Palestinian leader Mahmoud Abbas was KGB agent, researchers claim
September 8, 2016 Leave a comment

Mahmoud Abbas
Two Israeli researchers claim that a document from the archives of the Cold-War-era KGB identifies the current president of the Palestine Authority, Mahmoud Abbas, as a Soviet agent. The document was found in the United Kingdom, and was smuggled out of Russia by a former senior archivist of the Soviet KGB. Abbas is the leader of the largely secular Palestinian group Fatah, which controls the West Bank. Unlike Hamas, which is designated a terrorist group by Israel and its allies, Fatah is seen by Tel Aviv as the legitimate representative of the Palestinian people. That is disputed by Hamas, a religiously inspired group, which controls the Gaza Strip and maintains a tense relationship with Fatah and Abbas himself.
The allegation about Abbas’ past emerged on Wednesday in the Israeli media, after two local academic researchers disclosed the contents of a KGB document discovered at Cambridge University’s Churchill Archives Centre in Britain. The researchers, Gideon Remez and Isabella Ginor, of the Truman Institute at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, said the document dates from 1983. It was found among thousands of similar documents that were secretly smuggled out of Russia in the early 1990s by British intelligence, following the defection of Vasili Mitrokhin, an archivist in the First Chief Directorate of the KGB during the Cold War. Some of the documents later formed the basis of a two-volume edition on the activities of Soviet intelligence, which was edited by Cambridge University Professor Christopher Andrew.
According to Remez and Ginor, the document identifies Mahmoud Abbas as a “KGB agent” based in Damascus, Syria, codenamed krotov, which in Russian means ‘mole’. Abbas was born in Palestine in 1935, but his family fled to Syria in 1948, following the establishment of the state of Israel and the outbreak of the first Arab-Israeli war. The young Abbas grew up in Damascus, where he went to university and joined the local branch of the PLO, the Palestinian Liberation Organization, of which Fatah is a member. If true, the allegation that Abbas worked for the KGB will not come as a surprise to observers of Palestinian politics. For most of the Cold War, the PLO was known to be close to Moscow, while Abbas was intimately involved with the Palestinian-Soviet Friendship Association, a pro-Moscow group that was widely seen as an agent of communist influence in the Palestinian territories. But the document from the Mitrokhin archives may be the first concrete evidence that Abbas was handled by the KGB.
Palestinian officials quickly dismissed the document on Wednesday as a fabrication and a deliberate slander. Mohammed al-Madani, a member of the central committee of Fatah, and a close associate of Abbas, said the allegation was part of a “clear effort to damage [Abbas] by various actors, including the government of Israel”.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 08 August 2016 | Permalink
 A German court has given life sentences to two senior intelligence officers in Cold-War-era Yugoslavia, who masterminded the murder of a Croat dissident in 1983. Josip Perković and Zdravko Mustać, both former senior officials in the Yugoslav State Security Service, known as UDBA, were
A German court has given life sentences to two senior intelligence officers in Cold-War-era Yugoslavia, who masterminded the murder of a Croat dissident in 1983. Josip Perković and Zdravko Mustać, both former senior officials in the Yugoslav State Security Service, known as UDBA, were  In a development that is reminiscent of the Cold War, a radio station in North Korea appears to have resumed broadcasts of encrypted messages that are typically used to give instructions to spies stationed abroad. The station in question is the Voice of Korea, known in past years as Radio Pyongyang. It is operated by the North Korean government and airs daily programming consisting of music, current affairs and instructional propaganda in various languages, including Arabic, Chinese, Spanish, French, English, and Russian. Last week however, the station interrupted its normal programming to air a series of numbers that were clearly intended to be decoded by a few select listeners abroad.
