US intelligence has evidence Saudis planned to capture missing journalist
October 12, 2018 1 Comment
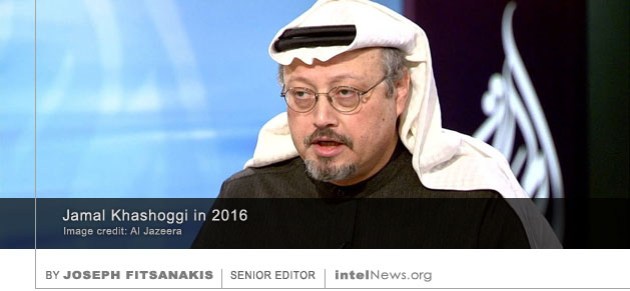 American intelligence agencies have evidence that the Saudi royal family tried to lure The Washington Post journalist Jamal Khashoggi back to Saudi Arabia, in order to capture him, according to sources. Khashoggi, 59, is a Saudi government adviser who in 2015 became a critic of the kingdom’s style of governance. He moved to the United States, from where he began to criticize Saudi Arabia’s involvement in the civil war in Yemen, its support for the repression of political freedoms in Egypt, and other issues. He also joined the staff of The Washington Post and penned columns in which he criticized Saudi policies. He has been missing since Tuesday, when he visited the Saudi consulate in Istanbul. He went there for a scheduled appointment in order to be issued a document certifying his divorce from his former wife in Saudi Arabia.
American intelligence agencies have evidence that the Saudi royal family tried to lure The Washington Post journalist Jamal Khashoggi back to Saudi Arabia, in order to capture him, according to sources. Khashoggi, 59, is a Saudi government adviser who in 2015 became a critic of the kingdom’s style of governance. He moved to the United States, from where he began to criticize Saudi Arabia’s involvement in the civil war in Yemen, its support for the repression of political freedoms in Egypt, and other issues. He also joined the staff of The Washington Post and penned columns in which he criticized Saudi policies. He has been missing since Tuesday, when he visited the Saudi consulate in Istanbul. He went there for a scheduled appointment in order to be issued a document certifying his divorce from his former wife in Saudi Arabia.
Last Sunday, Turkish government officials said that Khashoggi was brutally murdered inside the Saudi consulate during his visit, probably on orders of the Saudi government. Turkish media reports said on Sunday that a 15-member Saudi team arrived in Istanbul shortly prior to Khashoggi’s visit to the consulate. The team, whose members carried diplomatic passports, tortured and then killed Khashoggi, said Turkish sources. They then dismembered his body and took it out of the consulate hidden inside a diplomatic vehicle. Saudi Arabia has denied the charges and said that Khashoggi left the consulate in Istanbul less than an hour after entering it on Tuesday afternoon.
On Wednesday, The Washington Post cited anonymous US officials in claiming that the Saudi royal family had devised an elaborate plan to lure Khashoggi back to Saudi Arabia in order to capture him. The paper said that US intelligence agencies are in possession of communications intercepts of exchanges between Saudi officials, in which the plan to lure Khashoggi back to Saudi Arabia is discussed. The Post also cited “several of Khashoggi’s friends” who said that in recent months he received phone calls from Saudi officials close to the kingdom’s controversial crown prince Mohammed bin Salman. The officials reportedly offered Khashoggi political protection from prosecution if he returned to Saudi Arabia. They also offered him high-level government jobs, said The Post. But Khashoggi was skeptical of the offers and rejected them, his friends said.
The paper also cited an anonymous “former US intelligence official” who said that the travel details of the 15-member Saudi diplomatic team that went to Istanbul on the day of Khashoggi’s disappearance “bore the hallmarks of [an extralegal] rendition” —a person’s unauthorized removal from one country and detention and interrogation in another. Turkey has said that the Saudi team arrived in Istanbul in two separate groups using private aircraft, and departed from the country at different times going to different destinations in the hours after Khashoggi’s disappearance.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 12 October 2018 | Permalink
 A number of European intelligence agencies have reportedly warned the Turkish government of a possible assassination attempt against the country’s president, Recep Tayyip Erdoğan, during an official state visit to Bosnia and Herzegovina. On Sunday the Turkish leader embarked on a week-long visit to the Balkans, beginning with Bosnia, which along with Albania is seen as Turkey’s strongest political ally in Europe. During his visit to Bosnia, Mr. Erdoğan is scheduled to meet with Bakir Izetbegovic, one of the country’s three presidents. He is also scheduled to address a rally of expatriate Turks in the Bosnian capital Sarajevo, held in support of his ruling Justice and Development Party.
