Lebanese spy agency used Android app to spy on thousands, say researchers
January 19, 2018 Leave a comment
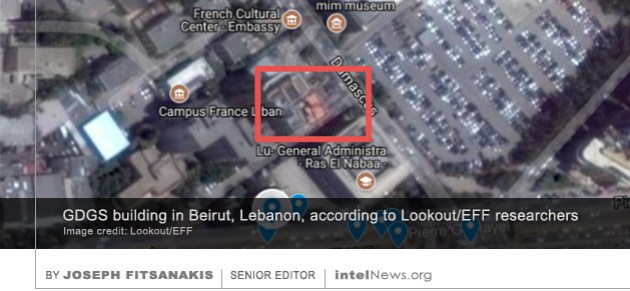 The spy agency of Lebanon used a virus designed for the Android mobile operating system to compromise the cell phones of thousands of people in at least 20 countries, according to a new mobile security report. The 50-page report was published on Thursday by a team of researchers from Lookout, a mobile security company, and the Electronic Frontier Foundation in Washington, DC. In an accompanying press release, the researchers said that the virus, which they named Dark Caracal, has been in existence for at least six years. They added that it was traced to a building in Beirut belonging to the General Directorate of General Security (GDGS), Lebanon’s primary external intelligence agency.
The spy agency of Lebanon used a virus designed for the Android mobile operating system to compromise the cell phones of thousands of people in at least 20 countries, according to a new mobile security report. The 50-page report was published on Thursday by a team of researchers from Lookout, a mobile security company, and the Electronic Frontier Foundation in Washington, DC. In an accompanying press release, the researchers said that the virus, which they named Dark Caracal, has been in existence for at least six years. They added that it was traced to a building in Beirut belonging to the General Directorate of General Security (GDGS), Lebanon’s primary external intelligence agency.
According to the Lookout/EFF research team, the trojanized phone application was camouflaged as a secure messaging service, resembling popular applications like Signal or WhatsApp. However, once an Android user downloaded it, it gave remote users access to the compromised phone’s cameras and microphone, thus turning it into a bugging device. The virus also stole email and text messages, pins and passwords, lists of contacts, call logs, photographs, as well as video and audio recordings stored on the compromised device. The report states that compromised devices were found in over 20 countries, including Lebanon, France, Canada, the United States and Germany. The majority of those targeted by the virus were civilian and military officials of foreign governments, defense contractors, and employees of manufacturing companies, financial institutions and utility providers.
On Thursday, Reuters contacted Major General Abbas Ibrahim, who serves as director general of GDGS. He insisted that the GDGS is known for collecting intelligence using human sources, not cyber technologies. “General Security does not have these type[s] of capabilities. We wish we had these capabilities”, General Ibrahim told the news agency.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 19 January 2018 | Permalink
 The Parliament of Australia is reportedly reviewing the use of cell phones built by a Chinese manufacturer, after an Australian news agency expressed concerns about the manufacturer’s links with the Chinese military. The cell phone in question is the popular Telstra Tough T55 handset. It is made available to Australian parliamentarians though the Information, Communications and Technology (ICT) unit of the Department of Parliamentary Services (DST). Any parliamentarian or worker in Australia’s Parliament House can order the device through the Parliament’s ICT website. According to data provided by the DST, 90 Telstra Tough T55 cell phones have been ordered through the ICT in the current financial year.
The Parliament of Australia is reportedly reviewing the use of cell phones built by a Chinese manufacturer, after an Australian news agency expressed concerns about the manufacturer’s links with the Chinese military. The cell phone in question is the popular Telstra Tough T55 handset. It is made available to Australian parliamentarians though the Information, Communications and Technology (ICT) unit of the Department of Parliamentary Services (DST). Any parliamentarian or worker in Australia’s Parliament House can order the device through the Parliament’s ICT website. According to data provided by the DST, 90 Telstra Tough T55 cell phones have been ordered through the ICT in the current financial year. The Israel Defense Forces told a press conference on Wednesday that hackers belonging to the Palestinian militant group Hamas lured Israeli soldiers by posing as young women online. Wednesday’s press conference was led by an IDF spokesman who requested to remain anonymous, as is often the case with the Israeli military. He told reporters that the hackers used carefully crafted online profiles of real Israeli women, whose personal details and photographs were expropriated from their publicly available social media profiles. The hackers then made contact with members of the IDF and struck conversations with them that in many cases became intimate over time. At various times in the process, the hackers would send the Israeli soldiers photographs of the women, which were copied from the women’s online public profiles.