In a development that is reminiscent of the Cold War, a radio station in North Korea appears to have resumed broadcasts of encrypted messages that are typically used to give instructions to spies stationed abroad. The station in question is the Voice of Korea, known in past years as Radio Pyongyang. It is operated by the North Korean government and airs daily programming consisting of music, current affairs and instructional propaganda in various languages, including Arabic, Chinese, Spanish, French, English, and Russian. Last week however, the station interrupted its normal programming to air a series of numbers that were clearly intended to be decoded by a few select listeners abroad. A former officer in the Cold-War-era Yugoslav intelligence service has begun testifying at a trial concerning the 1983 murder in Germany of a Yugoslav dissident by assassins sent by authorities in Belgrade. Stjepan Đureković, who was of Croatian nationality, defected from Yugoslavia to Germany in 1982, while he was director of Yugoslavia’s state-owned INA oil company. Upon his arrival in Germany, he was granted political asylum and began associating with Croatian nationalist émigré groups that were active in the country. He was killed on July 28, 1983, in Wolfratshausen, Bavaria. His killing was part of an operation codenamed DUNAV, which was conducted by the Yugoslav State Security Service, known by its Serbo-Croatian acronym, UDBA.
A former officer in the Cold-War-era Yugoslav intelligence service has begun testifying at a trial concerning the 1983 murder in Germany of a Yugoslav dissident by assassins sent by authorities in Belgrade. Stjepan Đureković, who was of Croatian nationality, defected from Yugoslavia to Germany in 1982, while he was director of Yugoslavia’s state-owned INA oil company. Upon his arrival in Germany, he was granted political asylum and began associating with Croatian nationalist émigré groups that were active in the country. He was killed on July 28, 1983, in Wolfratshausen, Bavaria. His killing was part of an operation codenamed DUNAV, which was conducted by the Yugoslav State Security Service, known by its Serbo-Croatian acronym, UDBA. Recently uncovered documents shed further light on an ultra-secret plan, devised by the British and American governments, to destroy oil facilities in the Middle East in the event the region was invaded by Soviet troops. The
Recently uncovered documents shed further light on an ultra-secret plan, devised by the British and American governments, to destroy oil facilities in the Middle East in the event the region was invaded by Soviet troops. The  Newly declassified files show that Ayatollah Khomeini, who led Iran after the 1979 Islamic Revolution, had a secret channel of communication with the United States, and even sent a personal letter to US President Jimmy Carter. On January 16, 1979, after nearly a year of street clashes and protests against his leadership, the king of Iran, Mohammad Reza Shah Pahlavi, fled the country for the US. His decision to leave was strongly influenced by his American advisors, who feared that Iran was heading toward a catastrophic civil war. The Shah’s departure did little to calm tensions in the country. Protesters —many of them armed— engaged in daily street battles with members of the police and the military, who remained loyal to Pahlavi. Meanwhile, a national strike had brought the Iranian oil sector to a standstill, thereby threatening to bring about a global energy crisis. Moreover, the country was home to thousands of American military advisors and the Iranian military was almost exclusively funded and supplied by Washington. The Carter administration worried that the weaponry and technical knowledge might fall into the hands of a new, pro-Soviet government in Tehran.
Newly declassified files show that Ayatollah Khomeini, who led Iran after the 1979 Islamic Revolution, had a secret channel of communication with the United States, and even sent a personal letter to US President Jimmy Carter. On January 16, 1979, after nearly a year of street clashes and protests against his leadership, the king of Iran, Mohammad Reza Shah Pahlavi, fled the country for the US. His decision to leave was strongly influenced by his American advisors, who feared that Iran was heading toward a catastrophic civil war. The Shah’s departure did little to calm tensions in the country. Protesters —many of them armed— engaged in daily street battles with members of the police and the military, who remained loyal to Pahlavi. Meanwhile, a national strike had brought the Iranian oil sector to a standstill, thereby threatening to bring about a global energy crisis. Moreover, the country was home to thousands of American military advisors and the Iranian military was almost exclusively funded and supplied by Washington. The Carter administration worried that the weaponry and technical knowledge might fall into the hands of a new, pro-Soviet government in Tehran. Nine days later, on January 27, Dr. Yazdi gave Zimmerman a letter written by Khomeini and addressed to President Carter. The letter, which addressed Carter in the first person, was cabled to the Department of State from the US embassy in Paris and, according to the BBC, reached the US president. In the letter, Khomeini promises to protect “America’s interests and citizens in Iran” if Washington pressured the Iranian military to stand aside and allow him and his advisers to return to Iran. Khomeini’s fear was that the royalist Iranian military would not allow a new government to take hold in Tehran. But the exiled cleric was aware of America’s influence in Iranian military circles, which at the time were effectively under the command of General Robert Huyser, Deputy Commander of US Forces in Europe, who had been dispatched to Tehran by President Carter. Before answering Khomeini’s letter, the White House sent a draft response to the embassy in Tehran for input and advice. But Khomeini did not wait for Washington’s response. On February 1, he returned to Iran, where he was greeted by millions of people in the streets and welcomed as the next leader of the country. Meanwhile, Washington had already instructed General Huyser to rule out the so-called “option C”, namely a military coup carried out by the Iranian armed forces.