A number of European intelligence agencies have reportedly warned the Turkish government of a possible assassination attempt against the country’s president, Recep Tayyip Erdoğan, during an official state visit to Bosnia and Herzegovina. On Sunday the Turkish leader embarked on a week-long visit to the Balkans, beginning with Bosnia, which along with Albania is seen as Turkey’s strongest political ally in Europe. During his visit to Bosnia, Mr. Erdoğan is scheduled to meet with Bakir Izetbegovic, one of the country’s three presidents. He is also scheduled to address a rally of expatriate Turks in the Bosnian capital Sarajevo, held in support of his ruling Justice and Development Party. The Turkish government has issued a warrant for the arrest of a former officer in the United States Central Intelligence Agency, which Ankara claims was instrumental in the failed July 2016 attempt to topple the government of Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan. The move comes amidst heightened tensions in relations between Ankara and Washington. The two NATO allies have
The Turkish government has issued a warrant for the arrest of a former officer in the United States Central Intelligence Agency, which Ankara claims was instrumental in the failed July 2016 attempt to topple the government of Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan. The move comes amidst heightened tensions in relations between Ankara and Washington. The two NATO allies have  The Turkish government has refused to comment on reports from Iraq, which suggest that Kurdish forces have captured at least two senior Turkish intelligence officers. News of the arrests first
The Turkish government has refused to comment on reports from Iraq, which suggest that Kurdish forces have captured at least two senior Turkish intelligence officers. News of the arrests first  American troops deployed in Syria have exchanged fire with rebels that were until recently supported by the United States Central Intelligence Agency. In 2013, soon after the outbreak of the Syrian Civil War, the then-US President Barack Obama instructed the Central Intelligence Agency to provide covert support to fighters in Syria. Acting on the president’s directive, the CIA promptly joined forces with spy agencies from Britain, France, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates, to assist fighters affiliated with the Free Syrian Army. At that time, Washington saw the Free Syrian Army and forces affiliated with it as ideologically moderate. It also agreed with the group’s main aim, which was to topple the regime of Syrian President Bashar al-Assad.
American troops deployed in Syria have exchanged fire with rebels that were until recently supported by the United States Central Intelligence Agency. In 2013, soon after the outbreak of the Syrian Civil War, the then-US President Barack Obama instructed the Central Intelligence Agency to provide covert support to fighters in Syria. Acting on the president’s directive, the CIA promptly joined forces with spy agencies from Britain, France, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates, to assist fighters affiliated with the Free Syrian Army. At that time, Washington saw the Free Syrian Army and forces affiliated with it as ideologically moderate. It also agreed with the group’s main aim, which was to topple the regime of Syrian President Bashar al-Assad. Earlier this week, it was
Earlier this week, it was  German intelligence and security agencies have publicly rejected a direct request made by Turkey’s intelligence chief to gather information on Turks who are living in Germany and are critical of the Turkish government. The request reportedly relates to attempts by the Turkish government to round up its critics, following a failed military coup in July of last year. The government of Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan accuses members of the so-called Gülen movement of orchestrating the coup, which included an armed attack on the country’s parliament and the murder of over 200 people across Turkey. The Gülen movement consists of supporters of Muslim cleric Fethullah Gülen, who runs a global network of schools, charities and businesses from his home in the United States. The government of Turkey has designated Gülen’s group a terrorist organization and claims that its members have stealthily infiltrated state institutions since the 1980s.
