August 23, 2016
by Joseph Fitsanakis
 Saturday’s suicide bombing, which killed over 50 and injured dozens at a wedding in Gaziantep, Turkey, was without doubt the work of the Islamic State. It was yet another attempt by the militant Sunni group to discourage the Kurds from confronting it in battle, by pointing to the deadly consequences. It was also fueled by the desire for vengeance against a population that has consistently resisted the Islamic State’s ideology. Additionally, if confirmed, the use of a child as a suicide bomber by the Islamic State may form a pattern of operational activity that can lead to broader conclusions about the current state of the organization.
Saturday’s suicide bombing, which killed over 50 and injured dozens at a wedding in Gaziantep, Turkey, was without doubt the work of the Islamic State. It was yet another attempt by the militant Sunni group to discourage the Kurds from confronting it in battle, by pointing to the deadly consequences. It was also fueled by the desire for vengeance against a population that has consistently resisted the Islamic State’s ideology. Additionally, if confirmed, the use of a child as a suicide bomber by the Islamic State may form a pattern of operational activity that can lead to broader conclusions about the current state of the organization.
It has become increasingly clear in the past two years that the armed Kurdish groups in northern Syria and Iraq, as well as Kurdish peshmerga units based in Turkey, are some of the most formidable opponents of militant Jihadists on the ground. By bombing soft targets inside Turkey, the Islamic State is sending a message to the Kurds that armed opposition on the ground will carry a heavy cost at home. Contrary to initial impressions, there was nothing special about the particular wedding ceremony that was targeted on Saturday. Any wedding would have been suitable for the Islamic State’s purpose. In fact, the randomness of the attack increases its shock value by demonstrating to the local population that any activity can be attacked, even if it does not involve notables. Additionally, the specific choice of a wedding magnifies the brutality of the attack, by targeting a young couple on what is typically the happiest day of their lives. The high concentration of children among the casualties may indicate that the bomber was given specific operational instructions to attack younger participants. The clear warning here is that the disruption will leave nothing untouched –including something as ‘off-limits’ as a couple on their wedding day, or groups of children– if the Kurds continue to fight the Islamic State.
Moreover, the Islamic State is trying to widen the already deep division between the Turkish state and the Kurds, by exposing the inability of the government in Ankara to protect its Kurdish population from attacks. The Kurds already resent Turkey’s ‘soft policy’ on the Islamic State. They and the rest of the world can see that Ankara has typically viewed the government of Bashar al-Assad in Damascus as far more threatening than the continuing rise of Islamist fundamentalism. Since the failed July 15 coup, the Turkish state has begun to revise its soft stance on the Islamic State, but this comes too late to pacify the country’s infuriated Kurdish population. This latest attack will only intensify the deep anger felt by the Kurds against the Turkish state.
Initial reports indicate the possible use of a child or a teenager to carry out the Gaziantep bombing. These may or may not be accurate. They could easily be an attempt by the Kurds to further-incense international public opinion against the Islamic State. If the reports are accurate, they do not necessarily represent some sort of break from the traditional tactics of the Islamic State. According to the group’s war-fighting doctrine, there is no differentiation between men and children when it comes to what it sees as the defense of Sunni religious doctrine. Every Muslim, regardless of race, gender, or age, is required to engage in holy war. Indeed, the Islamic State has deployed children before, in warfare, executions and suicide bombings against both hard and soft targets. However, even though the use of a child to carry out the Gaziantep bombing is not in itself unique, or particularly important, it matters if it forms part of a broader pattern. If it is verified that ISIS is increasingly using children in suicide bombings, or in warfare, it may signify two things: first, that the organization is finding it difficult to recruit able-bodied men for missions. Second, that adult ISIS recruits are becoming scarcer, so the organization is trying to preserve them for decisive battles.
