China-based Australian businessman charged with espionage
April 17, 2023 1 Comment
 AN AUSTRALIAN BUSINESSMAN, WHO has worked in China for over two decades, is facing up to 15 years in prison for allegedly selling secrets to two foreign intelligence officers. The businessman, Alexander Csergo, 55, grew up in Sydney, but moved to China in 2002 and currently works for a digital solutions firm in Shanghai. According to reports, Csergo describes himself on social media as a “business strategist” and an “operational transformation specialist”.
AN AUSTRALIAN BUSINESSMAN, WHO has worked in China for over two decades, is facing up to 15 years in prison for allegedly selling secrets to two foreign intelligence officers. The businessman, Alexander Csergo, 55, grew up in Sydney, but moved to China in 2002 and currently works for a digital solutions firm in Shanghai. According to reports, Csergo describes himself on social media as a “business strategist” and an “operational transformation specialist”.
Csergo was arrested by the Australian Federal Police (AFP) on Friday afternoon at his family home in the eastern Sydney suburb of Bondi. According to a press release, Csergo’s arrest resulted from an investigation by the Counter Foreign Interference Taskforce (CFITF), aa joint counterintelligence body led by the AFP and the Australian Security Intelligence Organisation. Established in 2021, the CFITF brings together counterintelligence units from across Australia’s federal government sectors in order to discover, disrupt and investigate foreign interference activity.
Australian government prosecutors claim that representatives of a foreign think-tank approached Csergo on social media while he was overseas —presumably in China. The think-tank representatives arranged for Csergo to come in contact with two individuals, calling themselves “Evelyn” and “Ken”. They offered to pay Csergo in return for reports that contained “information about Australian defence, economic and national security arrangements, as well as matters relating to other countries”.
Csergo allegedly agreed to provide the requested services and proceeded to compile a number of reports for the think-tank between February 2021 and April 14 of this year. The Australian government alleges that “Evelyn” and “Ken” are in fact emploees of a foreign intelligence service, which has not yet been publicly identified in Australian government press releases. The Australian government also claims that these individuals may have tried to recruit other Australians, or foreign citizens living in Australia.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 17 April 2023 | Permalink
 THE GOVERNMENT OF AUSTRALIA has ordered the deportation of a Kazakh-born Irish citizen, who is believed to be a spy for the Russian Federation, according to reports from Australia and Ireland. The woman in question has been identified as Marina Sologub, 39, an ethnic Russian who was born in Kazakhstan, but grew up in the Republic of Ireland.
THE GOVERNMENT OF AUSTRALIA has ordered the deportation of a Kazakh-born Irish citizen, who is believed to be a spy for the Russian Federation, according to reports from Australia and Ireland. The woman in question has been identified as Marina Sologub, 39, an ethnic Russian who was born in Kazakhstan, but grew up in the Republic of Ireland. • Australian spy agency seeks expanded powers. The Australian Security Intelligence Organisation (ASIO) says it needs
• Australian spy agency seeks expanded powers. The Australian Security Intelligence Organisation (ASIO) says it needs  As the Australian government has launched an official investigation into the claims made by a self-styled Chinese intelligence defector, some skeptics have begun to cast doubts about his revelations. The claims of Wang “William” Liqiang have dominated news headlines in Australia for over a week. The 26-year-old from China’s eastern Fujian province reportedly defected to Australia in October, while visiting his wife and newborn son in Sydney. He is currently reported to be in a safe house belonging to the Australian Security Intelligence Organization (ASIO).
