Alleged Afghan-born Russian spy tries to regain revoked British citizenship
February 12, 2024 1 Comment
 AN AFGHAN-BORN MAN, who became a naturalized British citizen and worked for British intelligence for over a decade, is attempting to regain his British citizenship, which was revoked after he was accused of being a Russian spy. The man, who is identified in court documents only as “C2”, was born in Afghanistan and grew up under the Soviet occupation in the 1980s. When the Soviets withdrew from Afghanistan he left the country alongside the Russian forces and resettled in Russia, where he attended university and married a Russian woman.
AN AFGHAN-BORN MAN, who became a naturalized British citizen and worked for British intelligence for over a decade, is attempting to regain his British citizenship, which was revoked after he was accused of being a Russian spy. The man, who is identified in court documents only as “C2”, was born in Afghanistan and grew up under the Soviet occupation in the 1980s. When the Soviets withdrew from Afghanistan he left the country alongside the Russian forces and resettled in Russia, where he attended university and married a Russian woman.
By 2000, when he entered the United Kingdom as an Afghan asylum seeker, he was in possession of Russian citizenship due to his marriage to a Russian citizen. He was eventually granted asylum in Britain and began to work as an interpreter for the Foreign Office and the Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ), Britain’s signals intelligence agency. His fluency in Russian, Dari, and Pashto, made him invaluable to British intelligence as the United States-led ‘war on terrorism’ escalated in Afghanistan. In the late 2000s, the British Foreign Office sent C2 to Afghanistan, where he worked to build ties between the nascent post-Taliban Afghan government and the British diplomatic corps stationed in the country.
It was in Afghanistan, according to Britain’s Security Service (MI5), that C2 began to develop contacts with Russian intelligence officials. The agency claims that two Russian military attaches stationed in the Afghan capital Kabul, identified in court documents as “Boris” and “Dimitri”, recruited C2 on behalf of the Main Directorate of the Russian Armed Forces’ General Staff, which is commonly known as GRU. The British government claims that, following his recruitment by GRU, C2 traveled to Russia at least six times and once to Cyprus, where he continued to hold regular meetings with his Russian handlers.
On 2019, after he had left government service, MI5 began to question C2 about his alleged connection to Russian military intelligence. He consistently denied that he was a Russian spy. Eventually, MI5 took him “to the roof of a hotel” in London, where he was administered a polygraph examination. A few weeks later, by which time he had returned to his base in Kabul, C2 was informed that his British citizenship would be revoked due to his espionage work for the Russians.
Ironically, the British government evacuated C2 from Afghanistan in 2021 as part of Operation PITTING, during which 15,000 Afghan nationals were transported to the United Kingdom as the Taliban descended on Kabul. Upon arriving in the United Kingdom, C2 was arrested and eventually released on bail. Last week he formally appealed against the British government’s decision to strip him of his citizenship. His case was heard in secrecy at a special hearing of the United Kingdom’s Special Immigration Appeal Commission (SIAC). The SIAC is expected to rule in March or April.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 12 February 2024 | Permalink
 A FORMER SOVIET KGB officer, who now lives in the United Kingdom under witness protection, can sue the British state for revealing his identity to Latvian authorities, which may have put his life in danger, a judge has ruled.
A FORMER SOVIET KGB officer, who now lives in the United Kingdom under witness protection, can sue the British state for revealing his identity to Latvian authorities, which may have put his life in danger, a judge has ruled.  AUTHORITIES IN BRITAIN HAVE arrested two individuals on charges of espionage, among them a researcher for the British parliament who is being investigated for spying for China.
AUTHORITIES IN BRITAIN HAVE arrested two individuals on charges of espionage, among them a researcher for the British parliament who is being investigated for spying for China. 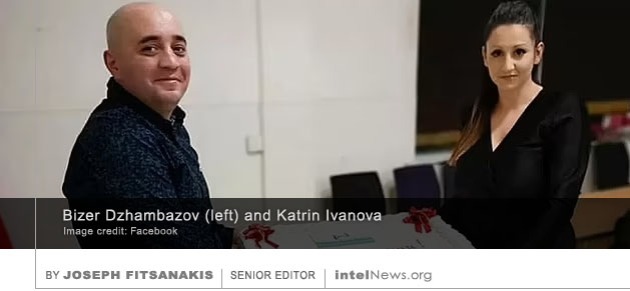 AUTHORITIES IN BRITAIN HAVE charged three Bulgarian nationals with spying for Russia, as part of “a major national security investigation” that led to at least five arrests as early as last February. Two of the Bulgarians appear to be legally married. They have been identified as Bizer Dzhambazov, 41, and Katrin Ivanova, 31, who live in Harrow, a northwestern borrow of Greater London. The third Bulgarian, Orlin Roussev, 45, was arrested in Great Yarmouth, a seaside town in the east coast identity dof England. None of the suspect appears to have a formal diplomatic connection to either Bulgaria or Russia.