Nine days later, on January 27, Dr. Yazdi gave Zimmerman a letter written by Khomeini and addressed to President Carter. The letter, which addressed Carter in the first person, was cabled to the Department of State from the US embassy in Paris and, according to the BBC, reached the US president. In the letter, Khomeini promises to protect “America’s interests and citizens in Iran” if Washington pressured the Iranian military to stand aside and allow him and his advisers to return to Iran. Khomeini’s fear was that the royalist Iranian military would not allow a new government to take hold in Tehran. But the exiled cleric was aware of America’s influence in Iranian military circles, which at the time were effectively under the command of General Robert Huyser, Deputy Commander of US Forces in Europe, who had been dispatched to Tehran by President Carter. Before answering Khomeini’s letter, the White House sent a draft response to the embassy in Tehran for input and advice. But Khomeini did not wait for Washington’s response. On February 1, he returned to Iran, where he was greeted by millions of people in the streets and welcomed as the next leader of the country. Meanwhile, Washington had already instructed General Huyser to rule out the so-called “option C”, namely a military coup carried out by the Iranian armed forces. The Supreme Court of Chile will request that the United States extradites three individuals, including an American former professional assassin, who are implicated in the kidnapping, torture and murder of a United Nations diplomat. Carmelo Soria was a Spanish diplomat with dual Chilean nationality, who in the early 1970s was employed in the United Nations Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean. In 1971, when the leftist Popular Unity party won Chile’s elections and became the nation’s governing coalition, Soria became an advisor to the country’s Marxist President, Salvador Allende. After the 1973 violent military coup, which killed Allende and overthrew his government, Soria used his diplomatic status to extend political asylum to a number of pro-Allende activists who were being hunted down by the new rightwing government of General August Pinochet.
The Supreme Court of Chile will request that the United States extradites three individuals, including an American former professional assassin, who are implicated in the kidnapping, torture and murder of a United Nations diplomat. Carmelo Soria was a Spanish diplomat with dual Chilean nationality, who in the early 1970s was employed in the United Nations Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean. In 1971, when the leftist Popular Unity party won Chile’s elections and became the nation’s governing coalition, Soria became an advisor to the country’s Marxist President, Salvador Allende. After the 1973 violent military coup, which killed Allende and overthrew his government, Soria used his diplomatic status to extend political asylum to a number of pro-Allende activists who were being hunted down by the new rightwing government of General August Pinochet. The arrest of Nelson Mandela in 1962, which led to his 28-year incarceration, came after a tip from the United States Central Intelligence Agency, according to an American diplomat who was in South Africa at the time. At the time of his arrest, Mandela was the head of uMkhonto we Sizwe (MK), an organization he founded in 1961 to operate as the armed wing of the anti-apartheid African National Congress (ANC). But the white minority government of South Africa accused Mandela of being a terrorist and an agent of the Soviet Union. The US-Soviet rivalry of that era meant that the ANC and its leader had few supporters in America during the early stages of the Cold War.
