Alleged Afghan-born Russian spy tries to regain revoked British citizenship
February 12, 2024 1 Comment
 AN AFGHAN-BORN MAN, who became a naturalized British citizen and worked for British intelligence for over a decade, is attempting to regain his British citizenship, which was revoked after he was accused of being a Russian spy. The man, who is identified in court documents only as “C2”, was born in Afghanistan and grew up under the Soviet occupation in the 1980s. When the Soviets withdrew from Afghanistan he left the country alongside the Russian forces and resettled in Russia, where he attended university and married a Russian woman.
AN AFGHAN-BORN MAN, who became a naturalized British citizen and worked for British intelligence for over a decade, is attempting to regain his British citizenship, which was revoked after he was accused of being a Russian spy. The man, who is identified in court documents only as “C2”, was born in Afghanistan and grew up under the Soviet occupation in the 1980s. When the Soviets withdrew from Afghanistan he left the country alongside the Russian forces and resettled in Russia, where he attended university and married a Russian woman.
By 2000, when he entered the United Kingdom as an Afghan asylum seeker, he was in possession of Russian citizenship due to his marriage to a Russian citizen. He was eventually granted asylum in Britain and began to work as an interpreter for the Foreign Office and the Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ), Britain’s signals intelligence agency. His fluency in Russian, Dari, and Pashto, made him invaluable to British intelligence as the United States-led ‘war on terrorism’ escalated in Afghanistan. In the late 2000s, the British Foreign Office sent C2 to Afghanistan, where he worked to build ties between the nascent post-Taliban Afghan government and the British diplomatic corps stationed in the country.
It was in Afghanistan, according to Britain’s Security Service (MI5), that C2 began to develop contacts with Russian intelligence officials. The agency claims that two Russian military attaches stationed in the Afghan capital Kabul, identified in court documents as “Boris” and “Dimitri”, recruited C2 on behalf of the Main Directorate of the Russian Armed Forces’ General Staff, which is commonly known as GRU. The British government claims that, following his recruitment by GRU, C2 traveled to Russia at least six times and once to Cyprus, where he continued to hold regular meetings with his Russian handlers.
On 2019, after he had left government service, MI5 began to question C2 about his alleged connection to Russian military intelligence. He consistently denied that he was a Russian spy. Eventually, MI5 took him “to the roof of a hotel” in London, where he was administered a polygraph examination. A few weeks later, by which time he had returned to his base in Kabul, C2 was informed that his British citizenship would be revoked due to his espionage work for the Russians.
Ironically, the British government evacuated C2 from Afghanistan in 2021 as part of Operation PITTING, during which 15,000 Afghan nationals were transported to the United Kingdom as the Taliban descended on Kabul. Upon arriving in the United Kingdom, C2 was arrested and eventually released on bail. Last week he formally appealed against the British government’s decision to strip him of his citizenship. His case was heard in secrecy at a special hearing of the United Kingdom’s Special Immigration Appeal Commission (SIAC). The SIAC is expected to rule in March or April.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 12 February 2024 | Permalink


 • UN report says Afghan Taliban still maintain ties with al-Qaida. The Taliban in Afghanistan still maintain close ties with the al-Qaida terror network, despite signing a peace deal with the United States in which they committed to fight militant groups, a UN
• UN report says Afghan Taliban still maintain ties with al-Qaida. The Taliban in Afghanistan still maintain close ties with the al-Qaida terror network, despite signing a peace deal with the United States in which they committed to fight militant groups, a UN  Russian hackers hijacked an Iranian cyber espionage group and used its infrastructure to launch attacks, hoping that their victims would blame Iran, according to British and American intelligence officials. The information,
Russian hackers hijacked an Iranian cyber espionage group and used its infrastructure to launch attacks, hoping that their victims would blame Iran, according to British and American intelligence officials. The information, 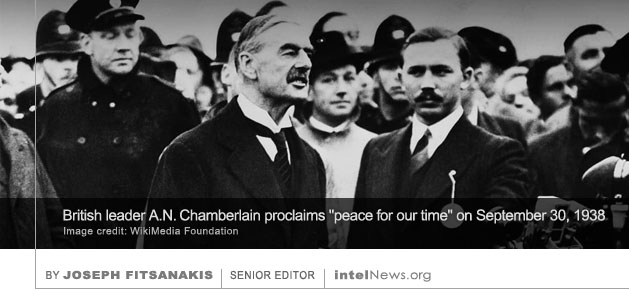 Nearly 2,000 missing British intelligence files relating to the so-called Munich Agreement, a failed attempt by Britain, France and Italy to appease Adolf Hitler in 1938, may not have been destroyed, according to historians. On September 30, 1938, the leaders of France, Britain and Italy signed a peace treaty with the Nazi government of German Chancellor Adolf Hitler. The treaty, which became known as the Munich Agreement, gave Hitler de facto control of Czechoslovakia’s German-speaking areas, in return for him promising to resign from territorial claims against other countries, such as Poland and Hungary. Hours after the treaty was formalized, British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain arrived by airplane at an airport near London, and boldly proclaimed that he had secured “peace for our time” (pictured above). Contrary to Chamberlain’s expectations, however, the German government was emboldened by what it saw as attempts to appease it, and promptly proceeded to invade Poland, thus firing the opening shots of World War II in Europe.