German intelligence and security agencies have publicly rejected a direct request made by Turkey’s intelligence chief to gather information on Turks who are living in Germany and are critical of the Turkish government. The request reportedly relates to attempts by the Turkish government to round up its critics, following a failed military coup in July of last year. The government of Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan accuses members of the so-called Gülen movement of orchestrating the coup, which included an armed attack on the country’s parliament and the murder of over 200 people across Turkey. The Gülen movement consists of supporters of Muslim cleric Fethullah Gülen, who runs a global network of schools, charities and businesses from his home in the United States. The government of Turkey has designated Gülen’s group a terrorist organization and claims that its members have stealthily infiltrated state institutions since the 1980s. Turkish state agencies have asked the country’s diplomats stationed all over Europe to spy on Turkish expatriate communities there, in an effort to identify those opposed to the government, according to a German report. The government of Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan accuses members of the so-called Gülen movement of orchestrating a military coup in July of last year, which resulted in an armed attack on the country’s parliament and the murder of over 200 people across Turkey. The Gülen movement consists of supporters of Muslim cleric Fethullah Gülen, who runs a global network of schools, charities and businesses from his home in the United States. The government of Turkey has designated Gülen’s group a terrorist organization and claims that its members have stealthily infiltrated state institutions since the 1980s.
Turkish state agencies have asked the country’s diplomats stationed all over Europe to spy on Turkish expatriate communities there, in an effort to identify those opposed to the government, according to a German report. The government of Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan accuses members of the so-called Gülen movement of orchestrating a military coup in July of last year, which resulted in an armed attack on the country’s parliament and the murder of over 200 people across Turkey. The Gülen movement consists of supporters of Muslim cleric Fethullah Gülen, who runs a global network of schools, charities and businesses from his home in the United States. The government of Turkey has designated Gülen’s group a terrorist organization and claims that its members have stealthily infiltrated state institutions since the 1980s. A leaked report by a European Union intelligence body states that Islamist forces were not behind last July’s failed coup in Turkey, and that the ruling party used the coup to neutralize its few remaining political rivals. The government of Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan accuses members of the so-called Gülen movement of orchestrating the coup, which included an armed attack on the country’s parliament and the murder of over 200 people across Turkey. The Gülen movement consists of supporters of Muslim cleric Fethullah Gülen, who runs a global network of schools, charities and businesses from his home in the United States. The government of Turkey has designated Gülen’s group a terrorist organization and claims that its members have stealthily infiltrated state institutions since the 1980s.
A leaked report by a European Union intelligence body states that Islamist forces were not behind last July’s failed coup in Turkey, and that the ruling party used the coup to neutralize its few remaining political rivals. The government of Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan accuses members of the so-called Gülen movement of orchestrating the coup, which included an armed attack on the country’s parliament and the murder of over 200 people across Turkey. The Gülen movement consists of supporters of Muslim cleric Fethullah Gülen, who runs a global network of schools, charities and businesses from his home in the United States. The government of Turkey has designated Gülen’s group a terrorist organization and claims that its members have stealthily infiltrated state institutions since the 1980s. A German retiree living in Greece, who admitted in court that he was part of a network of German and other Western European residents of Greece recruited as spies by Turkish intelligence, has been jailed for 14 years. The 65-year-old man, who has not been named, was arrested two years ago in the southeastern Aegean island of Kos. He was born in Cold-War-era East Germany and worked as a locksmith before serving for 15 years in the East German National People’s Army. From 2009 to 2012, he lived in Turkey before moving permanently to Greece.
A German retiree living in Greece, who admitted in court that he was part of a network of German and other Western European residents of Greece recruited as spies by Turkish intelligence, has been jailed for 14 years. The 65-year-old man, who has not been named, was arrested two years ago in the southeastern Aegean island of Kos. He was born in Cold-War-era East Germany and worked as a locksmith before serving for 15 years in the East German National People’s Army. From 2009 to 2012, he lived in Turkey before moving permanently to Greece. Ever since 2011, when the Syrian Civil War erupted, Turkey has refrained from directly intervening in the conflict, other than to provide material support to opponents of Syrian President Bashar al-Assad. The hope in Ankara was that Islamist and pro-Assad forces would exhaust each other. There is no evidence that Turkey was at any point seriously alarmed about the rise of Sunni militancy in Syria. Instead, the Turkish government of President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan made no secret of its primary concern, which was the rise of Kurdish nationalism in northern Syria.
