Despite imminent US-Taliban deal, CIA plans to keep proxy units in Afghanistan
August 9, 2019 3 Comments
 The United States Central Intelligence Agency plans to retain a strong presence on the ground in Afghanistan, despite reports that American troops may soon be leaving the country following a deal with the Taliban. Several news outlets reported this week that Washington has resolved its differences with the Taliban about withdrawing American troops from Afghanistan, after receiving assurances by the Taliban that they will not cooperate with other militant Islamist groups, including al-Qaeda. An announcement of an agreement between the United States and the Taliban may thus be imminent. But in an article for Foreign Policy, Stefanie Glinski points out that the CIA is not planning to leave the Central Asian country any time soon.
The United States Central Intelligence Agency plans to retain a strong presence on the ground in Afghanistan, despite reports that American troops may soon be leaving the country following a deal with the Taliban. Several news outlets reported this week that Washington has resolved its differences with the Taliban about withdrawing American troops from Afghanistan, after receiving assurances by the Taliban that they will not cooperate with other militant Islamist groups, including al-Qaeda. An announcement of an agreement between the United States and the Taliban may thus be imminent. But in an article for Foreign Policy, Stefanie Glinski points out that the CIA is not planning to leave the Central Asian country any time soon.
The American intelligence agency is known to support, arm and train several proxy forces throughout Afghanistan. Langley plans to keep those proxy forces operating in the country for the foreseeable future, regardless of whether US troops pull out, says Glinski. She gives the example of the Khost Protection Force (KPF), a 6,500-strong unit of Afghan soldiers who are “trained, equipped and funded by the CIA”. The KPF is the most active and visible of an extensive network of CIA-sponsored paramilitary groups in Afghanistan. It operates almost exclusively along the Afghan-Pakistani border and has a strong presence in Taliban strongholds like Ghazni, Paktia and Khost. The roots of the KPF go back to the days immediately after the attacks of September 11, 2001, which prompted the US military invasion of Afghanistan. It therefore precedes the Afghan National Army, Afghanistan’s state-run military apparatus, and does not operate under its command. Instead, it is solely directed by the CIA, which uses it to secure the Afghan-Pakistani border and disrupt the activities of Taliban, al-Qaeda and Islamic State fighters in the Afghan borderlands.
Members of the KPF claim that they are “better trained than the Afghan National Army”. They are also paid much better, over $1000.00 per month, which is an enormous sum for Afghanistan. Perhaps unsurprisingly, Glinski reports that most KPF fighters joined the group for the money and the ability to eventually seek permanent resettlement in the United States. But alongside the group’s elite image, KPF members have acquired notoriety and are often seen as trigger-happy and unaccountable. Several reports in Western media have said that the KPF’s tactical accomplishments have come at a high price, with countless reports of civilian deaths and, some claim, even war crimes. These risk “alienating the Afghan population”, said a New York Times report last year. Glinski says it is possible the KPF’s aggressive tactics may be “radicalizing portions of the very population it intends to pacify or frighten into submission”. In April of this year, a United Nations report alleged that more Afghan civilians died as a result of attacks by Afghan government and American military attacks than at the hands of the Taliban and other guerilla groups. The CIA did not respond to several requests for comment from Foreign Policy, says Glinski.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 09 August 2019 | Permalink
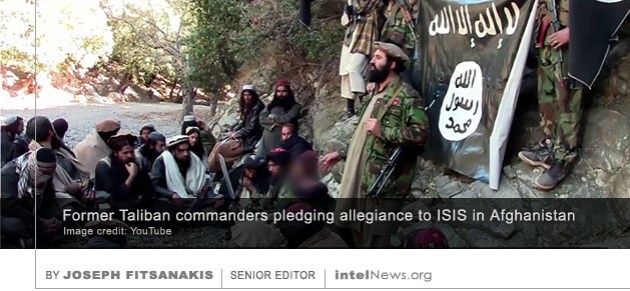 The Islamic State group in Afghanistan is now more threatening than the Taliban to both Afghan and Western interests, according to some experts, who warn that many of its fighters are moving there from the Middle East. It was in late 2014 when the Islamic State, known formerly as the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS), made its initial appearance in Afghanistan. Soon an official Islamic State affiliate emerged in Afghanistan, calling itself Islamic State – Khorasan Province. Security observers estimated the group’s strength to below 150 armed fighters, most of them Pakistani Taliban who had sought refuge in Afghanistan, or small cadres of Afghan Taliban who pursued a more globalized Salafist agenda. Aided by the growing worldwide notoriety of its parent organization in Iraq and Syria, the Islamic State – Khorasan Province grew in size in 2015 and 2016. Its armed cadres were joined by Salafist-jihadists from Central Asia and the Indian subcontinent, as well as by radical Muslims from China’s northwestern Xinjiang Province. In 2016, as the Islamic State began retreating in the Middle East, fighters from there gradually began to make their way to Afghanistan, adding to the numerical strength of the organization’s Khorasan Province branch.
