Russia retains massive global diplomatic footprint despite recent expulsions
March 30, 2018 1 Comment
 Though unprecedented in size, the recent expulsions of over 150 diplomats by nearly 30 countries and organizations around the world have hardly made a dent on Russia’s huge diplomatic footprint. The coordinated expulsions were announced last week in response to Britain’s allegation that the Kremlin tried to kill a Russian former spy living in England. Sergei Skripal, 66, who spied for Britain in the early 2000s, and has been living in England since 2010, is fighting for his life after being poisoned with what London claims was a military-grade nerve agent. Nearly every European country, as well as Canada, Australia and the United States, expelled Russian diplomats in response to the attack on Skripal.
Though unprecedented in size, the recent expulsions of over 150 diplomats by nearly 30 countries and organizations around the world have hardly made a dent on Russia’s huge diplomatic footprint. The coordinated expulsions were announced last week in response to Britain’s allegation that the Kremlin tried to kill a Russian former spy living in England. Sergei Skripal, 66, who spied for Britain in the early 2000s, and has been living in England since 2010, is fighting for his life after being poisoned with what London claims was a military-grade nerve agent. Nearly every European country, as well as Canada, Australia and the United States, expelled Russian diplomats in response to the attack on Skripal.
The largest share of the expulsions came from the United States, where the White House announced that 60 Russian diplomats had been ordered to leave by the end of the week. The majority of these diplomats are posted at the Russian embassy in Washington and consulate in New York. At least a dozen more are serving in Russia’s permanent mission at the United Nations in New York. On Thursday, several US media outlets said that all 60 Russians told to leave the US are undeclared intelligence officers serving under diplomatic cover. Fox News quoted an unnamed “senior administration official” in the US as saying that “these are not diplomats that we expelled […]. They are intelligence officers […] operating under diplomatic cover”. The official added that the Russians were expelled because they “were engaging in activities that were not commensurate with their diplomatic roles and functions”. That description is often used by governments to allude to diplomats who are in fact engaging in espionage or other intelligence-related activities.
But in an analysis piece written for the BBC, Alex Oliver, research director at the Lowy Institute in Australia, points out that the 150 diplomats expelled in recent days are but “a tiny part” of Russia’s massive diplomatic presence around the world. With 242 diplomatic posts around the world, Russia has the world’s fourth largest diplomatic footprint, behind the United States, China and France. Several thousand Russian diplomats are stationed at any one time in 143 Russian embassies, 87 consulates, and about a dozen other diplomatic missions in nearly every country in the world. Of these, approximately 170 serve in the United States. The 60 expulsions announced last week by the US government, will still leave Russia with over 100 accredited diplomats in America —many of whom are presumably intelligence officers. Earlier today, Moscow announced that it would expel 60 American diplomats, as well as nearly 100 more diplomats for other countries. The White House said that it may choose to respond with further expulsions of Russian diplomatic personnel.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 26 April 2018 | Permalink
 Relations between Russia and much of the West reached a new low on Monday, with the expulsion of over 100 Russian diplomats from two dozen countries around the world. The unprecedented expulsions were publicized on Monday with a series of coordinated announcements issued from nearly every European capital, as well as from Washington, Ottawa and Canberra. By the early hours of Tuesday, the number of Russian diplomatic expulsions had reached 118 —not counting the 23 Russian so-called “undeclared intelligence officers” that were expelled from Britain last week. Further expulsions of Russian diplomats are expected in the coming days.
Relations between Russia and much of the West reached a new low on Monday, with the expulsion of over 100 Russian diplomats from two dozen countries around the world. The unprecedented expulsions were publicized on Monday with a series of coordinated announcements issued from nearly every European capital, as well as from Washington, Ottawa and Canberra. By the early hours of Tuesday, the number of Russian diplomatic expulsions had reached 118 —not counting the 23 Russian so-called “undeclared intelligence officers” that were expelled from Britain last week. Further expulsions of Russian diplomats are expected in the coming days. predecessor, Barack Obama, and his Secretary of State Hillary Clinton, who is known for her hardline anti-Russian stance. In Europe, the move to expel dozens of Russian envoys from 23 different countries —most of them European Union members— was a rare act of unity that surprised European observers as much as it did the Russians.
predecessor, Barack Obama, and his Secretary of State Hillary Clinton, who is known for her hardline anti-Russian stance. In Europe, the move to expel dozens of Russian envoys from 23 different countries —most of them European Union members— was a rare act of unity that surprised European observers as much as it did the Russians. For the past year, the Netherlands has had a new law governing its two secret services, the AIVD and the MIVD. The new Intelligence and Security Services Act (Wet op de inlichtingen- en veiligheidsdiensten or Wiv) was and still is heavily criticized, especially because it allows untargeted access to cable-bound telephone and internet traffic. Under the previous law, which dates from 2002, the intelligence services were only allowed to conduct bulk interception of wireless transmissions, like satellite and radio communications —besides of course the traditional targeted telephone and internet taps aimed at individual targets.