Nearly 2,000 missing British intelligence files relating to the so-called Munich Agreement, a failed attempt by Britain, France and Italy to appease Adolf Hitler in 1938, may not have been destroyed, according to historians. On September 30, 1938, the leaders of France, Britain and Italy signed a peace treaty with the Nazi government of German Chancellor Adolf Hitler. The treaty, which became known as the Munich Agreement, gave Hitler de facto control of Czechoslovakia’s German-speaking areas, in return for him promising to resign from territorial claims against other countries, such as Poland and Hungary. Hours after the treaty was formalized, British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain arrived by airplane at an airport near London, and boldly proclaimed that he had secured “peace for our time” (pictured above). Contrary to Chamberlain’s expectations, however, the German government was emboldened by what it saw as attempts to appease it, and promptly proceeded to invade Poland, thus firing the opening shots of World War II in Europe. For the first time in its history, the United Kingdom has launched its first-ever military-style cyber campaign against an adversary, according to the director of the country’s primary cyber security agency. The target of the campaign was the Islamic State, the militant Sunni Muslim group that is also known as the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS). The existence of the all-out cyber war was announced last week by Jeremy Fleming, the newly appointed director of the Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ), Britain’s signals intelligence organization. Fleming, a former Security Service (MI5) officer, was
For the first time in its history, the United Kingdom has launched its first-ever military-style cyber campaign against an adversary, according to the director of the country’s primary cyber security agency. The target of the campaign was the Islamic State, the militant Sunni Muslim group that is also known as the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS). The existence of the all-out cyber war was announced last week by Jeremy Fleming, the newly appointed director of the Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ), Britain’s signals intelligence organization. Fleming, a former Security Service (MI5) officer, was  The collapse of the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria is giving rise to a host of successor groups, which are quickly regrouping, recruiting members and launching increasingly sophisticated attacks against government forces, according to experts. A military victory in the war against ISIS was officially declared by the Iraqi government in December of last year. In recent weeks, United States President Donald Trump has repeated his government’s claim that American forces are “knocking the hell out of ISIS”. The Sunni militant group, which rose to prominence in 2014 after conquering much of Syria and northwestern Iraq, is clearly on the retreat, having lost every major urban center that it used to control. However, the collapse of the organization has led to the emergence of numerous insurgent groups that are quickly forming in Iraq and Syria.
The collapse of the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria is giving rise to a host of successor groups, which are quickly regrouping, recruiting members and launching increasingly sophisticated attacks against government forces, according to experts. A military victory in the war against ISIS was officially declared by the Iraqi government in December of last year. In recent weeks, United States President Donald Trump has repeated his government’s claim that American forces are “knocking the hell out of ISIS”. The Sunni militant group, which rose to prominence in 2014 after conquering much of Syria and northwestern Iraq, is clearly on the retreat, having lost every major urban center that it used to control. However, the collapse of the organization has led to the emergence of numerous insurgent groups that are quickly forming in Iraq and Syria. A spokesman for Tony Blair has dismissed as “categorically absurd” allegations that the former British Prime Minister warned the White House that President Donald Trump was targeted by British spy agencies. The claims are made in the book Fire and Fury: Inside the Trump White House, which is due to be published next week. Its author, Michael Wolf, says he based the information in the book on more than 200 interviews that he held with President Trump and members of his inner circle during the past year.
A spokesman for Tony Blair has dismissed as “categorically absurd” allegations that the former British Prime Minister warned the White House that President Donald Trump was targeted by British spy agencies. The claims are made in the book Fire and Fury: Inside the Trump White House, which is due to be published next week. Its author, Michael Wolf, says he based the information in the book on more than 200 interviews that he held with President Trump and members of his inner circle during the past year. A new report authored by a consortium of government and private organizations in Britain has revealed the existence of a computer hacking operation, allegedly based in China, that is said to be “one of the largest ever” such campaigns globally. The operation is believed to have compromised sensitive information from an inestimable number of private companies in Southeast Asia, Europe and the United States. The
A new report authored by a consortium of government and private organizations in Britain has revealed the existence of a computer hacking operation, allegedly based in China, that is said to be “one of the largest ever” such campaigns globally. The operation is believed to have compromised sensitive information from an inestimable number of private companies in Southeast Asia, Europe and the United States. The  Documents accessed by a French newspaper show that American and British intelligence agencies worked together to spy on diplomats, academic researchers and defense contractors in Israel and the Palestinian territories. Last year, the German newsmagazine Der Spiegel and the American newspaper The Wall Street Journal
Documents accessed by a French newspaper show that American and British intelligence agencies worked together to spy on diplomats, academic researchers and defense contractors in Israel and the Palestinian territories. Last year, the German newsmagazine Der Spiegel and the American newspaper The Wall Street Journal 