It may be, of course, that a child or younger teenager was selected in order to avoid security profiling by the Kurds. Still, the use of children in warfare or suicide missions can result in a large degree of unpredictability. Children may be relatively easy targets for recruiters, for the obvious reason that they are young and impressionable. Their reality can therefore be effectively altered by fantastical tales of the supernatural, which the Islamic State is very skilled at. However, children are not necessarily very dependable in war, or terrorism. They can be easily frightened, can change their mind at the last minute, and they do not stay calm under pressure. There are several recent examples of children or teenagers who were recruited for suicide operations but surrendered after changing their mind.
Ultimately, shocking massacres such as Saturday’s attack in Gaziantep cannot be prevented. They can only be limited through careful police and intelligence work. In the case of Turkey, however, this will be difficult. The country’s police, intelligence and military structures have been significantly weakened following the failed July 15 coup. Thousands of government officials, police officers, intelligence and military personnel have been fired, demoted or imprisoned. The state, which is becoming increasingly synonymous with the President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan’s AKP party, is too preoccupied with preserving its own stability to concentrate on combating the terrorist spillover from Syria.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 23 August 2016 | Permalink
 Fake Syrian passports designed for use by members of the Islamic State trying to enter Europe have been found in refugee camps in Greece during an investigation by the law enforcement agency of the European Union (EU). Officials from Europol, the EU agency that coordinates intelligence operations against organized crime across EU-member-states, said that the fake travel documents were found during a fact-finding mission in Greek refugee camps. The mission was part of a larger investigation into the production and use of forged passports by the Islamic State, the Sunni militant group that is also known as the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS).
Fake Syrian passports designed for use by members of the Islamic State trying to enter Europe have been found in refugee camps in Greece during an investigation by the law enforcement agency of the European Union (EU). Officials from Europol, the EU agency that coordinates intelligence operations against organized crime across EU-member-states, said that the fake travel documents were found during a fact-finding mission in Greek refugee camps. The mission was part of a larger investigation into the production and use of forged passports by the Islamic State, the Sunni militant group that is also known as the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS). Saturday’s suicide bombing, which killed over 50 and injured dozens at a wedding in Gaziantep, Turkey, was without doubt the work of the Islamic State. It was yet another attempt by the militant Sunni group to discourage the Kurds from confronting it in battle, by pointing to the deadly consequences. It was also fueled by the desire for vengeance against a population that has consistently resisted the Islamic State’s ideology. Additionally, if confirmed, the use of a child as a suicide bomber by the Islamic State may form a pattern of operational activity that can lead to broader conclusions about the current state of the organization.
Saturday’s suicide bombing, which killed over 50 and injured dozens at a wedding in Gaziantep, Turkey, was without doubt the work of the Islamic State. It was yet another attempt by the militant Sunni group to discourage the Kurds from confronting it in battle, by pointing to the deadly consequences. It was also fueled by the desire for vengeance against a population that has consistently resisted the Islamic State’s ideology. Additionally, if confirmed, the use of a child as a suicide bomber by the Islamic State may form a pattern of operational activity that can lead to broader conclusions about the current state of the organization. The Turkish government has sent an official request to German intelligence for assistance in cracking down on the members of the so-called Gülen movement, which Ankara claims is behind July’s failed coup plot. The movement consists of supporters of Muslim cleric Fethullah Gülen, who runs a global network of schools, charities and businesses from his home in the United States. The government of Turkey has designated Gülen’s group a terrorist organization and claims it has stealthily infiltrated state institutions since the 1980s. The administration of Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan accuses Gülen’s supporters of orchestrating the July 15 coup that included an armed attack on the country’s parliament and the murder of over 200 people across Turkey.