The Islamic State group in Afghanistan is now more threatening than the Taliban to both Afghan and Western interests, according to some experts, who warn that many of its fighters are moving there from the Middle East. It was in late 2014 when the Islamic State, known formerly as the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS), made its initial appearance in Afghanistan. Soon an official Islamic State affiliate emerged in Afghanistan, calling itself Islamic State – Khorasan Province. Security observers estimated the group’s strength to below 150 armed fighters, most of them Pakistani Taliban who had sought refuge in Afghanistan, or small cadres of Afghan Taliban who pursued a more globalized Salafist agenda. Aided by the growing worldwide notoriety of its parent organization in Iraq and Syria, the Islamic State – Khorasan Province grew in size in 2015 and 2016. Its armed cadres were joined by Salafist-jihadists from Central Asia and the Indian subcontinent, as well as by radical Muslims from China’s northwestern Xinjiang Province. In 2016, as the Islamic State began retreating in the Middle East, fighters from there gradually began to make their way to Afghanistan, adding to the numerical strength of the organization’s Khorasan Province branch.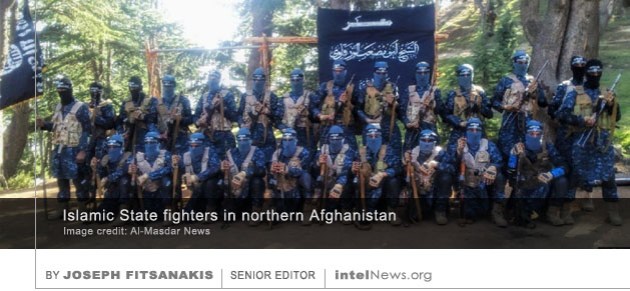
 The government of Afghanistan is facing one of its most serious crises since the end of the Taliban reign in 2001, as the country’s most senior security and intelligence officials tendered their resignations this week. The unprecedented move followed a dramatic escalation in attacks against Afghan government installations by Taliban and Islamic State forces, which have resulted in dozens of casualties throughout the Central Asian country. On Saturday, Mohammad Haneef Atmar, long time national security adviser to President Ashraf Ghani and one of the Afghanistan’s most recognizable and powerful political figures, tendered his
The government of Afghanistan is facing one of its most serious crises since the end of the Taliban reign in 2001, as the country’s most senior security and intelligence officials tendered their resignations this week. The unprecedented move followed a dramatic escalation in attacks against Afghan government installations by Taliban and Islamic State forces, which have resulted in dozens of casualties throughout the Central Asian country. On Saturday, Mohammad Haneef Atmar, long time national security adviser to President Ashraf Ghani and one of the Afghanistan’s most recognizable and powerful political figures, tendered his  Russia, the United States and Tajikistan have all denied that they were behind a series of mystery airstrikes that took place along the Tajik-Afghan border on Sunday, while the identity of the targets also remains unknown. The 800-mile border between Afghanistan and Tajikistan consists of mountainous terrain. Unlike the Afghan-Pakistani border, which is rife with skirmishes and firefights, the Afghan-Tajik border is usually peaceful and sparsely guarded. But on Sunday, August 26, local officials from both sides of the Afghan-Tajik border
