New director appointed to head Pakistan’s all-powerful intelligence agency
December 13, 2016 Leave a comment
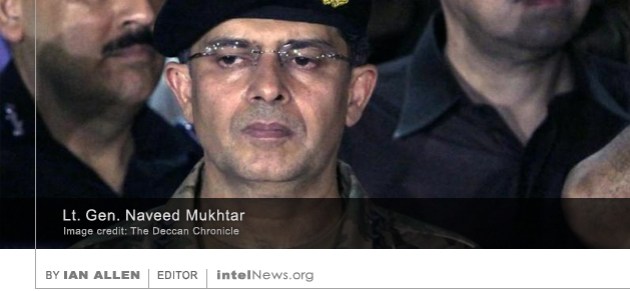 A new director, with considerable experience in counterterrorism, has been appointed to lead Pakistan’s Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI), believed by some to be one of the most powerful spy agencies in the world. Pakistan’s Ministry of Defense announced on Sunday that Lt. Gen. Naveed Mukhtar will be replacing Lt. Gen. Rizwan Akhtar, who has led the ISI since November of 2014. The appointment of Gen. Mukhtar comes less than a month after a major change of leadership in the Pakistani military, which saw the appointment of General Javed Qamar Bajwa as the new Chief of Army Staff. It is believed that the appointment of the new ISI director represents a personal choice of the newly appointed Gen. Bajwa.
A new director, with considerable experience in counterterrorism, has been appointed to lead Pakistan’s Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI), believed by some to be one of the most powerful spy agencies in the world. Pakistan’s Ministry of Defense announced on Sunday that Lt. Gen. Naveed Mukhtar will be replacing Lt. Gen. Rizwan Akhtar, who has led the ISI since November of 2014. The appointment of Gen. Mukhtar comes less than a month after a major change of leadership in the Pakistani military, which saw the appointment of General Javed Qamar Bajwa as the new Chief of Army Staff. It is believed that the appointment of the new ISI director represents a personal choice of the newly appointed Gen. Bajwa.
Both the outgoing and incoming directors of the ISI are from the same generation of military officers, having been commissioned in 1982 and 1983 respectively. Both attended Pakistan’s prestigious National Defense University and earned graduate degrees at the United States Army War College in Pennsylvania. But while Gen. Akhtar specializes in counterinsurgency, and spent much of his career in Pakistan’s Federally Administered Tribal Areas, his successor, Gen. Mukhtar, has a background in intelligence with a focus on counterterrorism. Although he most recently served in Karachi, Pakistan’s largest and most populous metropolitan center, Gen. Mukhtar made his mark in the military by leading the ISI’s counterterrorism branch in the capital Islamabad. It is said, therefore, that his appointment to the directorship of the ISI may signal a turn away from running Taliban agents in Afghanistan, for which the ISI is notorious, and concentrating instead of combatting militant groups at home.
The change in the ISI’s leadership comes at a particularly complicated period in Pakistani security. The country’s relations with its neighbor and arch-nemesis India are experiencing a major crisis following the so-called ‘summer of unrest’ in Kashmir. The term refers to a period of tension between the two countries, sparked by popular unrest and violent protests by the predominantly Muslim inhabitants of the Indian-administered region of Jammu and Kashmir. The region remained under a military curfew for nearly two months, during which nearly 100 people died and over 15,000 were injured. There are some in Islamabad who believe that Gen. Akhtar was removed from the ISI because he failed to contain the unrest in Kashmir. He has now been appointed president of Pakistan’s National Defense University in Islamabad.
► Author: Ian Allen | Date: 13 December 2016 | Permalink
 Russian authorities say they prevented a large-scale cyber attack by “a foreign intelligence service”, which had been designed to destabilize the country’s financial system and subvert its economy. In an official
Russian authorities say they prevented a large-scale cyber attack by “a foreign intelligence service”, which had been designed to destabilize the country’s financial system and subvert its economy. In an official  The United States’ senior intelligence officer has told Congress that new legislation requiring spy agencies to act against alleged Russian covert operations constitutes “micromanagement” of the American Intelligence Community. The Intelligence Authorization bill, which includes a number of intelligence-related requirements and provisions, is debated and enacted each year by Congress. This year’s legislation has already been approved by the intelligence committees of the Senate and House of Representatives. Last week it was enacted by the House, while the Senate is preparing to debate it this week.