The arrest of Nelson Mandela in 1962, which led to his 28-year incarceration, came after a tip from the United States Central Intelligence Agency, according to an American diplomat who was in South Africa at the time. At the time of his arrest, Mandela was the head of uMkhonto we Sizwe (MK), an organization he founded in 1961 to operate as the armed wing of the anti-apartheid African National Congress (ANC). But the white minority government of South Africa accused Mandela of being a terrorist and an agent of the Soviet Union. The US-Soviet rivalry of that era meant that the ANC and its leader had few supporters in America during the early stages of the Cold War. A videotaped lecture by Kim Philby, one of the Cold War’s most recognizable espionage figures, has been unearthed in the archives of the Stasi, the Ministry of State Security of the former East Germany. During the one-hour lecture, filmed in 1981, Philby addresses a select audience of Stasi operations officers and offers them advice on espionage, drawn from his own career. While working as a senior member of British intelligence, Harold Adrian Russell Philby, known as ‘Kim’ to his friends, spied on behalf of the Soviet NKVD and KGB from the early 1930s until 1963, when he secretly defected to the USSR from his home in Beirut, Lebanon. Philby’s defection sent ripples of shock across Western intelligence and is often seen as one of the most dramatic moments of the Cold War.
A videotaped lecture by Kim Philby, one of the Cold War’s most recognizable espionage figures, has been unearthed in the archives of the Stasi, the Ministry of State Security of the former East Germany. During the one-hour lecture, filmed in 1981, Philby addresses a select audience of Stasi operations officers and offers them advice on espionage, drawn from his own career. While working as a senior member of British intelligence, Harold Adrian Russell Philby, known as ‘Kim’ to his friends, spied on behalf of the Soviet NKVD and KGB from the early 1930s until 1963, when he secretly defected to the USSR from his home in Beirut, Lebanon. Philby’s defection sent ripples of shock across Western intelligence and is often seen as one of the most dramatic moments of the Cold War.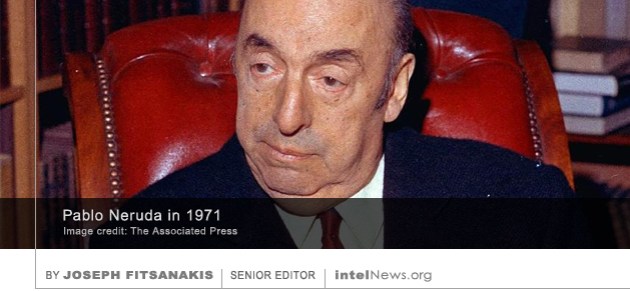 Two teams of international experts will examine the exhumed remains of Chilean Nobel Laureate poet Pablo Neruda, who some say was deliberately injected with poison by the Chilean intelligence services. The literary icon died on September 23, 1973, less than two weeks after a coup d’état, led by General Augusto Pinochet, toppled the democratically elected government of Salvador Allende, a Marxist who was a close friend of Neruda. The death of the internationally acclaimed poet, who was 69 at the time, was officially attributed to prostate cancer and the effects of acute mental stress caused by the military coup. In 2013, however, an
Two teams of international experts will examine the exhumed remains of Chilean Nobel Laureate poet Pablo Neruda, who some say was deliberately injected with poison by the Chilean intelligence services. The literary icon died on September 23, 1973, less than two weeks after a coup d’état, led by General Augusto Pinochet, toppled the democratically elected government of Salvador Allende, a Marxist who was a close friend of Neruda. The death of the internationally acclaimed poet, who was 69 at the time, was officially attributed to prostate cancer and the effects of acute mental stress caused by the military coup. In 2013, however, an  Poland’s first post-communist president, Lech Wałęsa, has denied allegations that he was secretly a communist spy and has called for a public debate so he can respond to his critics. In 1980, when Poland was still under communist rule, Wałęsa was among the founders of Solidarność (Solidarity), the communist bloc’s first independent trade union. After winning the Nobel Peace Prize in 1983, Wałęsa intensified his criticism of Poland’s communist government. In 1990, following the end of communist rule, Wałęsa, was elected Poland’s president by receiving nearly 75% of the vote in a nationwide election. After stepping down from the presidency, in 1995, Wałęsa officially retired from politics and is today considered a major Polish and Eastern European statesman.