Russia, the United States and Tajikistan have all denied that they were behind a series of mystery airstrikes that took place along the Tajik-Afghan border on Sunday, while the identity of the targets also remains unknown. The 800-mile border between Afghanistan and Tajikistan consists of mountainous terrain. Unlike the Afghan-Pakistani border, which is rife with skirmishes and firefights, the Afghan-Tajik border is usually peaceful and sparsely guarded. But on Sunday, August 26, local officials from both sides of the Afghan-Tajik border  In a dramatic change to longstanding policy, senior United States diplomats have reportedly held secret meetings with Taliban leaders without the presence –and presumably knowledge– of the Afghan government. For over a decade, the Taliban have refused to negotiate with the Afghan government, which they view as a puppet regime controlled by Washington. They have instead sought to speak directly with the United States, without Kabul’s mediation. In 2015, the United States sought to initiate peace talks with the Taliban in the Qatari capital Doha, but the effort collapsed after the Afghan government denounced it and demanded a seat at the table. The negotiation process has remained dormant since then.
In a dramatic change to longstanding policy, senior United States diplomats have reportedly held secret meetings with Taliban leaders without the presence –and presumably knowledge– of the Afghan government. For over a decade, the Taliban have refused to negotiate with the Afghan government, which they view as a puppet regime controlled by Washington. They have instead sought to speak directly with the United States, without Kabul’s mediation. In 2015, the United States sought to initiate peace talks with the Taliban in the Qatari capital Doha, but the effort collapsed after the Afghan government denounced it and demanded a seat at the table. The negotiation process has remained dormant since then.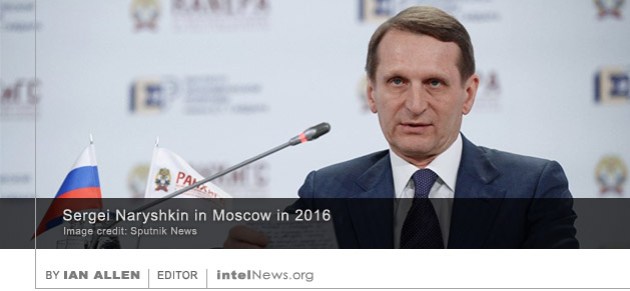 Intelligence directors from Russia, China, Iran and Pakistan met on Tuesday to discuss regional cooperation with particular reference to combating the Islamic State in Afghanistan. Information about the high-level meeting was
Intelligence directors from Russia, China, Iran and Pakistan met on Tuesday to discuss regional cooperation with particular reference to combating the Islamic State in Afghanistan. Information about the high-level meeting was  Nearly half a billion of American taxpayers’ funds were wasted by contractors hired by the United States government to train Afghan intelligence personnel, according to a scathing report by a Congressional body. The funds were spent between 2010 and 2013 by the US Department of Defense, in order to train several thousand members and a few dozen aspiring trainees of the Afghanistan National Defense and Security Forces (ANDSF). Two companies, Legacy Afghanistan R&D and Afghanistan Source Operations Management, oversaw the training program. It was primarily executed by a contractor, Imperatis Corporation, and a subcontractor, New Century Consulting, at a total cost of $457 million to the US taxpayer.