The Turkish government has sent an official request to German intelligence for assistance in cracking down on the members of the so-called Gülen movement, which Ankara claims is behind July’s failed coup plot. The movement consists of supporters of Muslim cleric Fethullah Gülen, who runs a global network of schools, charities and businesses from his home in the United States. The government of Turkey has designated Gülen’s group a terrorist organization and claims it has stealthily infiltrated state institutions since the 1980s. The administration of Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan accuses Gülen’s supporters of orchestrating the July 15 coup that included an armed attack on the country’s parliament and the murder of over 200 people across Turkey. A high-ranking North Korean diplomat, who defected with his wife and children in London, and is now in South Korea, is from a privileged family with a long revolutionary pedigree in North Korean politics. South Korea’s Ministry of Unification confirmed on Wednesday that Thae Yong-Ho, the second-in-command at the North Korean embassy in the United Kingdom, had defected with his wife and children and had been given political asylum in South Korea. As intelNews
A high-ranking North Korean diplomat, who defected with his wife and children in London, and is now in South Korea, is from a privileged family with a long revolutionary pedigree in North Korean politics. South Korea’s Ministry of Unification confirmed on Wednesday that Thae Yong-Ho, the second-in-command at the North Korean embassy in the United Kingdom, had defected with his wife and children and had been given political asylum in South Korea. As intelNews  A senior member of North Korea’s diplomatic representation in the United Kingdom, who is considered one of his country’s leading specialists in Western European affairs, has reportedly defected “to a third country” with his family. The alleged defection was first
A senior member of North Korea’s diplomatic representation in the United Kingdom, who is considered one of his country’s leading specialists in Western European affairs, has reportedly defected “to a third country” with his family. The alleged defection was first  The United States Department of Defense has released details of an agreement with a private intelligence contractor, which experts believe involves the provision of services to American Special Forces working clandestinely inside Syria. The
The United States Department of Defense has released details of an agreement with a private intelligence contractor, which experts believe involves the provision of services to American Special Forces working clandestinely inside Syria. The 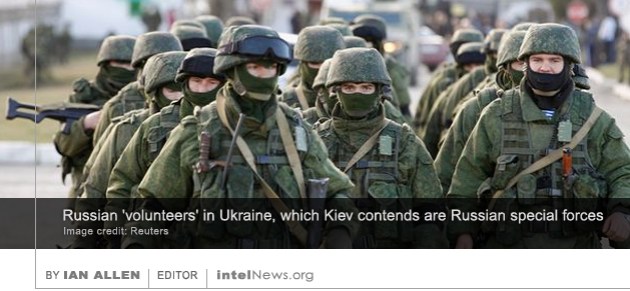 Ukrainian intelligence and defense officials are sharing intelligence with Britain about cutting-edge Russian military tactics in the Crimea and parts of eastern Ukraine. Since the 2014 Russian military intervention in Ukraine, observers have noted the sophisticated tactics used by Moscow. The Russian forces seem to be combining their advanced conventional arsenal with electronic warfare and information operations. The latter include the use of deception, spreading propaganda through social media, and computer hacking. Some experts have described Russia’s tactics in the Crimean Peninsula and the Donbass region of Ukraine as a form of “
Ukrainian intelligence and defense officials are sharing intelligence with Britain about cutting-edge Russian military tactics in the Crimea and parts of eastern Ukraine. Since the 2014 Russian military intervention in Ukraine, observers have noted the sophisticated tactics used by Moscow. The Russian forces seem to be combining their advanced conventional arsenal with electronic warfare and information operations. The latter include the use of deception, spreading propaganda through social media, and computer hacking. Some experts have described Russia’s tactics in the Crimean Peninsula and the Donbass region of Ukraine as a form of “ An investigation by Republican lawmakers in the United States House of Representatives has reportedly found that military intelligence analysts were pressured into changing reports on the Islamic State by their superiors. The investigation follows
An investigation by Republican lawmakers in the United States House of Representatives has reportedly found that military intelligence analysts were pressured into changing reports on the Islamic State by their superiors. The investigation follows 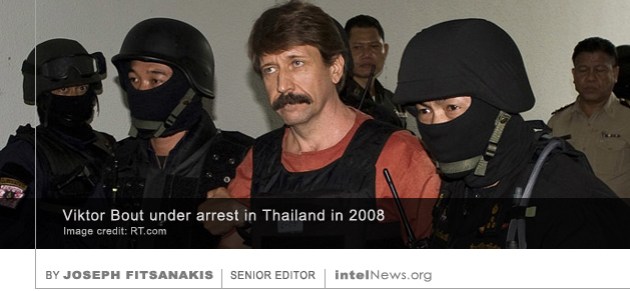 The wife of Viktor Bout, the imprisoned Russian arms dealer dubbed ‘the merchant of death’, said he rejected an offer by his American captors who asked him to testify against a senior Russian government official. Born in Soviet Tajikistan, Bout was a former translator for the Soviet military. After the end of the Cold War, he set up several low-profile international air transport companies and used them to transfer large shipments of weapons that fueled wars in Africa, Asia, Latin America and Europe. He made millions in the process and acquired international notoriety, which inspired the Hollywood blockbuster Lord of War. But his business ventures ceased in 2008, when he was