For the past year, the Netherlands has had a new law governing its two secret services, the AIVD and the MIVD. The new Intelligence and Security Services Act (Wet op de inlichtingen- en veiligheidsdiensten or Wiv) was and still is heavily criticized, especially because it allows untargeted access to cable-bound telephone and internet traffic. Under the previous law, which dates from 2002, the intelligence services were only allowed to conduct bulk interception of wireless transmissions, like satellite and radio communications —besides of course the traditional targeted telephone and internet taps aimed at individual targets. With
With  On March 21, the Dutch public cast their vote about the new Intelligence and Security Services Act, in Dutch
On March 21, the Dutch public cast their vote about the new Intelligence and Security Services Act, in Dutch  As expected, Moscow snubbed the British government’s demand for information into how a Russian-produced military-grade nerve agent ended up being used in the streets of Salisbury, England. As British Prime Minister Theresa May addressed the House of Commons on Wednesday afternoon, Sergei Skripal continued to fight for his life in a hospital in southern England. His daughter, Yulia, was also comatose, having been poisoned with the same Cold-War-era nerve agent as her father. This blog has
As expected, Moscow snubbed the British government’s demand for information into how a Russian-produced military-grade nerve agent ended up being used in the streets of Salisbury, England. As British Prime Minister Theresa May addressed the House of Commons on Wednesday afternoon, Sergei Skripal continued to fight for his life in a hospital in southern England. His daughter, Yulia, was also comatose, having been poisoned with the same Cold-War-era nerve agent as her father. This blog has  the latest expulsions are dwarfed by the dramatic expulsion in 1971 of no fewer than 105 Soviet diplomats from Britain, following yet another defection of a Soviet intelligence officer, who remained anonymous.
the latest expulsions are dwarfed by the dramatic expulsion in 1971 of no fewer than 105 Soviet diplomats from Britain, following yet another defection of a Soviet intelligence officer, who remained anonymous. Most state-sponsored assassinations tend to be covert operations, which means that the sponsoring party cannot be conclusively identified, even if it is suspected. Because of their covert nature, assassinations tend to be extremely complex intelligence-led operations, which are designed to provide plausible deniability to their sponsors. Consequently, the planning and implementation of these operations usually involves a large number of people, each with a narrow set of unique skills. But —and herein lies an interesting contradiction— their execution is invariably simple, both in style and method. The
Most state-sponsored assassinations tend to be covert operations, which means that the sponsoring party cannot be conclusively identified, even if it is suspected. Because of their covert nature, assassinations tend to be extremely complex intelligence-led operations, which are designed to provide plausible deniability to their sponsors. Consequently, the planning and implementation of these operations usually involves a large number of people, each with a narrow set of unique skills. But —and herein lies an interesting contradiction— their execution is invariably simple, both in style and method. The  Skripal, who continued to provide his services to British intelligence as a consultant while living in the idyllic surroundings of Wiltshire. Like the late Russian defector Alexander Litvinenko, who died in London of radioactive poisoning in 2006, Skripal entrusted his personal safety to the British state. But in a country that today hosts nearly half a million Russians of all backgrounds and political persuasions, such a decision is exceedingly risky.
Skripal, who continued to provide his services to British intelligence as a consultant while living in the idyllic surroundings of Wiltshire. Like the late Russian defector Alexander Litvinenko, who died in London of radioactive poisoning in 2006, Skripal entrusted his personal safety to the British state. But in a country that today hosts nearly half a million Russians of all backgrounds and political persuasions, such a decision is exceedingly risky. from abroad. It is, in other words, a simple weapon that can be dispensed using a simple method, with little risk to the assailant(s). It fits the profile of a state-sponsored covert killing: carefully planned and designed, yet simply executed, thus ensuring a high probability of success.
