Concerns about Israeli spying prompt debate on EU security measures
February 15, 2016 2 Comments
 A debate on information security measures in the European Union was prompted last week after some officials voiced concerns that the proceedings of a closed-door meeting were secretly monitored by Israel. The meeting took place on January 15 as part of regular proceedings by the EU’s Political and Security Committee (PSC). The main item on the agenda was the EU’s Middle Eastern policy. According to some meeting participants, Israeli diplomats appeared to be aware of a statement discussed during the PSC meeting “in real time”, which prompted a wider debate on EU information security policies.
A debate on information security measures in the European Union was prompted last week after some officials voiced concerns that the proceedings of a closed-door meeting were secretly monitored by Israel. The meeting took place on January 15 as part of regular proceedings by the EU’s Political and Security Committee (PSC). The main item on the agenda was the EU’s Middle Eastern policy. According to some meeting participants, Israeli diplomats appeared to be aware of a statement discussed during the PSC meeting “in real time”, which prompted a wider debate on EU information security policies.
According to the Brussels-based EU Observer, which reported on the story, EU member state ambassadors present at the meeting worded a statement that contained a sentence deemed critical to Israel’s policy on Palestine. The sentence allegedly stated: “The EU will continue to unequivocally and explicitly make the distinction between Israel and all territories occupied by Israel in 1967”. According to some ambassadors who were present at the PSC meeting, “Israeli contacts sent text messages to them with requests to alter wording shortly after each new draft [of the PSC statement] went around”. Further suspicions were raised when, at the conclusion of the meeting, the Greek delegate vetoed the contentious line, standing alone against the remaining 27 delegates who had earlier supported it.
Last week, sources told the EU Observer that Israel may have placed bugs in the room where the PSC meeting took place. They added that the committee was debating whether to begin holding meetings in a secure room located in the EU headquarters building in Brussels, where the use of cell phones by meeting participants is not possible. They also said that a stricter classification policy should apply to PSC documents. Others, however, said that the source of the leak may have been the Greek delegate —the sole participant at the meeting who assumed a seemingly pro-Israeli stance. The Greek ambassador may have shared the details of the proceedings with Israeli officials, thus effectively spying on the conference on behalf of Israel, speculated the EU Observer. Another PSC meeting delegate told the paper that “the spy theory” was effectively concocted “in order to avoid confrontation” with the Greek delegation.
The EU Observer contacted the Greek mission to the EU, but was told that the Greek ambassador would never spy on the EU “as a matter of principle”. The Israeli mission to the EU declined to comment.
► Author: Ian Allen | Date: 15 February 2016 | Permalink
 Two leading Turkish journalists, who claimed in a series of articles that Ankara has been arming militant Islamists in Syria, are facing espionage charges for “airing Turkish state secrets”. The two, Can Dündar and Erdem Gül, work for Cumhuriyet, (The Republic), Turkey’s oldest newspaper, which typically voices staunchly secularist views representing the center-left of the political spectrum. Last year Dündar, who is the paper’s editor, and Gül, who serves as the paper’s bureau chief in Ankara, published a series of articles claiming that the Turkish government was secretly supporting Salafi Jihadist groups in Syria.
Two leading Turkish journalists, who claimed in a series of articles that Ankara has been arming militant Islamists in Syria, are facing espionage charges for “airing Turkish state secrets”. The two, Can Dündar and Erdem Gül, work for Cumhuriyet, (The Republic), Turkey’s oldest newspaper, which typically voices staunchly secularist views representing the center-left of the political spectrum. Last year Dündar, who is the paper’s editor, and Gül, who serves as the paper’s bureau chief in Ankara, published a series of articles claiming that the Turkish government was secretly supporting Salafi Jihadist groups in Syria.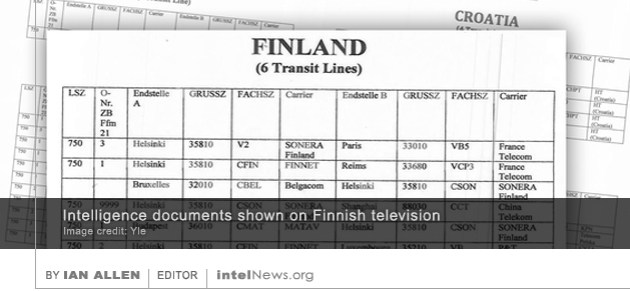 German intelligence, possibly with the collaboration of the United States, monitored communications lines connecting Finland with at least five countries in the early 2000s,
German intelligence, possibly with the collaboration of the United States, monitored communications lines connecting Finland with at least five countries in the early 2000s,  A member of a hacker group that took responsibility for breaking into the personal email account of the director of the Central Intelligence Agency last year has now hacked the email of the most senior intelligence official in the United States. In October 2015, the hacker group referred to by its members as “Crackas With Attitude” —CWA for short—