The Israel Defense Forces told a press conference on Wednesday that hackers belonging to the Palestinian militant group Hamas lured Israeli soldiers by posing as young women online. Wednesday’s press conference was led by an IDF spokesman who requested to remain anonymous, as is often the case with the Israeli military. He told reporters that the hackers used carefully crafted online profiles of real Israeli women, whose personal details and photographs were expropriated from their publicly available social media profiles. The hackers then made contact with members of the IDF and struck conversations with them that in many cases became intimate over time. At various times in the process, the hackers would send the Israeli soldiers photographs of the women, which were copied from the women’s online public profiles. Dozens of cell phones belonging to senior government officials in South Korea were compromised by North Korean hackers who systematically targeted them with texts containing malicious codes, according to reports. The National Intelligence Service (NIS), South Korea’s primary intelligence agency, said the cell phone penetrations were part of a concerted campaign by North Korea to target smart phones belonging to South Korean senior government officials. Once they managed to compromise a cell phone, the hackers were able to access the call history stored on the device, the content of text messages exchanged with other users and, in some cases, the content of telephone calls placed on the compromised device. Moreover, according to the NIS, the hackers were able to access the contact lists stored on compromised cell phones, which means that more attacks may be taking place against cell phones belonging to South Korean government officials.
Dozens of cell phones belonging to senior government officials in South Korea were compromised by North Korean hackers who systematically targeted them with texts containing malicious codes, according to reports. The National Intelligence Service (NIS), South Korea’s primary intelligence agency, said the cell phone penetrations were part of a concerted campaign by North Korea to target smart phones belonging to South Korean senior government officials. Once they managed to compromise a cell phone, the hackers were able to access the call history stored on the device, the content of text messages exchanged with other users and, in some cases, the content of telephone calls placed on the compromised device. Moreover, according to the NIS, the hackers were able to access the contact lists stored on compromised cell phones, which means that more attacks may be taking place against cell phones belonging to South Korean government officials. The head of the main intelligence agency of the island state of Cyprus has resigned after an invoice leaked online showed that the agency made several purchases of controversial surveillance software. Andreas Pentaras, who has led the Cyprus Intelligence Service (KYP) since 2013,
The head of the main intelligence agency of the island state of Cyprus has resigned after an invoice leaked online showed that the agency made several purchases of controversial surveillance software. Andreas Pentaras, who has led the Cyprus Intelligence Service (KYP) since 2013, 














US government publicly admits existence of rogue phone-tapping devices in DC
April 4, 2018 by Joseph Fitsanakis 1 Comment
Many governments have expressed concerns about the use of these devices, which are known to be used by intelligence agencies to monitor cellular communications on foreign soil. Major cities around the world, including Washington, are major targets of cellphone-site simulators, which are frequently located inside foreign embassies. However, the US government has never publicly commented on this issue, despite intense rumors that government agencies headquartered in Washington are major targets of Stingray devices. This changed recently, however, after Senator Ron Wyden (D-OR) wrote a letter to the Department of Homeland Security seeking information about the use of such devices in Washington. Wyden received a written response from Christopher Krebs, who heads the DHS’ National Protection and Programs Directorate. In the letter, dated March 26, Krebs confirmed that the DHS detected a number of active Stingrays in the DC area in 2017, which he referred to as “anomalous activity consistent with Stingrays”. But he added that the DHS lacks both funding and equipment needed to detect the full number of the devices and the full spectrum of Stingrays that are active in the nation’s capital.
The Associated Press, which published Krebs’ letter, said it acquired it from Wyden’s office in the US Senate. The news agency noted that the letter from DHS did not provide the technical specifications of the cellphone-site simulators, and did not enter into speculation about who might be employing them. Additionally the letter did not provide the exact number of Stingrays detected in DC in 2017, nor did it provide the exact locations in DC where Stingray activity was traced. In response to Krebs’ letter, Senator Wyden’s office released a statement blaming the US Federal Communications Commission for having failed to hold the cellular telecommunications industry accountable for the lack of security against Stingrays. “Leaving security to the phone companies has proven to be disastrous”, Senator Wyden’s statement concluded.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 4 April 2018 | Permalink
Filed under Expert news and commentary on intelligence, espionage, spies and spying Tagged with cellular telephony, Christopher Krebs, communications interception, News, Ron Wyden, Stingrays, United States, US Department of Homeland Security, warrantless communications interception, Washington DC, wireless communications interception