Ever since 2011, when the Syrian Civil War erupted, Turkey has refrained from directly intervening in the conflict, other than to provide material support to opponents of Syrian President Bashar al-Assad. The hope in Ankara was that Islamist and pro-Assad forces would exhaust each other. There is no evidence that Turkey was at any point seriously alarmed about the rise of Sunni militancy in Syria. Instead, the Turkish government of President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan made no secret of its primary concern, which was the rise of Kurdish nationalism in northern Syria. At least 35 Turkish nationals with diplomatic passports have applied for political asylum in Germany following last July’s failed military coup in Turkey, according to German authorities. The administration of Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan accuses members of the so-called Gülen movement of orchestrating the coup, which included an armed attack on the country’s parliament and the murder of over 200 people across Turkey. The Gülen movement consists of supporters of Muslim cleric Fethullah Gülen, who runs a global network of schools, charities and businesses from his home in the United States. The government of Turkey has designated Gülen’s group a terrorist organization and claims its members have stealthily infiltrated state institutions since the 1980s.
At least 35 Turkish nationals with diplomatic passports have applied for political asylum in Germany following last July’s failed military coup in Turkey, according to German authorities. The administration of Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan accuses members of the so-called Gülen movement of orchestrating the coup, which included an armed attack on the country’s parliament and the murder of over 200 people across Turkey. The Gülen movement consists of supporters of Muslim cleric Fethullah Gülen, who runs a global network of schools, charities and businesses from his home in the United States. The government of Turkey has designated Gülen’s group a terrorist organization and claims its members have stealthily infiltrated state institutions since the 1980s.






Suicide bomb threat reportedly leads to evacuation of Iranian envoy to Turkey
October 16, 2018 by Joseph Fitsanakis Leave a comment
At 2 pm local time, reports stated that Iran’s ambassador to Turkey, Mohammad Ebrahim Taherian Fard, had been hurriedly evacuated from the Iranian embassy by Turkish security forces. By that time, all roads leading to the Iranian embassy, located next to the Ankara Hilton in one of the Turkish capital’s leafiest areas, had been cordoned off. Reporters from the Reuters news agency and Agence France Presse said that Turkish police and special forces had shut down Tahran Road, where the Iranian embassy is located, and were searching cars. Armed security forces had also surrounded the Iranian embassy, according to Reuters.
Strangely, however, reports of a possible bomb attack and of the ambassador’s evacuation were strongly refuted by the Iranian government, which denounced them as “sheer lies” and “complete fabrications”. In a statement published online on Monday afternoon, Iran’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs said that its diplomats in Ankara had noticed “an increased Turkish security presence” around the Iranian embassy. However, they continued working normally, as they were unaware of the reasons for the heightened security. They assumed that Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan was appearing nearby, said the statement. A statement by the Iranian embassy in Ankara said that consular employees were present at the embassy and that all scheduled services were being offered without interruption.
In the past month, the embassies of Iran in Paris and Athens have come under attack by Kurdish separatists and leftwing groups protesting against Tehran’s alleged oppression of ethnic minorities in the country. In the past, the Islamic Republic has been rarely targeted by ISIS, whose members dismiss Shiite Islam as a heresy. In June 2017, two attacks were carried out simultaneously in Tehran, targeting the Iranian parliament and the Mausoleum of Ruhollah Khomeini, founder of post-1979 Iran. In September of this year, ISIS claimed responsibility for an attack in Iran’s southwestern city of Ahvaz, which killed 25 soldiers and civilians during a military parade.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 16 October 2018 | Permalink
Filed under Expert news and commentary on intelligence, espionage, spies and spying Tagged with Iran, Iranian embassy in Turkey, Islamic State, Mohammad Ebrahim Taherian Fard, News, suicide bombings, Turkey