Cambridge spy’s last years in Russia are detailed in new biography
September 4, 2015 Leave a comment
 The life of Guy Burgess, one of the so-called ‘Cambridge Five’ double agents, who spied on Britain for the Soviet Union before defecting to Moscow in 1951, is detailed in a new biography of the spy, written by Andrew Lownie. Like his fellow spies Kim Philby, Donald Maclean, Anthony Blunt and John Cairncross, Burgess was recruited by the Soviets when he was a student at Cambridge University. He shook the British intelligence establishment to its very core when he defected to the USSR along with Maclean, after the two felt that they were being suspected of spying for the Soviets.
The life of Guy Burgess, one of the so-called ‘Cambridge Five’ double agents, who spied on Britain for the Soviet Union before defecting to Moscow in 1951, is detailed in a new biography of the spy, written by Andrew Lownie. Like his fellow spies Kim Philby, Donald Maclean, Anthony Blunt and John Cairncross, Burgess was recruited by the Soviets when he was a student at Cambridge University. He shook the British intelligence establishment to its very core when he defected to the USSR along with Maclean, after the two felt that they were being suspected of spying for the Soviets.
A few years after his defection, Burgess wrote to a close friend back in the UK: “I am really […] very well and things are going much better for me here than I ever expected. I’m very glad I came”. However, in his book, entitled Stalin’s Englishman: The Lives of Guy Burgess, Lownie suggests that Burgess’ life in the USSR was far from ideal. After being welcomed by the Soviets as a hero, the Cambridge University graduate was transported to the isolated Siberian city of Kuybyshev. He lived for several months in a ‘grinder’, a safe house belonging to Soviet intelligence, where he was debriefed and frequently interrogated until his Soviet handlers were convinced that has indeed a genuine defector.
It was many years later that Burgess was able to leave Kuybyshev for Moscow, under a new name, Jim Andreyevitch Eliot, which had been given to him by the KGB. Initially he lived in a dacha outside Moscow, but was moved to the city in 1955, after he and Maclean spoke publicly about their defection from Britain. He was often visited in his one-bedroom apartment by Yuri Modin, his Soviet intelligence handler back in the UK. According to Lownie, Burgess often complained to Modin about the way he was being treated by the Soviet authorities. His apartment had apparently been bugged by the KGB, and he was constantly followed each time he stepped outside.
The British defector worked for a Soviet publishing house and produced foreign-policy analyses for the Soviet Ministry of Foreign Affairs. He also produced a training manual for KGB officers about British culture and the British way of life. But he did not like living in the USSR and argued that he should be allowed to return to the UK, insisting that he could successfully defend himself if interrogated by British counterintelligence. Eventually, Burgess came to the realization that he would never return to his home country. He became depressed, telling friends that he “did not want to die in Russia”. But in the summer of 1963 he was taken to hospital, where he eventually died from acute liver failure caused by his excessive drinking.
Andrew Lownie’s Stalin’s Englishman: The Lives of Guy Burgess, is published by Hodder & Stoughton in the UK and by St Martins’ Press in the US. It is scheduled to come out in both countries on September 10.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 04 September 2015 | Permalink
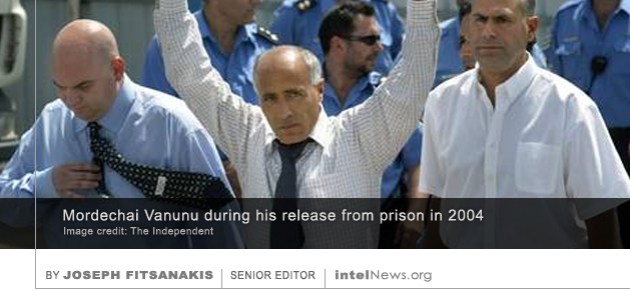 Israeli nuclear whistleblower Mordechai Vanunu, who spent 18 years in prison for revealing the existence of Israel’s nuclear program, has spoken for the first time about his 1986abduction by the Mossad in Rome. Vanunu was an employee at Israel’s top-secret Negev Nuclear Research Center, located in the desert city of Dimona, which was used to develop the country’s nuclear arsenal. But he became a fervent opponent of nuclear proliferation and in 1986 fled to the United Kingdom, where he revealed the existence of the Israeli nuclear weapons program to the The Times of London. His action was in direct violation of the non-disclosure agreement he had signed with the government of Israel; moreover, it went against Israel’s official policy of ‘nuclear ambiguity’, which means that the country refuses to confirm or deny that it maintains a nuclear weapons program.