Nearly half a billion of American taxpayers’ funds were wasted by contractors hired by the United States government to train Afghan intelligence personnel, according to a scathing report by a Congressional body. The funds were spent between 2010 and 2013 by the US Department of Defense, in order to train several thousand members and a few dozen aspiring trainees of the Afghanistan National Defense and Security Forces (ANDSF). Two companies, Legacy Afghanistan R&D and Afghanistan Source Operations Management, oversaw the training program. It was primarily executed by a contractor, Imperatis Corporation, and a subcontractor, New Century Consulting, at a total cost of $457 million to the US taxpayer. Frequent trips to Iran caused the demise of the late leader of the Afghan Taliban, Mullah Akhtar Mohammad Mansour, who was
Frequent trips to Iran caused the demise of the late leader of the Afghan Taliban, Mullah Akhtar Mohammad Mansour, who was  The American operation that killed the leader of the Afghan Taliban, Mullah Akhtar Mohammad Mansoor, on May 21, was unprecedented in more ways than one. It marked the first known effort by the United States to neutralize the leadership of the Afghan Taliban. It was also the first US drone strike in Pakistani Baluchistan, a region that is far removed from the Federally Administered Tribal Areas, where American operations have traditionally focused. Mullah Mansour’s killing also marked the most high-profile American incursion into Pakistani territory since the May 1, 2011 attack that killed al-Qaeda co-founder Osama bin Laden.
The American operation that killed the leader of the Afghan Taliban, Mullah Akhtar Mohammad Mansoor, on May 21, was unprecedented in more ways than one. It marked the first known effort by the United States to neutralize the leadership of the Afghan Taliban. It was also the first US drone strike in Pakistani Baluchistan, a region that is far removed from the Federally Administered Tribal Areas, where American operations have traditionally focused. Mullah Mansour’s killing also marked the most high-profile American incursion into Pakistani territory since the May 1, 2011 attack that killed al-Qaeda co-founder Osama bin Laden.  Ironically, just hours before killing Mansour, Washington was calling the Taliban to join the negotiation table for peace talks with the Afghan government. So what exactly was America’s intention in killing the leader of the Afghan Taliban?
Ironically, just hours before killing Mansour, Washington was calling the Taliban to join the negotiation table for peace talks with the Afghan government. So what exactly was America’s intention in killing the leader of the Afghan Taliban? killed the group’s leader.
killed the group’s leader. An expanding alliance between two of the most powerful armed groups in Afghanistan, the Taliban and the Haqqani Network, is reshaping regional power dynamics and possibly altering the course of the ongoing Afghan war. It was last summer when it was announced that Sirajuddin Haqqani, the leader of the notorious Haqqani Network based in southeastern Afghanistan, had been appointed deputy leader of the Taliban. The move, which brought together two groups that traditionally acted autonomously, was seen as largely symbolic at the time. But observers are now suggesting that the two groups are actively integrating more than ever before, and that their increasing cooperation is drastically changing the dynamics of the bloody Afghan war.
An expanding alliance between two of the most powerful armed groups in Afghanistan, the Taliban and the Haqqani Network, is reshaping regional power dynamics and possibly altering the course of the ongoing Afghan war. It was last summer when it was announced that Sirajuddin Haqqani, the leader of the notorious Haqqani Network based in southeastern Afghanistan, had been appointed deputy leader of the Taliban. The move, which brought together two groups that traditionally acted autonomously, was seen as largely symbolic at the time. But observers are now suggesting that the two groups are actively integrating more than ever before, and that their increasing cooperation is drastically changing the dynamics of the bloody Afghan war. tactical priorities.
tactical priorities. system, job centers, taxation offices and community militias. The administrative and military efficiency of the Haqqani Network only adds to the strength of the Taliban and places them in a renewed position of power vis-à-vis Kabul.
system, job centers, taxation offices and community militias. The administrative and military efficiency of the Haqqani Network only adds to the strength of the Taliban and places them in a renewed position of power vis-à-vis Kabul. Russia’s official envoy to Afghanistan has said that Moscow is now working with the Afghan Taliban in order to stop the growth of the Islamic State in the region. Many Taliban fighters are direct descendants of the Afghan and Pakistani Pashtuns who fought the Soviet Red Army in the 1980s, when the USSR invaded Afghanistan and fought a bloody decade-long war there. But the militant group, which today continues to control much of Afghanistan, despite a prolonged American-led military effort to defeat it, is now being challenged by the Islamic State. Known also as the Islamic State in Iraq and Syria (ISIS), the group enjoys growing popularity in Afghanistan, and some tribal warlords have already declared their allegiance to it. In contrast, the leadership of the Taliban has rejected the legitimacy of ISIS and refused to recognize its leader, Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, as the caliph of all Sunni Muslims. According to Sunni doctrine, a caliph is the recognized political and religious successor to Muhammad, Islam’s prophet, and thus commands the Muslim ummah, or community.
