Tradecraft observations on the Reichenbach/Fischer espionage case
May 3, 2024 2 Comments
 SEVERAL CASES OF CHINESE espionage have been announced recently in Europe. Thomas Reichenbach and Herwig and Ina Fischer —a married couple— were arrested on April 22, 2024, for illegal exports of dual use technology with military (naval) applications.
SEVERAL CASES OF CHINESE espionage have been announced recently in Europe. Thomas Reichenbach and Herwig and Ina Fischer —a married couple— were arrested on April 22, 2024, for illegal exports of dual use technology with military (naval) applications.
Reichenbach lists himself as a contract marketing manager for the Hong Kong Trade Development Council. He studied at Peking University in the mid-1980s. He worked in China, speaks Mandarin, and has a Chinese wife.
Herwig and Ina Fischer own a small engineering consulting company named Innovative Dragon in Duesseldorf. Both have travelled extensively in China. Innovative Dragon contracts for technical research with universities. Herwig studied mechanical engineering and aircraft and spacecraft construction at the Rhine-Westphalia Higher Technical School, focusing on guidance technology and composite fiber materials. The company headquarters are in London and there are offices in Duesseldorf and Shanghai (Donghua University Science and Technology Park). The London office does not appear to have a functioning telephone number.
Reichenbach is suspected of having been recruited by the Ministry of State Security (MSS) in China. The German government has accused the trio of having illegally exported dual use technology since at least 2022. At the time of the arrests, the suspects were in negotiations on additional research projects useful for expanding the combat strength of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army Navy.
Status: Alleged
Tradecraft observations:
- Use of a potential front company in London to facilitate allegedly illegal exports.
- Use of third countries to facilitate allegedly illegal exports.
- Reichenbach allegedly recruited Herwig and Ina Fischer and handled them as in-country assets.
- It is alleged that the MSS probably recruited Reichenbach in China.
- An MSS officer allegedly handled Reichenbach from China (linear control).
- The MSS allegedly funded the operation through front companies.
► Author: Nicholas Eftimiades* | Date: 03 May 2024 | Permalink
* Nicholas Eftimiades is a Senior Fellow at the Atlantic Council. He retired from a 34-year government career that included employment in the United States Central Intelligence Agency, the Department of State, and the Defense Intelligence Agency. He held appointments on the Department of Defense’s Defense Science Board and the Economic Security Subcommittee of the Department of Homeland Security’s Homeland Security Advisory Council. He is an advisor to the United States Intelligence Community. Eftimiades authored numerous works on China’s espionage methods. His books, Chinese Intelligence Operations (1994) and Chinese Espionage: Operations and Tactics (2020) are examinations of the structure, operations, and methodology of China’s intelligence services. They are widely regarded as seminal works in the field.
 AUTHORITIES IN GERMANY HAVE arrested a sixth person in less than a month, in connection with three separate cases of espionage orchestrated by Russian or Chinese intelligence. Last Tuesday, police in the east German city of Dresden arrested an assistant to a leading politician of the far-right Alternative für Deutschland party (AfD). The assistant, who is a dual German-Chinese citizen, is accused of spying for Chinese intelligence, while the far-right politician who employed him is also being investigated, according to reports.
AUTHORITIES IN GERMANY HAVE arrested a sixth person in less than a month, in connection with three separate cases of espionage orchestrated by Russian or Chinese intelligence. Last Tuesday, police in the east German city of Dresden arrested an assistant to a leading politician of the far-right Alternative für Deutschland party (AfD). The assistant, who is a dual German-Chinese citizen, is accused of spying for Chinese intelligence, while the far-right politician who employed him is also being investigated, according to reports. ON GOOD FRIDAY, MARCH 29, Egisto Ott, a former member of Austria’s now-dissolved domestic intelligence agency, the Federal Office for the Protection of the Constitution and Counterterrorism (BVT), was arrested in his house in Carinthia, Austria’s southernmost state. Ott had frequently been at the center of media attention in the past year, in connection with the network surrounding the fugitive
ON GOOD FRIDAY, MARCH 29, Egisto Ott, a former member of Austria’s now-dissolved domestic intelligence agency, the Federal Office for the Protection of the Constitution and Counterterrorism (BVT), was arrested in his house in Carinthia, Austria’s southernmost state. Ott had frequently been at the center of media attention in the past year, in connection with the network surrounding the fugitive  These included contacts in friendly foreign police services, whom Ott knew from his time as a liaison officer in Italy and Turkey. According to Gridling, these contacts were unaware that Ott had been removed from the BVT under suspicion of being unreliable and potentially even working for Russia. They therefore continued to help him when asked. Ott allegedly deceived his contacts by claiming that he needed information on cases relating to different kinds of extremism. As it turned out, according to the leaked arrest warrant, several of the individuals referred to by Ott as “suspects” in terrorism investigations were in fact Russian dissidents or intelligence defectors who were living as protected persons in Austria and elsewhere outside Russia.