from abroad. It is, in other words, a simple weapon that can be dispensed using a simple method, with little risk to the assailant(s). It fits the profile of a state-sponsored covert killing: carefully planned and designed, yet simply executed, thus ensuring a high probability of success. Since 2008, when we launched intelNews, it has been our
Since 2008, when we launched intelNews, it has been our  04. Unprecedented security changes are taking place in Saudi Arabia. Analysts agree that the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia is undergoing its most important political changes in generations. On November 4, 2017, nearly 50 senior Saudi officials, including at least 11 princes, some of them among the world’s wealthiest people, were suddenly
04. Unprecedented security changes are taking place in Saudi Arabia. Analysts agree that the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia is undergoing its most important political changes in generations. On November 4, 2017, nearly 50 senior Saudi officials, including at least 11 princes, some of them among the world’s wealthiest people, were suddenly  taking place in the intelligence infrastructure of South Korea, which are arguably as important as developments north of the 38th parallel. In June, the new center-left government of President Moon Jae-in
taking place in the intelligence infrastructure of South Korea, which are arguably as important as developments north of the 38th parallel. In June, the new center-left government of President Moon Jae-in  assist policy-makers, including the president. So when the CIA and the FBI conclude that the Russian government launched an extensive and sophisticated campaign to undermine the 2016 US presidential election, one expects the president to take that advisement under serious consideration. However, the US leader has openly dismissed the conclusions of his own Intelligence Community and has
assist policy-makers, including the president. So when the CIA and the FBI conclude that the Russian government launched an extensive and sophisticated campaign to undermine the 2016 US presidential election, one expects the president to take that advisement under serious consideration. However, the US leader has openly dismissed the conclusions of his own Intelligence Community and has  Since 2008, when we launched intelNews, it has been our
Since 2008, when we launched intelNews, it has been our  as a result of “acute poisoning from an undefined substance”, according to his doctors. Also in February, Kim Jong-nam, half-brother of North Korean Supreme Leader Kim Jong-un, was killed in an
as a result of “acute poisoning from an undefined substance”, according to his doctors. Also in February, Kim Jong-nam, half-brother of North Korean Supreme Leader Kim Jong-un, was killed in an  support for the rebels could backfire by causing the suddenly unemployed fighters to join jihadist organizations. In August, there were reports that US troops
support for the rebels could backfire by causing the suddenly unemployed fighters to join jihadist organizations. In August, there were reports that US troops  Since 2008, when we launched intelNews, it has been our
Since 2008, when we launched intelNews, it has been our  10.
10.  the alleged device may have been deployed by an intelligence service of a third country —possibly Russia— without the knowledge of the Cuban authorities. In October, the White House expelled 15 Cuban diplomats from the US in response to the incident. But the question of what harmed the health of at least 20 employees at the US embassy in Havana remains largely unanswered.
the alleged device may have been deployed by an intelligence service of a third country —possibly Russia— without the knowledge of the Cuban authorities. In October, the White House expelled 15 Cuban diplomats from the US in response to the incident. But the question of what harmed the health of at least 20 employees at the US embassy in Havana remains largely unanswered.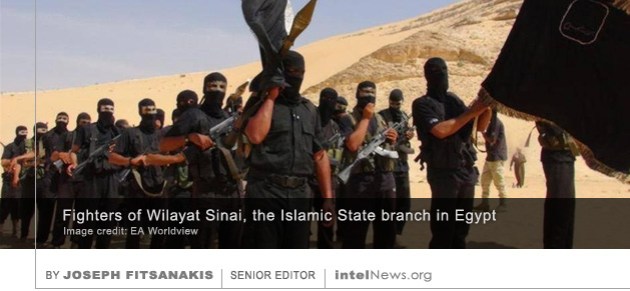 Through a series of meticulously planned terrorist strikes and assassinations, Wilayat Sinai has emerged as the strongest international arm of the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS), according to some experts. Known officially as ISIS – Sinai Province, Wilayat Sinai claimed responsibility for the October 2015 downing of Metrojet Flight 9268. All 224 passengers and crew, most of them Russians, died when the plane blew up in midair over Egypt’s Sinai Peninsula. The incident marked the worst aviation disaster in Russian history. The same group, Wilayat Sinai, was behind last month’s attack on the Al Rawda Sufi mosque in bir al-Abed, Egypt. The massacre resulted in the deaths of 311 people, making it the worst terrorist attack in the history of modern Egypt.