Israeli nuclear whistleblower Mordechai Vanunu, who spent 18 years in prison for revealing the existence of Israel’s nuclear program, has spoken for the first time about his 1986abduction by the Mossad in Rome. Vanunu was an employee at Israel’s top-secret Negev Nuclear Research Center, located in the desert city of Dimona, which was used to develop the country’s nuclear arsenal. But he became a fervent opponent of nuclear proliferation and in 1986 fled to the United Kingdom, where he revealed the existence of the Israeli nuclear weapons program to the The Times of London. His action was in direct violation of the non-disclosure agreement he had signed with the government of Israel; moreover, it went against Israel’s official policy of ‘nuclear ambiguity’, which means that the country refuses to confirm or deny that it maintains a nuclear weapons program.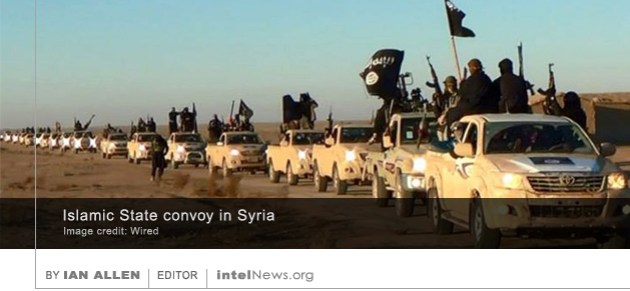 The United States Central Intelligence Agency is collaborating with the country’s Special Forces in a targeted killing program aimed against senior members of the Islamic State and other militant groups in Syria. The program, which has been directly authorized by US President Barack Obama, is limited in scope and has so far involved fewer than a dozen strikes against suspected militants. But it is believed to reflect increasing frustration in Washington about the lack of progress shown by the military campaign against the Islamic State. Recent reports by American intelligence agencies
The United States Central Intelligence Agency is collaborating with the country’s Special Forces in a targeted killing program aimed against senior members of the Islamic State and other militant groups in Syria. The program, which has been directly authorized by US President Barack Obama, is limited in scope and has so far involved fewer than a dozen strikes against suspected militants. But it is believed to reflect increasing frustration in Washington about the lack of progress shown by the military campaign against the Islamic State. Recent reports by American intelligence agencies  Frederick Forsyth, the esteemed British author of novels such as The Day of the Jackal, has confirmed publicly for the first time that he was an agent of British intelligence for two decades. Forsyth, who is 77, worked for many decades as an international correspondent for the BBC and Reuters news agency, covering some of the world’s most sensitive areas, including postcolonial Nigeria, apartheid South Africa and East Germany during the Cold War. But he became famous for authoring novels that have sold over 70 million copies worldwide, including The Odessa File, Dogs of War and The Day of the Jackal, many of which were adapted into film. Several of his intelligence-related novels are based on his experiences as a news correspondent, which have prompted his loyal fans to suspect that he might have some intelligence background.
Frederick Forsyth, the esteemed British author of novels such as The Day of the Jackal, has confirmed publicly for the first time that he was an agent of British intelligence for two decades. Forsyth, who is 77, worked for many decades as an international correspondent for the BBC and Reuters news agency, covering some of the world’s most sensitive areas, including postcolonial Nigeria, apartheid South Africa and East Germany during the Cold War. But he became famous for authoring novels that have sold over 70 million copies worldwide, including The Odessa File, Dogs of War and The Day of the Jackal, many of which were adapted into film. Several of his intelligence-related novels are based on his experiences as a news correspondent, which have prompted his loyal fans to suspect that he might have some intelligence background. The United States Department of Defense is investigating claims that some of its officials doctored intelligence reports to give a falsely optimistic account of the campaign against the Islamic State.
The United States Department of Defense is investigating claims that some of its officials doctored intelligence reports to give a falsely optimistic account of the campaign against the Islamic State.  A Maltese ultra-nationalist group believed to be behind a string of bombings in the 1980s was believed by British intelligence to have links to the United States Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), according to recently declassified documents. The Front Freedom Fighters (FFF) was a staunchly anticommunist group whose members violently objected to what they saw as Malta’s overly close contacts with the Communist Bloc. During the 16-year rule of the Maltese Labour Party, which began in 1971, the Mediterranean island maintained close relations with countries during such as Libya and North Korea. The Maltese Nationalist Party, which formed the main opposition to Labour, was highly critical of these contacts, but failed to win three consecutive electoral contests and was thus unable to influence the country’s foreign policy in any significant way.