A member of a hacker group that took responsibility for breaking into the personal email account of the director of the Central Intelligence Agency last year has now hacked the email of the most senior intelligence official in the United States. In October 2015, the hacker group referred to by its members as “Crackas With Attitude” —CWA for short—  Intelligence agencies outside North Korea, including those of South Korea and the United States, are skeptical of Pyongyang’s claims that it conducted a successful test of a hydrogen bomb. On the surface, North Korea’s
Intelligence agencies outside North Korea, including those of South Korea and the United States, are skeptical of Pyongyang’s claims that it conducted a successful test of a hydrogen bomb. On the surface, North Korea’s  The director of Russia’s powerful military intelligence agency has died unexpectedly at 58, according to the Kremlin, which has yet to release precise information about the circumstances of his death. General Igor Sergun had led the Main Intelligence Directorate, known as GRU, since 2011, when he replaced his predecessor, Colonel General Aleksandr Shlyakhturov, in a Kremlin-instigated reshuffle. The Russian government
The director of Russia’s powerful military intelligence agency has died unexpectedly at 58, according to the Kremlin, which has yet to release precise information about the circumstances of his death. General Igor Sergun had led the Main Intelligence Directorate, known as GRU, since 2011, when he replaced his predecessor, Colonel General Aleksandr Shlyakhturov, in a Kremlin-instigated reshuffle. The Russian government  A senior Central Intelligence Agency official, who led the agency as its acting director before retiring in 2013, has said that not having sources in the Iraqi government’s upper echelons led to the intelligence failure of 2003. Michael Morell retired as deputy director of the CIA, after having served twice as its acting director, in 2011 and from 2012 to 2013. A Georgetown University graduate, Morell joined the agency in 1980 and rose through the ranks to lead the Asia, Pacific and Latin America divisions. In May 2015, Morell published his book, The Great War of Our Time: The CIA’s Fight against Terrorism from al Qa’ida to ISIS, which he has been promoting while working as a consultant in the private sector.
A senior Central Intelligence Agency official, who led the agency as its acting director before retiring in 2013, has said that not having sources in the Iraqi government’s upper echelons led to the intelligence failure of 2003. Michael Morell retired as deputy director of the CIA, after having served twice as its acting director, in 2011 and from 2012 to 2013. A Georgetown University graduate, Morell joined the agency in 1980 and rose through the ranks to lead the Asia, Pacific and Latin America divisions. In May 2015, Morell published his book, The Great War of Our Time: The CIA’s Fight against Terrorism from al Qa’ida to ISIS, which he has been promoting while working as a consultant in the private sector. Authorities in Bosnia and Herzegovina have announced the arrest of several people on suspicion of having direct links with the Islamic State and other militant groups fighting in Iraq and Syria. At least 11 people were arrested by police in simultaneous raids at a number of locations on Tuesday, including businesses and private homes, across the Bosnian capital Sarajevo. A police spokeswoman said the eleven men had been charged with having links to terrorist groups, financing terrorist groups, or inciting and helping organize criminal acts. A number of them were also charged with recruiting young men and women to join militant groups in Syria and Iraq, she said.
Authorities in Bosnia and Herzegovina have announced the arrest of several people on suspicion of having direct links with the Islamic State and other militant groups fighting in Iraq and Syria. At least 11 people were arrested by police in simultaneous raids at a number of locations on Tuesday, including businesses and private homes, across the Bosnian capital Sarajevo. A police spokeswoman said the eleven men had been charged with having links to terrorist groups, financing terrorist groups, or inciting and helping organize criminal acts. A number of them were also charged with recruiting young men and women to join militant groups in Syria and Iraq, she said. Following a request from the White House, the United States Department of Defense is putting together options to launch offensive cyber operations of an unprecedented scale against the Islamic State. The White House
Following a request from the White House, the United States Department of Defense is putting together options to launch offensive cyber operations of an unprecedented scale against the Islamic State. The White House  One of the guns used by Islamist militants to attack locations in downtown Paris on November 13 was purchased legally through a dealer in the United States, according to a report by the Associated Press. Investigators have confirmed that several of the weapons used in the attack, which killed 130 and injured hundreds more, were manufactured in Serbia. Most are slightly modified versions of the Soviet-era AK-47, known in the West as “shortened Kalashnikov”. All were produced in a weapons factory called Zastava, which is located in the city of Kragujevac, in central Serbia. They were made in the 1980s and sold within the former Yugoslavia.