Through a series of meticulously planned terrorist strikes and assassinations, Wilayat Sinai has emerged as the strongest international arm of the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS), according to some experts. Known officially as ISIS – Sinai Province, Wilayat Sinai claimed responsibility for the October 2015 downing of Metrojet Flight 9268. All 224 passengers and crew, most of them Russians, died when the plane blew up in midair over Egypt’s Sinai Peninsula. The incident marked the worst aviation disaster in Russian history. The same group, Wilayat Sinai, was behind last month’s attack on the Al Rawda Sufi mosque in bir al-Abed, Egypt. The massacre resulted in the deaths of 311 people, making it the worst terrorist attack in the history of modern Egypt. Dozens of Saudi senior figures, some of them among the world’s wealthiest people, have been fired or arrested, as the king and his son appeared to be removing their last remaining critics from the ranks of the security services. The unprecedented arrests took place without warning less than two hours after state-run media announced the creation of a new “supreme committee to combat corruption”. A
Dozens of Saudi senior figures, some of them among the world’s wealthiest people, have been fired or arrested, as the king and his son appeared to be removing their last remaining critics from the ranks of the security services. The unprecedented arrests took place without warning less than two hours after state-run media announced the creation of a new “supreme committee to combat corruption”. A  News reports hastened to
News reports hastened to  violence, rather than risk failure by breaking new ground. But at a time like this, when the very existence of the Islamic State hangs in the balance, one would think that the group would consciously try to intimidate its opponents by showing off some kind of revolutionary new weapon. That did not happen on Tuesday.
violence, rather than risk failure by breaking new ground. But at a time like this, when the very existence of the Islamic State hangs in the balance, one would think that the group would consciously try to intimidate its opponents by showing off some kind of revolutionary new weapon. That did not happen on Tuesday. the heavily attended annual Village Halloween Parade was scheduled to take place on the very same street, just two hours after he launched his deranged attack.
the heavily attended annual Village Halloween Parade was scheduled to take place on the very same street, just two hours after he launched his deranged attack. A German newspaper reported last week that at least one European intelligence agency has already warned that the Islamic State is exploring the use of chemicals for attacks in Europe. Such an eventuality would be a radical departure from prior attacks by the Islamic State in the West. In the past, the militant group has shown a strong preference for low-tech means of dispensing violence, such as firearms, vehicles and knives. But it has utilized chemical substances in Iraq and Syria, and its technical experts have amassed significant knowledge about weaponized chemicals.
A German newspaper reported last week that at least one European intelligence agency has already warned that the Islamic State is exploring the use of chemicals for attacks in Europe. Such an eventuality would be a radical departure from prior attacks by the Islamic State in the West. In the past, the militant group has shown a strong preference for low-tech means of dispensing violence, such as firearms, vehicles and knives. But it has utilized chemical substances in Iraq and Syria, and its technical experts have amassed significant knowledge about weaponized chemicals.






Analysis: New legal framework for Dutch intelligence services becomes law
May 8, 2018 by Joseph Fitsanakis Leave a comment
On May 1, 2018, the legal framework for the Dutch intelligence community changed as the new Intelligence and Security Services Act became operational. Previously, both chambers of parliament discussed and accepted the Act on February 14 and July 11, 2018. A group of Amsterdam-based students, however, were worried that the Act —which includes the power to intercept cable-bound communication in bulk— would induce a surveillance state. They initiated a public referendum, which was held on March 21, 2018.
In what was an intense and prolonged public debate in the months leading up to the referendum, critics of the new Act advanced their views against it. Among them was the digital civil rights group Bits of Freedom, which argued that the power to intercept cable-bound communication in bulk would destroy “the core value of our free society, that a law-abiding citizen will not be monitored”. The Act also allows the General Intelligence and Security Service (known by its Dutch acronym AIVD) and the Military Intelligence and Security service (abbreviated as MIVD) to exchange large sets of unevaluated data with their foreign counterparts without prior approval by the new independent review commission. The services see this quid pro quo data sharing as essential for their counter-terrorism mission. But in the view of opponents, the fact that unevaluated and unanalyzed datasets are exchanged is unacceptable.
Additionally, Bits of Freedom was opposed to the real-time access to databases of partners (such as tax authorities, other governmental agencies, but also banks) that was granted to the intelligence and security services. They argued that the oversight bodies and the responsible minister should have to sign off on this (it should be noted however, that such database access will be only granted on a hit/no-hit basis, so there will be no free searches. Finally, and more broadly, it was argued that the new Act contained too many “open norms”. This was in line with the cabinet’s goal to formulate a new act that would be more independent of technological developments —the Act of 2002 was not, and therefore the update was seen as necessary. But it also remains unspecified in which specific circumstances and under what criteria and norms the new powers can and cannot be applied. Read more of this post
Filed under Expert news and commentary on intelligence, espionage, spies and spying Tagged with Analysis, civil liberties, communications interception, intelligence legislation, Netherlands