The United States’ senior intelligence officer has told Congress that new legislation requiring spy agencies to act against alleged Russian covert operations constitutes “micromanagement” of the American Intelligence Community. The Intelligence Authorization bill, which includes a number of intelligence-related requirements and provisions, is debated and enacted each year by Congress. This year’s legislation has already been approved by the intelligence committees of the Senate and House of Representatives. Last week it was enacted by the House, while the Senate is preparing to debate it this week. Several former and current intelligence officers, including a former director of the national spy service, have appeared in court in Macedonia, accused of illegally wiretapping thousands of people on orders of the government. The wiretap scandal has sparked the deepest political crisis in the impoverished Balkan country, which has existed since declaring independence from Yugoslavia in 1991.
Several former and current intelligence officers, including a former director of the national spy service, have appeared in court in Macedonia, accused of illegally wiretapping thousands of people on orders of the government. The wiretap scandal has sparked the deepest political crisis in the impoverished Balkan country, which has existed since declaring independence from Yugoslavia in 1991. In a move that highlights the thaw in relations between South Korea and Japan, the two nations appear to be closer than ever to entering an intelligence agreement with each other. In 2014, Washington, Seoul and Tokyo signed a trilateral intelligence-sharing agreement on regional security issues, with the United States acting as an intermediary. But a proposed new agreement between South Korea and Japan would remove the US from the equation and would facilitate direct intelligence-sharing between the two East Asian nations for the first time in history.
In a move that highlights the thaw in relations between South Korea and Japan, the two nations appear to be closer than ever to entering an intelligence agreement with each other. In 2014, Washington, Seoul and Tokyo signed a trilateral intelligence-sharing agreement on regional security issues, with the United States acting as an intermediary. But a proposed new agreement between South Korea and Japan would remove the US from the equation and would facilitate direct intelligence-sharing between the two East Asian nations for the first time in history. Two Russian intelligence officers, who defected to the United States in 2008, claim that they had to fend for themselves after American spy agencies failed to protect them despite promises to the contrary. Janosh Neumann (born Alexey Yurievich Artamonov) and his wife Victorya were employees of Russia’s Federal Security Service (FSB) specializing in investigations of money laundering and corruption. But in 2008 they traveled from Russia to Germany and from there to the Dominican Republic. Once in the Caribbean island, they entered the US embassy and offered to work for the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA).
Two Russian intelligence officers, who defected to the United States in 2008, claim that they had to fend for themselves after American spy agencies failed to protect them despite promises to the contrary. Janosh Neumann (born Alexey Yurievich Artamonov) and his wife Victorya were employees of Russia’s Federal Security Service (FSB) specializing in investigations of money laundering and corruption. But in 2008 they traveled from Russia to Germany and from there to the Dominican Republic. Once in the Caribbean island, they entered the US embassy and offered to work for the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). Authorities in the former Yugoslav Republic of Montenegro say that “nationalists from Russia” and Serbia were behind a failed plot to kill the country’s prime minister and spark a pro-Russian coup in the country. As intelNews
Authorities in the former Yugoslav Republic of Montenegro say that “nationalists from Russia” and Serbia were behind a failed plot to kill the country’s prime minister and spark a pro-Russian coup in the country. As intelNews  A weapons cache that was found buried last week near the apartment of Serbia’s prime minister has fuelled tensions in the Balkan country, amid rumors that a failed coup in neighboring Montenegro was planned in Serbia by Russian spies. Serbian authorities announced the discovery of the stockpile on October 29; it included ammunition, hand grenades and a portable missile launcher and was located near the residence of Prime Minister Aleksandar Vučić. The government later said that the weapons find dated back to the Balkan wars of the 1990s and was not connected with at Vučić’s administration. But politics in the country remain tense, following allegations made earlier in October that Russian intelligence agents used Serbia as a base to plan a military coup in Montenegro.