The wife of Viktor Bout, the imprisoned Russian arms dealer dubbed ‘the merchant of death’, said he rejected an offer by his American captors who asked him to testify against a senior Russian government official. Born in Soviet Tajikistan, Bout was a former translator for the Soviet military. After the end of the Cold War, he set up several low-profile international air transport companies and used them to transfer large shipments of weapons that fueled wars in Africa, Asia, Latin America and Europe. He made millions in the process and acquired international notoriety, which inspired the Hollywood blockbuster Lord of War. But his business ventures ceased in 2008, when he was  The Islamic State has set up a secretive intelligence agency whose task is to set up sleeper cells abroad and has already sent “hundreds of operatives” to Europe and Asia, according to information emerging from interrogations of suspects. According to The New York Times, the information about the intelligence agency comes from “thousands of pages” of intelligence files from American, French, Belgian, Austrian and German agencies. The documents include information from interviews with captured members or defectors from the Islamic State, which is otherwise known as the Islamic State in Iraq and Syria (ISIS).
The Islamic State has set up a secretive intelligence agency whose task is to set up sleeper cells abroad and has already sent “hundreds of operatives” to Europe and Asia, according to information emerging from interrogations of suspects. According to The New York Times, the information about the intelligence agency comes from “thousands of pages” of intelligence files from American, French, Belgian, Austrian and German agencies. The documents include information from interviews with captured members or defectors from the Islamic State, which is otherwise known as the Islamic State in Iraq and Syria (ISIS). Authorities in Iran have admitted that they executed a former scientist for the country’s nuclear program, who claimed that he was abducted by the United States after disappearing from Iran for a year. Shahram Amiri worked for the Atomic Energy Organization of Iran, the government body that is responsible for operating and regulating the country’s nuclear installations. But in the summer of 2009, while on a religious pilgrimage to the Saudi Arabian city of Mecca, Amiri disappeared. Iranian authorities
Authorities in Iran have admitted that they executed a former scientist for the country’s nuclear program, who claimed that he was abducted by the United States after disappearing from Iran for a year. Shahram Amiri worked for the Atomic Energy Organization of Iran, the government body that is responsible for operating and regulating the country’s nuclear installations. But in the summer of 2009, while on a religious pilgrimage to the Saudi Arabian city of Mecca, Amiri disappeared. Iranian authorities  A German court has given life sentences to two senior intelligence officers in Cold-War-era Yugoslavia, who masterminded the murder of a Croat dissident in 1983. Josip Perković and Zdravko Mustać, both former senior officials in the Yugoslav State Security Service, known as UDBA, were
A German court has given life sentences to two senior intelligence officers in Cold-War-era Yugoslavia, who masterminded the murder of a Croat dissident in 1983. Josip Perković and Zdravko Mustać, both former senior officials in the Yugoslav State Security Service, known as UDBA, were  Turkish police have detained nine citizens of Trinidad and Tobago who were on their way to Syria, allegedly to join the Islamic State. They are believed to have traveled from Trinidad and Tobago to Caracas in Venezuela, and from there to Amsterdam, Holland, before flying to Turkey. Turkey’s Daily Sabah newspaper said on Monday that the nine men were
Turkish police have detained nine citizens of Trinidad and Tobago who were on their way to Syria, allegedly to join the Islamic State. They are believed to have traveled from Trinidad and Tobago to Caracas in Venezuela, and from there to Amsterdam, Holland, before flying to Turkey. Turkey’s Daily Sabah newspaper said on Monday that the nine men were  An internet website that offered free URL shortening services appears to have been a front created by British intelligence in order to spread messages and monitor activists involved in protests in Iran and the Arab world. The website was used heavily during the Iranian presidential election protests of 2009, which became known as the Iranian Green Movement. After a brief hiatus, the website was used again in 2011, as the Arab Spring revolts in North Africa and the Middle East were intensifying. The information pointing to the use of the website comes from documents leaked by Edward Snowden, the American former intelligence employee who has been granted political asylum in Russia.