AUTHORITIES IN BRITAIN HAVE charged three Bulgarian nationals with spying for Russia, as part of “a major national security investigation” that led to at least five arrests as early as last February. Two of the Bulgarians appear to be legally married. They have been identified as Bizer Dzhambazov, 41, and Katrin Ivanova, 31, who live in Harrow, a northwestern borrow of Greater London. The third Bulgarian, Orlin Roussev, 45, was arrested in Great Yarmouth, a seaside town in the east coast identity dof England. None of the suspect appears to have a formal diplomatic connection to either Bulgaria or Russia. A DIPLOMAT STATIONED AT the embassy of the Russian Federation in London proposed to channel Russian funds to the British Conservative Party, according to a formal complaint made by a Conservative Party activist. The information was
A DIPLOMAT STATIONED AT the embassy of the Russian Federation in London proposed to channel Russian funds to the British Conservative Party, according to a formal complaint made by a Conservative Party activist. The information was  IRAN ANNOUNCED ON SATURDAY one of the most high-profile executions in its recent history, involving Alireza Akbari, who served as the Islamic Republic’s deputy minister of defense in the 2000s. Akbari, 61, a dual Iranian-British citizen, was
IRAN ANNOUNCED ON SATURDAY one of the most high-profile executions in its recent history, involving Alireza Akbari, who served as the Islamic Republic’s deputy minister of defense in the 2000s. Akbari, 61, a dual Iranian-British citizen, was  THE NORTHERN IRISH CONFLICT was a 30-year irregular war involving the government of the United Kingdom and an assortment of paramilitary groups. By the mid-1990s, when most of these groups had declared ceasefire, over 3,600 people had been killed and over 40,000 injured. The major paramilitary groups that participated in the conflict were the separatist Provisional Irish Republican Army (IRA) and Irish National Liberation Army (INLA), and the pro-UK, or ‘loyalist’, Ulster Volunteer Force (UVF) and Ulster Defence Association (UDA).
THE NORTHERN IRISH CONFLICT was a 30-year irregular war involving the government of the United Kingdom and an assortment of paramilitary groups. By the mid-1990s, when most of these groups had declared ceasefire, over 3,600 people had been killed and over 40,000 injured. The major paramilitary groups that participated in the conflict were the separatist Provisional Irish Republican Army (IRA) and Irish National Liberation Army (INLA), and the pro-UK, or ‘loyalist’, Ulster Volunteer Force (UVF) and Ulster Defence Association (UDA). TELEPHONE SYSTEMS BELONGING TO the British government were compromised by the Pegasus surveillance software, according to a Canadian research group. The allegation was made on Monday in an investigative
TELEPHONE SYSTEMS BELONGING TO the British government were compromised by the Pegasus surveillance software, according to a Canadian research group. The allegation was made on Monday in an investigative  IN A VIDEO MESSAGE described by observers as “extraordinary”, the British Ministry of Defence has warned that at least half of the Russian military’s ground combat units have now encircled much of Ukraine. The report describes this as “the largest gathering of Russian troops” anywhere in the world since 1991—the year when the Soviet Union collapsed.
IN A VIDEO MESSAGE described by observers as “extraordinary”, the British Ministry of Defence has warned that at least half of the Russian military’s ground combat units have now encircled much of Ukraine. The report describes this as “the largest gathering of Russian troops” anywhere in the world since 1991—the year when the Soviet Union collapsed. THE BRITISH GOVERNMENT IS citing a rarely used “breach of confidence” clause in an effort to stop the country’s public broadcaster from revealing the identity of a British intelligence officer working abroad. According to
THE BRITISH GOVERNMENT IS citing a rarely used “breach of confidence” clause in an effort to stop the country’s public broadcaster from revealing the identity of a British intelligence officer working abroad. According to  THE BRITISH GOVERNMENT IS seeking to stop the nation’s public broadcaster from airing a story that would allegedly reveal the identity of a British intelligence officer working abroad. The news
THE BRITISH GOVERNMENT IS seeking to stop the nation’s public broadcaster from airing a story that would allegedly reveal the identity of a British intelligence officer working abroad. The news  DOCUMENTS RELEASED LAST WEEK by the National Archives of Ireland show the extraordinary support given by the government of Libya to Irish republican separatists in Britain during the 1970s and 1980s. The previously classified documents were released last Tuesday by Ireland’s National Archives, which is the country’s official repository of state records. According to reports, the
DOCUMENTS RELEASED LAST WEEK by the National Archives of Ireland show the extraordinary support given by the government of Libya to Irish republican separatists in Britain during the 1970s and 1980s. The previously classified documents were released last Tuesday by Ireland’s National Archives, which is the country’s official repository of state records. According to reports, the  BRITISH, AMERICAN AND OTHER Western intelligence agencies are quietly preparing Ukrainian military and security experts to withstand a possible Russian attack, according to a number of media reports. The New York Times reported on Monday that cyberwarfare units from the United States and the United Kingdom have been dispatched to Ukraine. Their mission is believed to be helping the former Soviet republic in confronting possible large-scale cyberattacks from Moscow.
BRITISH, AMERICAN AND OTHER Western intelligence agencies are quietly preparing Ukrainian military and security experts to withstand a possible Russian attack, according to a number of media reports. The New York Times reported on Monday that cyberwarfare units from the United States and the United Kingdom have been dispatched to Ukraine. Their mission is believed to be helping the former Soviet republic in confronting possible large-scale cyberattacks from Moscow. THE CONSENSUS VIEW OF British intelligence in the weeks leading to the fall of Kabul to the Taliban was that the Afghan government would be challenged, but that the rebels were unlikely to take over the country in 2021. This was revealed on Wednesday in the House of Commons by Britain’s Foreign Secretary, Dominic Raab.
THE CONSENSUS VIEW OF British intelligence in the weeks leading to the fall of Kabul to the Taliban was that the Afghan government would be challenged, but that the rebels were unlikely to take over the country in 2021. This was revealed on Wednesday in the House of Commons by Britain’s Foreign Secretary, Dominic Raab. 