These included contacts in friendly foreign police services, whom Ott knew from his time as a liaison officer in Italy and Turkey. According to Gridling, these contacts were unaware that Ott had been removed from the BVT under suspicion of being unreliable and potentially even working for Russia. They therefore continued to help him when asked. Ott allegedly deceived his contacts by claiming that he needed information on cases relating to different kinds of extremism. As it turned out, according to the leaked arrest warrant, several of the individuals referred to by Ott as “suspects” in terrorism investigations were in fact Russian dissidents or intelligence defectors who were living as protected persons in Austria and elsewhere outside Russia. AUTHORITIES IN INDIA HAVE arrested a security employee at the Indian High Commission in Russia, accusing him of spying for Pakistani intelligence. The embassy of India in Moscow is one of its largest in the world and is viewed as critical to New Delhi’s strategic relations with Russia. Employees that staff the Moscow embassy are highly vetted and typically represent the cream of the crop of India’s Ministry of External Affairs. It follows that news of the arrest of a Moscow embassy security employee on espionage charges must have raised eyebrows in India.
AUTHORITIES IN INDIA HAVE arrested a security employee at the Indian High Commission in Russia, accusing him of spying for Pakistani intelligence. The embassy of India in Moscow is one of its largest in the world and is viewed as critical to New Delhi’s strategic relations with Russia. Employees that staff the Moscow embassy are highly vetted and typically represent the cream of the crop of India’s Ministry of External Affairs. It follows that news of the arrest of a Moscow embassy security employee on espionage charges must have raised eyebrows in India. IN AN UNPRECEDENTED AND potentially highly consequential decision, a judge has barred a Chinese PhD student from entering Canada over concerns he might be pressured to spy by the government of China. The case could have “ripple effects” on universities across Canada and possibly even all of North America,
IN AN UNPRECEDENTED AND potentially highly consequential decision, a judge has barred a Chinese PhD student from entering Canada over concerns he might be pressured to spy by the government of China. The case could have “ripple effects” on universities across Canada and possibly even all of North America,  GERMANY HAS CHARGED TWO men, among them a German intelligence officer, with spying for Russia, in a case that has shocked German public opinion and
GERMANY HAS CHARGED TWO men, among them a German intelligence officer, with spying for Russia, in a case that has shocked German public opinion and  LAST WEEK, LEBANON’S GENERAL Security Directorate
LAST WEEK, LEBANON’S GENERAL Security Directorate  ONE OF GERMANY’S LEADING universities has suspended researchers funded by the Chinese government, citing concerns about academic freedom and industrial espionage. The Friedrich Alexander University of Erlangen-Nuremberg (FAU) announced the suspension of Chinese government-funded researchers in June of this year. In announcing the measure, the university stated that the move was designed to protect academic freedom and freedom of expression among its faculty and staff. Earlier this week, however, German media reported the contents of an internal FAU email, which expressed concerns that the Chinese state could be utilizing government-funded researches as spies.
ONE OF GERMANY’S LEADING universities has suspended researchers funded by the Chinese government, citing concerns about academic freedom and industrial espionage. The Friedrich Alexander University of Erlangen-Nuremberg (FAU) announced the suspension of Chinese government-funded researchers in June of this year. In announcing the measure, the university stated that the move was designed to protect academic freedom and freedom of expression among its faculty and staff. Earlier this week, however, German media reported the contents of an internal FAU email, which expressed concerns that the Chinese state could be utilizing government-funded researches as spies. FOR THE SECOND TIME in 10 days, the government of China has announced the arrest of a Chinese government employee on suspicion of spying for the United States Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). In a statement issued on Monday, China’s civilian intelligence agency, the Ministry of State Security (MSS), said it had launched an investigation into an official of a government ministry, who was allegedly caught conducting espionage on behalf of the CIA.
