik. Their death came when Syrian government forces repeatedly shelled a media center in the city of Homs, which housed the two reporters. With
With 






Saudi state spies on dissidents in Canada using software built by Israeli firm
October 2, 2018 1 Comment
Abdulaziz, 27, arrived in Canada on a student visa in 2009. In 2014, having publicly voiced criticisms of the Saudi royal family and Saudi Arabia’s repressive political system, and having been threatened by Saudi authorities, Abdulaziz successfully applied for political asylum in Canada. In 2017 he was granted permanent residency status. For the past eight years, Abdulaziz has become increasingly vocal in his criticism of the Saudi government, mostly through his satirical channel on YouTube. The channel, called Yakathah, has over 120,000 subscribers and its content has angered Saudi authorities. The latter have warned Abdulaziz’s parents and last summer arrested two of his brothers, in what he describes as attempts to silence him.
Researchers from Citizen Lab claim that the Saudi government has been targeting expatriate dissidents such as Abdulaziz using various techniques, such as sending them spyware-infested messages that express support for anti-government demonstrations in Saudi Arabia. The report also notes that these messages make use of Pegasus, a surveillance software system that has been previously implicated in surveillance activities against political dissidents from Gulf countries. The software was designed by NSO Group Technologies, an Israeli digital surveillance company based in Herzliya, a small coastal town located north of Tel Aviv.
The Citizen Lab report comes at a time of heightened tensions in relations between Canada and Saudi Arabia. In August, Canada’s Global Affairs Ministry issued sharp criticisms of the Saudi government’s human rights record, while Foreign Affairs Minister Chrystia Freeland said she was “gravely concerned” about the suppression of political speech in the Kingdom. She also urged the Saudi government to release a number of jailed political activists and stop censoring Saudi women activists seeking gender equality. But her comments enraged the Saudi royal family, which controls the Kingdom. Within days, the Saudi government expelled Canada’s ambassador from Riyadh and restricted its economic ties with Canada. The Kingdom also recalled several thousand Saudi students who were studying in Canadian universities on Saudi government scholarships.
► Author: Ian Allen | Date: 02 October 2018 | Permalink
Filed under Expert news and commentary on intelligence, espionage, spies and spying Tagged with Canada, human rights, News, NSO Group Technologies, Omar Abdulaziz, Pegasus software, Saudi Arabia, technical surveillance, University of Toronto