As the Australian government has launched an official investigation into the claims made by a self-styled Chinese intelligence defector, some skeptics have begun to cast doubts about his revelations. The claims of Wang “William” Liqiang have dominated news headlines in Australia for over a week. The 26-year-old from China’s eastern Fujian province reportedly defected to Australia in October, while visiting his wife and newborn son in Sydney. He is currently reported to be in a safe house belonging to the Australian Security Intelligence Organization (ASIO). A Chinese intelligence defector has reportedly given the Australian government information about entire networks of Chinese undercover spies in Hong Kong, Taiwan and Australia, according to reports. The story of Wang “William” Liqiang, made headlines all over Australia during the weekend, culminating in an entire
A Chinese intelligence defector has reportedly given the Australian government information about entire networks of Chinese undercover spies in Hong Kong, Taiwan and Australia, according to reports. The story of Wang “William” Liqiang, made headlines all over Australia during the weekend, culminating in an entire  The director of Australia’s main national security agency has warned in a public speech that the threat from espionage —including cyber espionage— is greater than terrorism, and poses an “existential” danger to established states. Duncan Lewis was appointed director of the Australian Security Intelligence Organisation (ASIO) in 2014, having already served for more than four decades in the Australian military and civilian government sectors. On Wednesday, Lewis gave a rare
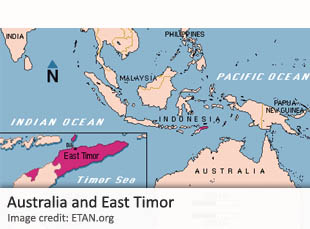
The director of Australia’s main national security agency has warned in a public speech that the threat from espionage —including cyber espionage— is greater than terrorism, and poses an “existential” danger to established states. Duncan Lewis was appointed director of the Australian Security Intelligence Organisation (ASIO) in 2014, having already served for more than four decades in the Australian military and civilian government sectors. On Wednesday, Lewis gave a rare  Australia continues to deny freedom of movement to a former intelligence officer who revealed that Canberra bugged government offices in the small island nation of Timor-Leste, in an effort to secure a lucrative oil deal. The former intelligence officer, known only as “Witness K.”, is believed to be a former director of technical operations in the Australian Secret Intelligence Service (ASIS), Australia’s foreign-intelligence agency. In 2013, he publicly objected to an intelligence-collection operation that targeted the impoverished Pacific island nation of Timor-Leste, known also as East Timor.
Australia continues to deny freedom of movement to a former intelligence officer who revealed that Canberra bugged government offices in the small island nation of Timor-Leste, in an effort to secure a lucrative oil deal. The former intelligence officer, known only as “Witness K.”, is believed to be a former director of technical operations in the Australian Secret Intelligence Service (ASIS), Australia’s foreign-intelligence agency. In 2013, he publicly objected to an intelligence-collection operation that targeted the impoverished Pacific island nation of Timor-Leste, known also as East Timor. Foreign intelligence collection and espionage threats against Australia are greater today than at any time during the Cold War, according to a senior Australian intelligence official. The claim was made on Wednesday by Peter Vickery, deputy director general of the Australian Security Intelligence Organisation (ASIO), the country’s primary counterintelligence agency. He was speaking before a parliamentary committee that is considering aspects of a proposed bill, which aims to combat foreign influence on Australian political and economic life. If enacted, the bill would require anyone who is professionally advocating or campaigning in favor of “foreign entities” to register with the government. Several opposition parties and groups, including the Catholic Church, have
Foreign intelligence collection and espionage threats against Australia are greater today than at any time during the Cold War, according to a senior Australian intelligence official. The claim was made on Wednesday by Peter Vickery, deputy director general of the Australian Security Intelligence Organisation (ASIO), the country’s primary counterintelligence agency. He was speaking before a parliamentary committee that is considering aspects of a proposed bill, which aims to combat foreign influence on Australian political and economic life. If enacted, the bill would require anyone who is professionally advocating or campaigning in favor of “foreign entities” to register with the government. Several opposition parties and groups, including the Catholic Church, have  An ambitious new personnel exchange program between intelligence agencies in Australia and Indonesia aims to combat the unprecedented rise of militant Islamism in Southeast Asia, which is fueled by the Islamic State. The program, which is already underway, aims to strengthen intelligence cooperation between two traditionally adversarial regional powers.
An ambitious new personnel exchange program between intelligence agencies in Australia and Indonesia aims to combat the unprecedented rise of militant Islamism in Southeast Asia, which is fueled by the Islamic State. The program, which is already underway, aims to strengthen intelligence cooperation between two traditionally adversarial regional powers.