A weapons cache that was found buried last week near the apartment of Serbia’s prime minister has fuelled tensions in the Balkan country, amid rumors that a failed coup in neighboring Montenegro was planned in Serbia by Russian spies. Serbian authorities announced the discovery of the stockpile on October 29; it included ammunition, hand grenades and a portable missile launcher and was located near the residence of Prime Minister Aleksandar Vučić. The government later said that the weapons find dated back to the Balkan wars of the 1990s and was not connected with at Vučić’s administration. But politics in the country remain tense, following allegations made earlier in October that Russian intelligence agents used Serbia as a base to plan a military coup in Montenegro. Russia’s ambassador to the United Kingdom has accused the British Foreign Office of deliberately delaying the issuance of visas for its diplomatic officials who have been assigned to join the Russian embassy in London. Alexander Yakovenko, Russia’s former Deputy Minister of Foreign Affairs, who has been heading the Russian embassy in London since 2011,
Russia’s ambassador to the United Kingdom has accused the British Foreign Office of deliberately delaying the issuance of visas for its diplomatic officials who have been assigned to join the Russian embassy in London. Alexander Yakovenko, Russia’s former Deputy Minister of Foreign Affairs, who has been heading the Russian embassy in London since 2011,  The most famous intelligence operative in Germany went on trial last week after his name was linked to dozens of offshore bank accounts and shell companies. But he claims he used these accounts to rescue hostages as part of his undercover work. Werner Mauss became known in 1997, when he was
The most famous intelligence operative in Germany went on trial last week after his name was linked to dozens of offshore bank accounts and shell companies. But he claims he used these accounts to rescue hostages as part of his undercover work. Werner Mauss became known in 1997, when he was  A Syrian former intelligence officer, who was given American citizenship several years ago, is being sought by authorities in the United States. The man was named by the Federal Bureau of Investigation last week as Moustafa Abed Ayoub, a 75-year-old resident of Fort Lauderdale, Florida. A
A Syrian former intelligence officer, who was given American citizenship several years ago, is being sought by authorities in the United States. The man was named by the Federal Bureau of Investigation last week as Moustafa Abed Ayoub, a 75-year-old resident of Fort Lauderdale, Florida. A  Voters in Switzerland have strongly approved a proposed law that aims to expand the surveillance powers of Swiss intelligence agencies. The move is uncharacteristic of the Swiss, who have historically been skeptical of giving far-reaching surveillance powers to their government. In the late 1980s, Swiss public opinion was shocked by the revelation that the country’s Federal Military Department had spied without permission on tens of thousands of Swiss citizens for many decades under a top-secret project codenamed P-27. In response to the revelations, P-27 was ended, the Swiss intelligence agencies were reorganized, and stricter parliamentary controls were imposed on their activities. Today, even CCTV cameras are rarely used in Switzerland, while Google has not been given permission to incorporate the country’s streets into its Streetview application due to strict local privacy laws.
Voters in Switzerland have strongly approved a proposed law that aims to expand the surveillance powers of Swiss intelligence agencies. The move is uncharacteristic of the Swiss, who have historically been skeptical of giving far-reaching surveillance powers to their government. In the late 1980s, Swiss public opinion was shocked by the revelation that the country’s Federal Military Department had spied without permission on tens of thousands of Swiss citizens for many decades under a top-secret project codenamed P-27. In response to the revelations, P-27 was ended, the Swiss intelligence agencies were reorganized, and stricter parliamentary controls were imposed on their activities. Today, even CCTV cameras are rarely used in Switzerland, while Google has not been given permission to incorporate the country’s streets into its Streetview application due to strict local privacy laws. The volume of domestic communications that were intercepted by Canada’s spy agency increased 26 times between 2014 and 2015, according to a recently released report by a government watchdog. The same report states that intercepted information about Canadian citizens, which is given to Canada’s spy agency by the intelligence organizations of other Western countries, has increased so much that it now requires an elaborate mechanism to analyze it. When asked to explain the reasons for these increases, Canadian government officials said they could not do so without divulging secrets of national importance.