An internet website that offered free URL shortening services appears to have been a front created by British intelligence in order to spread messages and monitor activists involved in protests in Iran and the Arab world. The website was used heavily during the Iranian presidential election protests of 2009, which became known as the Iranian Green Movement. After a brief hiatus, the website was used again in 2011, as the Arab Spring revolts in North Africa and the Middle East were intensifying. The information pointing to the use of the website comes from documents leaked by Edward Snowden, the American former intelligence employee who has been granted political asylum in Russia.






Did domestic snooping by Canadian spy agency increase 26-fold in a year?
August 25, 2016 by Ian Allen 1 Comment
Information about these increases is contained in the latest annual report by the Office of the Commissioner of the Communications Security Establishment. The body was set up in 1996 to review the operations of the Communications Security Establishment (CSE). Founded in 1946, CSE is Canada’s primary signals intelligence agency. It is responsible for interception foreign communications while at the same time securing the communications of the Canadian government. The Office of the Commissioner monitors CSE’s activities and ensures that they conform with Canadian law. It also investigates complaints against the CSE’s conduct of and its officers.
Canadian law forbids the CSE from intercepting communications in which at least one of the parties participating in the exchange is located in Canada. If that happens, the message exchange is termed “private communication” and CSE is not allowed to intercept it, unless it gets written permission from Canada’s National Defense minister. Such permission is usually given only if the interception is deemed essential to protect Canadian national security or national defense. If a “private communication” is inadvertently intercepted, CSE is required to take “satisfactory measures” to protect the personal privacy of the participant in the exchange that is located inside Canada.
According to the CSE commissioner’s report for 2015, which was released in July, but was only recently made available to the media, CSE intercepted 342 “private communications” in 2014-2015. The year before, the spy agency had intercepted just 13 such exchanges. The report states that all 342 instances of interception during 2014-2015 were either unintentional or critical for the protection of Canada’s security. It further states that the reason for the huge increase is to be found in “the technical characteristics of a particular communications technology and of the manner in which private communications are counted”.
Canadian newspaper The Ottawa Citizen asked the CSE commissioner, Jean-Pierre Plouffe, to explain what he meant by “technical characteristics of a particular communications technology” in his report. His office responded that the commissioner could not explain the subject in more detail, because doing so would “reveal CSE operational capabilities” and thus hurt Canada’s national security. The newspaper also contacted CSE, but was given a similar answer. Some telecommunications security experts speculate that the increase in intercepted “private communications” may be due to exchanges in social media, whereby each message is counted separately.
► Author: Ian Allen | Date: 25 August 2016 | Permalink
Filed under Expert news and commentary on intelligence, espionage, spies and spying Tagged with Canada, communications interception, Communications Security Establishment (Canada), domestic intelligence, intelligence oversight, Jean-Pierre Plouffe, News, privacy