Russia’s official envoy to Afghanistan has said that Moscow is now working with the Afghan Taliban in order to stop the growth of the Islamic State in the region. Many Taliban fighters are direct descendants of the Afghan and Pakistani Pashtuns who fought the Soviet Red Army in the 1980s, when the USSR invaded Afghanistan and fought a bloody decade-long war there. But the militant group, which today continues to control much of Afghanistan, despite a prolonged American-led military effort to defeat it, is now being challenged by the Islamic State. Known also as the Islamic State in Iraq and Syria (ISIS), the group enjoys growing popularity in Afghanistan, and some tribal warlords have already declared their allegiance to it. In contrast, the leadership of the Taliban has rejected the legitimacy of ISIS and refused to recognize its leader, Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, as the caliph of all Sunni Muslims. According to Sunni doctrine, a caliph is the recognized political and religious successor to Muhammad, Islam’s prophet, and thus commands the Muslim ummah, or community. The bleak landscape of Afghan national politics became even bleaker on Thursday, after the sudden resignation of the country’s spy chief, allegedly due to “disagreements” with the government in Kabul. Rahmatullah Nabil led Afghanistan’s National Directorate of Security (NDS) from 2010 to 2012 before returning to the post in 2013, while his predecessor, Asadullah Khalid, recovered from injuries suffered from an unsuccessful assassination attempt against him by the Taliban. But on Thursday afternoon, Nabil
The bleak landscape of Afghan national politics became even bleaker on Thursday, after the sudden resignation of the country’s spy chief, allegedly due to “disagreements” with the government in Kabul. Rahmatullah Nabil led Afghanistan’s National Directorate of Security (NDS) from 2010 to 2012 before returning to the post in 2013, while his predecessor, Asadullah Khalid, recovered from injuries suffered from an unsuccessful assassination attempt against him by the Taliban. But on Thursday afternoon, Nabil 






Pakistani Taliban leaders found dead in Kabul hotel, culprits unknown
February 10, 2020 by Joseph Fitsanakis Leave a comment
According to the BBC, which reported on the incident on Friday, the bodies of the two men were found in or near the Inter-Continental, a five-star hotel located in western Kabul. According to Afghan government sources, the two men were carrying forged identification papers. In a statement issued on Thursday, the Pakistani Taliban identified the dead men as Sheikh Khalid Haqqani and Qari Saif Younis. Sheikh Haqqani had served as the group’s deputy leader, and was a member of its leadership council. Younis was among the group’s most powerful military commanders.
The Pakistani Taliban said that the two men had secretly traveled to Kabul from Paktika, a Taliban stronghold in the east-central region of Afghanistan, in order to attend a high-level meeting. The group did not say who the two men were meeting and why. But it is rare for leading figures of the Pakistani Taliban to leave the areas that the group controls, and even rarer for them to travel to Kabul or any other big city in the region.
The statement from the Pakistani Taliban claimed that the two men were killed “in a clash with American forces”. But the BBC quoted an unnamed “source within the group” who said that they could also have been targeted by militant groups linked to the Pakistani government, which is a sworn enemy of the Pakistani Taliban. United States officials have yet to comment on this developing story.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 10 February 2020 | Permalink
Filed under Expert news and commentary on intelligence, espionage, spies and spying Tagged with Afghanistan, assassinations, Inter-Continental Hotel (Kabul), Kabul (Afghanistan), News, Pakistani Taliban, Qari Saif Younis, Sheikh Khalid Haqqani, suspicious deaths