The volume of domestic communications that were intercepted by Canada’s spy agency increased 26 times between 2014 and 2015, according to a recently released report by a government watchdog. The same report states that intercepted information about Canadian citizens, which is given to Canada’s spy agency by the intelligence organizations of other Western countries, has increased so much that it now requires an elaborate mechanism to analyze it. When asked to explain the reasons for these increases, Canadian government officials said they could not do so without divulging secrets of national importance.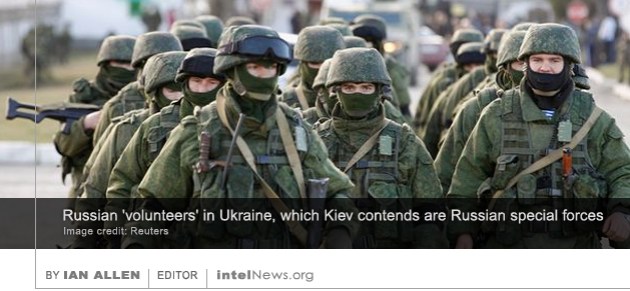 Ukrainian intelligence and defense officials are sharing intelligence with Britain about cutting-edge Russian military tactics in the Crimea and parts of eastern Ukraine. Since the 2014 Russian military intervention in Ukraine, observers have noted the sophisticated tactics used by Moscow. The Russian forces seem to be combining their advanced conventional arsenal with electronic warfare and information operations. The latter include the use of deception, spreading propaganda through social media, and computer hacking. Some experts have described Russia’s tactics in the Crimean Peninsula and the Donbass region of Ukraine as a form of “
Ukrainian intelligence and defense officials are sharing intelligence with Britain about cutting-edge Russian military tactics in the Crimea and parts of eastern Ukraine. Since the 2014 Russian military intervention in Ukraine, observers have noted the sophisticated tactics used by Moscow. The Russian forces seem to be combining their advanced conventional arsenal with electronic warfare and information operations. The latter include the use of deception, spreading propaganda through social media, and computer hacking. Some experts have described Russia’s tactics in the Crimean Peninsula and the Donbass region of Ukraine as a form of “






German security agencies had watched Berlin market attacker for a year
December 22, 2016 2 Comments
On Wednesday, German newspaper Süddeutsche Zeitung revealed that Amiri’s cell phone and email accounts had been monitored by German security agencies at least since January of this year. The decision to monitor his telecommunications was reportedly taken by officials at Germany’s Center for Terrorism Defense (GTAZ). The agency functions as a fusion center for intelligence cooperation between German police and spy services. The newspaper said that Amiri was deemed suspicious because of his connections with several radical Islamists, who were arrested in Germany in recent months. They include Abu Walaa, a vocal supporter of the Islamic State who was captured in Northern Germany in November. According to anonymous German officials, Amiri had also told friends that he was seeking people to help him purchase weapons and use them to carry out attacks on civilians in Europe.
Last summer, Amiri was involved in a scuffle between rival drug gangs in Berlin, in which at least one knife was used. But he disappeared for several weeks when police tried to question him about it. He was eventually arrested and questioned by police in Berlin. It was discovered that, according to one German official, Amiri “was highly mobile”, moving between Berlin and northern Germany every few weeks. But, according to the Süddeutsche Zeitung, German authorities did not have enough evidence against him to keep him in detention. Shortly after Amiri’s arrest and subsequent release, German authorities decided to turn down his application for asylum due to security concerns. He was due to be deported from Germany before December 31. The German police is now offering up to €100,000 for Amiri’s capture.
► Author: Ian Allen | Date: 22 December 2016 | Permalink
Filed under Expert news and commentary on intelligence, espionage, spies and spying Tagged with 2016 Berlin Christmas market attack, Anis Amiri, Center for Terrorism Defense (Germany), counterterrorism, Germany, GTAZ (Germany), News, terrorism, Tunisia