One of the guns used by Islamist militants to attack locations in downtown Paris on November 13 was purchased legally through a dealer in the United States, according to a report by the Associated Press. Investigators have confirmed that several of the weapons used in the attack, which killed 130 and injured hundreds more, were manufactured in Serbia. Most are slightly modified versions of the Soviet-era AK-47, known in the West as “shortened Kalashnikov”. All were produced in a weapons factory called Zastava, which is located in the city of Kragujevac, in central Serbia. They were made in the 1980s and sold within the former Yugoslavia. Russian intelligence officials have warned authorities in Thailand that the Islamic State is planning to strike at Russian targets in the Southeast Asian country. Thai authorities received the warning in a memorandum dated November 27, 2015, which came from the Russian Federal Security Service (FSB). The document, marked ‘urgent’, warned of a series of coordinated attacks against Russian-related businesses and facilities in several cities across Thailand. Several Thai news sites, as well as CNN in the United States,
Russian intelligence officials have warned authorities in Thailand that the Islamic State is planning to strike at Russian targets in the Southeast Asian country. Thai authorities received the warning in a memorandum dated November 27, 2015, which came from the Russian Federal Security Service (FSB). The document, marked ‘urgent’, warned of a series of coordinated attacks against Russian-related businesses and facilities in several cities across Thailand. Several Thai news sites, as well as CNN in the United States,  Police in Moldova says it
Police in Moldova says it  A powerful South Korean parliamentary committee has accused the North Korean government of ties to the Islamic State, an allegation that is vehemently denied by Pyongyang. On November 18, members of the Intelligence Committee of the National Assembly of Korea stated in a press conference that they believed North Korea had “possible ties to ISIS”. They were referring to the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria, which calls itself Islamic State. On Monday, North Korea’s state-run media blasted the South Korean allegations as “slander and fabrications”, and said they threatened to derail collaboration efforts between Seoul and Pyongyang.
A powerful South Korean parliamentary committee has accused the North Korean government of ties to the Islamic State, an allegation that is vehemently denied by Pyongyang. On November 18, members of the Intelligence Committee of the National Assembly of Korea stated in a press conference that they believed North Korea had “possible ties to ISIS”. They were referring to the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria, which calls itself Islamic State. On Monday, North Korea’s state-run media blasted the South Korean allegations as “slander and fabrications”, and said they threatened to derail collaboration efforts between Seoul and Pyongyang. The governments of Russia and the Islamic Republic of Iran are arguably the two most important allies of Syrian President Bashar al-Assad. But the Russian-Iranian alliance over Syria is not as solid —and may not be as durable— as some believe. On Monday, Iranian news agency ISNA reported that Iran’s minister for intelligence condemned Russia’s increased military involvement in Syria and said it would weaken Iran’s security. The minister, Mahmoud Alavi,
The governments of Russia and the Islamic Republic of Iran are arguably the two most important allies of Syrian President Bashar al-Assad. But the Russian-Iranian alliance over Syria is not as solid —and may not be as durable— as some believe. On Monday, Iranian news agency ISNA reported that Iran’s minister for intelligence condemned Russia’s increased military involvement in Syria and said it would weaken Iran’s security. The minister, Mahmoud Alavi, 






Israel says it foiled attempt to smuggle spy drones into Gaza
February 22, 2016 1 Comment
According to the Israeli government report, the spy drones were found hidden inside boxes of toys that had been marked for export to Gaza. The drones were of different sizes, types and capabilities, but all were equipped with sophisticated cameras and related software, said the report. Israeli media reported on Sunday that, according to Israeli government sources in Tel Aviv, the drones were almost certainly going to be used by Hamas to spy on possible targets inside Israel. A source in the Israeli Department of Defense said Hamas was known to employ drones in order to explore and map the terrain that is adjacent to the Gaza Strip.
In March of last year, Egyptian authorities reported seeing several spy drones flying out of the Gaza Strip and conducting reconnaissance over Egyptian airspace in the Sinai Peninsula, which borders Gaza. According to some reports, a number of the spy drones that flew out of Gaza were seen as far as 50 kilometers (35 miles) inside Egyptian territory. The latest information from Israel is that the government in Tel Aviv believes that the pattern and frequency of attempts to smuggle spy drones into the Gaza Strip justify an investigation, which is now underway.
► Author: Ian Allen | Date: 22 February 2016 | Permalink
Filed under Expert news and commentary on intelligence, espionage, spies and spying Tagged with aerial reconnaissance, Gaza Strip, Israel, Kerem Shalom, News, Palestine, surveillance drones