FOR THE SECOND TIME in 10 days, the government of China has announced the arrest of a Chinese government employee on suspicion of spying for the United States Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). In a statement issued on Monday, China’s civilian intelligence agency, the Ministry of State Security (MSS), said it had launched an investigation into an official of a government ministry, who was allegedly caught conducting espionage on behalf of the CIA. A SEVENTH PERSON HAS been detained in Taiwan as a result of a broadening investigation into a Chinese spy ring that allegedly provided Beijing with sensitive military intelligence. The existence of the investigation was
A SEVENTH PERSON HAS been detained in Taiwan as a result of a broadening investigation into a Chinese spy ring that allegedly provided Beijing with sensitive military intelligence. The existence of the investigation was 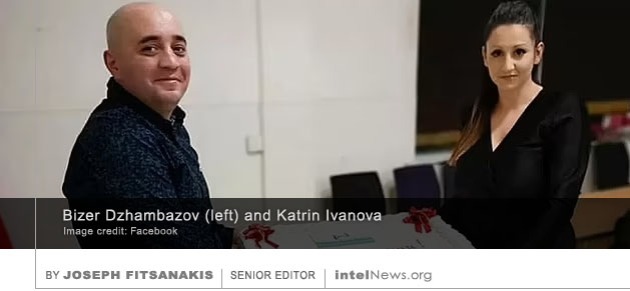 AUTHORITIES IN BRITAIN HAVE charged three Bulgarian nationals with spying for Russia, as part of “a major national security investigation” that led to at least five arrests as early as last February. Two of the Bulgarians appear to be legally married. They have been identified as Bizer Dzhambazov, 41, and Katrin Ivanova, 31, who live in Harrow, a northwestern borrow of Greater London. The third Bulgarian, Orlin Roussev, 45, was arrested in Great Yarmouth, a seaside town in the east coast identity dof England. None of the suspect appears to have a formal diplomatic connection to either Bulgaria or Russia.
AUTHORITIES IN BRITAIN HAVE charged three Bulgarian nationals with spying for Russia, as part of “a major national security investigation” that led to at least five arrests as early as last February. Two of the Bulgarians appear to be legally married. They have been identified as Bizer Dzhambazov, 41, and Katrin Ivanova, 31, who live in Harrow, a northwestern borrow of Greater London. The third Bulgarian, Orlin Roussev, 45, was arrested in Great Yarmouth, a seaside town in the east coast identity dof England. None of the suspect appears to have a formal diplomatic connection to either Bulgaria or Russia. A CHINESE GOVERNMENT EMPLOYEE gave “core information” about China’s military to the United States, after he was recruited by a Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) officer in Italy, a Chinese state agency has said. The allegation was made in a statement that was issued on Friday by China’s civilian intelligence agency, the Ministry of State Security (MSS), on its WeChat social media account.
A CHINESE GOVERNMENT EMPLOYEE gave “core information” about China’s military to the United States, after he was recruited by a Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) officer in Italy, a Chinese state agency has said. The allegation was made in a statement that was issued on Friday by China’s civilian intelligence agency, the Ministry of State Security (MSS), on its WeChat social media account. THE BRAZILIAN GOVERNMENT IS blocking requests from the United States and Russia to extradite an alleged Russian deep-cover spy, whose forged Brazilian identity papers were discovered by Dutch counterintelligence. Sergey Cherkasov was
THE BRAZILIAN GOVERNMENT IS blocking requests from the United States and Russia to extradite an alleged Russian deep-cover spy, whose forged Brazilian identity papers were discovered by Dutch counterintelligence. Sergey Cherkasov was  INTENSIFYING COMPETITION BETWEEN THE superpowers has turned Switzerland into an espionage battlefield, with more foreign spies being active there than in most other European countries, according to a new report. The
INTENSIFYING COMPETITION BETWEEN THE superpowers has turned Switzerland into an espionage battlefield, with more foreign spies being active there than in most other European countries, according to a new report. The 