A Maltese ultra-nationalist group believed to be behind a string of bombings in the 1980s was believed by British intelligence to have links to the United States Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), according to recently declassified documents. The Front Freedom Fighters (FFF) was a staunchly anticommunist group whose members violently objected to what they saw as Malta’s overly close contacts with the Communist Bloc. During the 16-year rule of the Maltese Labour Party, which began in 1971, the Mediterranean island maintained close relations with countries during such as Libya and North Korea. The Maltese Nationalist Party, which formed the main opposition to Labour, was highly critical of these contacts, but failed to win three consecutive electoral contests and was thus unable to influence the country’s foreign policy in any significant way. The British government has released a nine-volume file on an influential film critic who
The British government has released a nine-volume file on an influential film critic who  A German intelligence officer, who is accused of spying for the United States Central Intelligence Agency, has been
A German intelligence officer, who is accused of spying for the United States Central Intelligence Agency, has been  General Hamid Gul, a controversial Pakistani spymaster who helped facilitate America’s covert involvement during the closing stages of the Soviet-Afghan war,
General Hamid Gul, a controversial Pakistani spymaster who helped facilitate America’s covert involvement during the closing stages of the Soviet-Afghan war,  A Soviet double spy was able to penetrate the senior echelons of Australia’s intelligence agency during the Cold War, according to a retired Australian intelligence officer who has spoken out for the first time. Molly Sasson, was born in Britain, but worked for the Australian Security Intelligence Organisation (ASIO) from 1969 until her retirement in 1983. A fluent German speaker, Sasson was first recruited during World War II by the Royal Air Force, where she worked as an intelligence officer before transferring to the Security Service (MI5), Britain’s domestic intelligence agency. At the onset of the Cold War, Sasson helped facilitate the defection to Britain of Colonel Grigori Tokaty, an influential rocket scientist who later became a professor of aeronautics in London. But in the late 1960s, Sasson moved with her husband to Australia, where she took up a job with ASIO, following a personal invitation by its Director, Sir Charles Spry. Upon her arrival in Canberra, Sasson took a post with ASIO’s Soviet counterintelligence desk, which monitored Soviet espionage activity on Australian soil.
A Soviet double spy was able to penetrate the senior echelons of Australia’s intelligence agency during the Cold War, according to a retired Australian intelligence officer who has spoken out for the first time. Molly Sasson, was born in Britain, but worked for the Australian Security Intelligence Organisation (ASIO) from 1969 until her retirement in 1983. A fluent German speaker, Sasson was first recruited during World War II by the Royal Air Force, where she worked as an intelligence officer before transferring to the Security Service (MI5), Britain’s domestic intelligence agency. At the onset of the Cold War, Sasson helped facilitate the defection to Britain of Colonel Grigori Tokaty, an influential rocket scientist who later became a professor of aeronautics in London. But in the late 1960s, Sasson moved with her husband to Australia, where she took up a job with ASIO, following a personal invitation by its Director, Sir Charles Spry. Upon her arrival in Canberra, Sasson took a post with ASIO’s Soviet counterintelligence desk, which monitored Soviet espionage activity on Australian soil. A Russian former officer in the Soviet KGB, who defied deportation orders issued against him by the Canadian government by taking refuge in a Vancouver church for six consecutive years, has voluntarily left the country. Mikhail Lennikov, who spent five years working for the KGB in the 1980s, had been living in Canada with his wife and son since 1992. But in 2009, Canada’s Public Safety Ministry rejected Lennikov’s refugee claim and
A Russian former officer in the Soviet KGB, who defied deportation orders issued against him by the Canadian government by taking refuge in a Vancouver church for six consecutive years, has voluntarily left the country. Mikhail Lennikov, who spent five years working for the KGB in the 1980s, had been living in Canada with his wife and son since 1992. But in 2009, Canada’s Public Safety Ministry rejected Lennikov’s refugee claim and  The White House has warned the Chinese government to stop deploying on American soil intelligence operatives masquerading as tourists, business executives or other false covers. Nowadays the standard practice for intelligence personnel deployed abroad is to be posted as diplomatic staff in a foreign embassy or consulate. But there are some intelligence officers who do not follow that practice. These are known as non-official-cover operatives, or NOCs in American intelligence parlance. NOCs are typically high-level principal agents or officers of an intelligence agency, who operate without official connection to the diplomatic authorities of the country that is employing them. They typically pose as business executives, students, academics, journalists, or non-profit agency workers. Unlike official-cover officers, who are protected by diplomatic immunity, NOCs have no such protection. If
The White House has warned the Chinese government to stop deploying on American soil intelligence operatives masquerading as tourists, business executives or other false covers. Nowadays the standard practice for intelligence personnel deployed abroad is to be posted as diplomatic staff in a foreign embassy or consulate. But there are some intelligence officers who do not follow that practice. These are known as non-official-cover operatives, or NOCs in American intelligence parlance. NOCs are typically high-level principal agents or officers of an intelligence agency, who operate without official connection to the diplomatic authorities of the country that is employing them. They typically pose as business executives, students, academics, journalists, or non-profit agency workers. Unlike official-cover officers, who are protected by diplomatic immunity, NOCs have no such protection. If  The government of Rwanda uses intelligence operatives to systematically spy on, harass, and even kill opposition figures living abroad, according to a report issued by a Canadian security agency. The report was written by the National Security Screening Division of the Canada Border Services Agency, and was partly based on information from the Canadian Security Intelligence Service (CSIS). It was released as part of a court case involving a Rwandan man living in Canada, who was accused of working as a spy for the government of Rwanda.
