No prison for Australian former spy who disclosed controversial espionage operation
June 21, 2021 Leave a comment

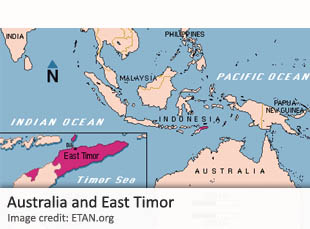
A FORMER AUSTRALIAN SPY, who prompted international outcry by revealing a controversial espionage operation by Canberra against the impoverished nation of East Timor, has been given a suspended prison sentence. The case against the former spy, known only as “Witness K.”, first emerged in 2013. It is believed that Witness K. served as director of technical operations in the Australian Secret Intelligence Service (ASIS), Australia’s foreign-intelligence agency.
In 2013, Witness K. revealed an espionage operation that targeted the impoverished Pacific island nation of Timor-Leste, also known as East Timor. He alleged that ASIS officers, disguised as a renovation crew, bugged an East Timorese government complex. The information gathered from the spy operation allegedly allowed the Australian government to gain the upper hand in a series of complex negotiations that led to the 2004 Certain Maritime Arrangements in the Timor Sea (CMATS) treaty. The treaty awards Australia a share from profits from oil exploration in the Greater Sunrise oil and gas field, which is claimed by both Australia and East Timor.
In 2013, the East Timorese government took Australia to the Permanent Court of Arbitration in The Hague, claiming that the Australian government was in possession of intelligence acquired through illegal bugging. The claim was supported by Witness K., who argued that ASIS’ espionage operation was both “immoral and wrong” because it was designed to benefit the interests of large energy conglomerates and had nothing to do with Australian national security. It is worth noting that Witness K. said he decided to reveal the ASIS bugging operation after he learned that Australia’s former Minister of Foreign Affairs, Alexander Downer, had been hired as an adviser to Woodside Petroleum, an energy company that was directly benefiting from the CMATS treaty.
 The head of Germany’s domestic intelligence agency has warned of security risks resulting from Chinese direct investment in high-technology German and other European companies. Since 2012, Hans-Georg Maassen has served as director of the Federal Office for the Protection of the Constitution, Germany’s domestic security and counterintelligence agency.
The head of Germany’s domestic intelligence agency has warned of security risks resulting from Chinese direct investment in high-technology German and other European companies. Since 2012, Hans-Georg Maassen has served as director of the Federal Office for the Protection of the Constitution, Germany’s domestic security and counterintelligence agency.  The intelligence agency of New Zealand has issued a report warning that the country is being targeted by foreign spies who operate using fake covers. Many of them aim to infiltrate some of the highest levels of the government, according to the agency. The warning appeared in the annual report of the New Zealand Security Intelligence Service (NZSIS), the country’s main national intelligence organization, which is responsible for intelligence, counterintelligence and counter- terrorism. The NZSIS’
The intelligence agency of New Zealand has issued a report warning that the country is being targeted by foreign spies who operate using fake covers. Many of them aim to infiltrate some of the highest levels of the government, according to the agency. The warning appeared in the annual report of the New Zealand Security Intelligence Service (NZSIS), the country’s main national intelligence organization, which is responsible for intelligence, counterintelligence and counter- terrorism. The NZSIS’  Russian authorities say they prevented a large-scale cyber attack by “a foreign intelligence service”, which had been designed to destabilize the country’s financial system and subvert its economy. In an official
Russian authorities say they prevented a large-scale cyber attack by “a foreign intelligence service”, which had been designed to destabilize the country’s financial system and subvert its economy. In an official  New information published by international whistleblower website WikiLeaks seems to suggest that the United States National Security Agency (NSA) collected information on export contracts by French companies and sought inside information on France’s position in international trade negotiations. According to the website, which
New information published by international whistleblower website WikiLeaks seems to suggest that the United States National Security Agency (NSA) collected information on export contracts by French companies and sought inside information on France’s position in international trade negotiations. According to the website, which 


 By JOSEPH FITSANAKIS | intelNews.org
By JOSEPH FITSANAKIS | intelNews.org