The government of Rwanda uses intelligence operatives to systematically spy on, harass, and even kill opposition figures living abroad, according to a report issued by a Canadian security agency. The report was written by the National Security Screening Division of the Canada Border Services Agency, and was partly based on information from the Canadian Security Intelligence Service (CSIS). It was released as part of a court case involving a Rwandan man living in Canada, who was accused of working as a spy for the government of Rwanda. Swedish Air Force spy planes conducted reconnaissance flights over Russia on Wednesday —and there was nothing the Kremlin could do about it. The flights were part of the 1992 Treaty on Open Skies, an international agreement designed to build trust among former Cold War rivals. The treaty was first proposed by the United States in 1990, with the intention of covering all member-states of the Warsaw Pact and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization. When it was eventually signed, on March 24, 1992, it was ratified by 23 countries, including the US and Russia. An additional 11 states have joined the treaty at various times since, with Sweden joining in 2002. On Wednesday, Swedish reconnaissance airplanes conducted flights over a number of Russian military installations as part of the treaty, as they do every year during predetermined times.
Swedish Air Force spy planes conducted reconnaissance flights over Russia on Wednesday —and there was nothing the Kremlin could do about it. The flights were part of the 1992 Treaty on Open Skies, an international agreement designed to build trust among former Cold War rivals. The treaty was first proposed by the United States in 1990, with the intention of covering all member-states of the Warsaw Pact and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization. When it was eventually signed, on March 24, 1992, it was ratified by 23 countries, including the US and Russia. An additional 11 states have joined the treaty at various times since, with Sweden joining in 2002. On Wednesday, Swedish reconnaissance airplanes conducted flights over a number of Russian military installations as part of the treaty, as they do every year during predetermined times.






Secret program gave CIA ‘unfiltered access’ to German communications
September 8, 2015 by Joseph Fitsanakis 1 Comment
The existence of joint collection programs between the BND and American intelligence agencies has been established in the past, and has prompted the creation of a special investigative committee in the German parliament. The Committee of Inquiry into Intelligence Operations was set up in 2014, after files leaked by American defector Edward Snowden revealed that the US had been spying on the telephone communications of German Chancellor Angela Merkel. But it has also been investigating whether the BND’s collaboration with American intelligence agencies violated the rights of German citizens.
The committee had previously been told that all telecommunications data given to the US by German agencies had previously been vetted by BND officers. But the GLOTAIC documents published by Der Spiegel states that audio recordings of intercepted telephone calls were “directly routed to the US” in the interests of technical efficiency. The parliamentary committee had also been told that the data shared with the CIA concerned non-German citizens using German telecommunications networks. But the documents published last week state that a “technical glitch” in the GLOTAIC system allowed “massive German traffic” to be directly accessed by the CIA without having been first filtered by the BND.
Another document published by Spiegel reveals that the BND warned project CLOTAIC supervisors that the agency faced “serious risks” should the secret operation become public, because it had allegedly violated German federal privacy regulations.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 08 September 2015 | Permalink
Filed under Expert news and commentary on intelligence, espionage, spies and spying Tagged with BND, CIA, communications interception, Germany, Hilden (Germany), intelligence cooperation, MCI Communications, News, Project GLOTAIC, United States, Verizon