Poland’s first post-communist president, Lech Wałęsa, has denied allegations that he was secretly a communist spy and has called for a public debate so he can respond to his critics. In 1980, when Poland was still under communist rule, Wałęsa was among the founders of Solidarność (Solidarity), the communist bloc’s first independent trade union. After winning the Nobel Peace Prize in 1983, Wałęsa intensified his criticism of Poland’s communist government. In 1990, following the end of communist rule, Wałęsa, was elected Poland’s president by receiving nearly 75% of the vote in a nationwide election. After stepping down from the presidency, in 1995, Wałęsa officially retired from politics and is today considered a major Polish and Eastern European statesman. A tightly knit group of Dutch technical experts helped American spies bug foreign embassies at the height of the Cold War, new research has shown. The research, carried out by Dutch intelligence expert Cees Wiebes and journalist Maurits Martijn, has brought to light a previously unknown operation, codenamed EASY CHAIR. Initiated in secret in 1952, the operation was a collaboration between the United States Central Intelligence Agency and a small Dutch technology company called the Nederlands Radar Proefstation (Dutch Radar Research Station).
A tightly knit group of Dutch technical experts helped American spies bug foreign embassies at the height of the Cold War, new research has shown. The research, carried out by Dutch intelligence expert Cees Wiebes and journalist Maurits Martijn, has brought to light a previously unknown operation, codenamed EASY CHAIR. Initiated in secret in 1952, the operation was a collaboration between the United States Central Intelligence Agency and a small Dutch technology company called the Nederlands Radar Proefstation (Dutch Radar Research Station). Marcus Klingberg, who is believed to be the highest-ranking Soviet spy ever caught in Israel, and whose arrest in 1983 prompted one of the largest espionage scandals in the Jewish state’s history, has died in Paris. Born Avraham Marek Klingberg in 1918, Klingberg left his native Poland following the joint German-Soviet invasion of 1939. Fearing persecution by the Germans due to his Jewish background, and being a committed communist, he joined the Soviet Red Army and served in the eastern front until 1941, when he was injured. He then received a degree in epidemiology from the Belarusian State University in Minsk, before returning to Poland at the end of World War II, where he met and married Adjia Eisman, a survivor of the Warsaw Ghetto uprising. Together they moved to Sweden, from where they emigrated to Israeli in 1948. It is believed that Klingberg was recruited by the Soviet KGB while in Sweden, and that he moved to Israel after being asked to do so by his Soviet handlers –though he himself always denied it.
Marcus Klingberg, who is believed to be the highest-ranking Soviet spy ever caught in Israel, and whose arrest in 1983 prompted one of the largest espionage scandals in the Jewish state’s history, has died in Paris. Born Avraham Marek Klingberg in 1918, Klingberg left his native Poland following the joint German-Soviet invasion of 1939. Fearing persecution by the Germans due to his Jewish background, and being a committed communist, he joined the Soviet Red Army and served in the eastern front until 1941, when he was injured. He then received a degree in epidemiology from the Belarusian State University in Minsk, before returning to Poland at the end of World War II, where he met and married Adjia Eisman, a survivor of the Warsaw Ghetto uprising. Together they moved to Sweden, from where they emigrated to Israeli in 1948. It is believed that Klingberg was recruited by the Soviet KGB while in Sweden, and that he moved to Israel after being asked to do so by his Soviet handlers –though he himself always denied it. A report prepared by the Chilean government considers it “highly likely” that Chile’s Nobel laureate poet, Pablo Neruda, died as a result of deliberate poisoning. The literary icon, who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1971, died on September 23, 1973. His death occurred less than two weeks after a coup d’état, led by General Augusto Pinochet, toppled the democratically elected government of Salvador Allende, a Marxist who was a close friend of Neruda.
A report prepared by the Chilean government considers it “highly likely” that Chile’s Nobel laureate poet, Pablo Neruda, died as a result of deliberate poisoning. The literary icon, who was awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1971, died on September 23, 1973. His death occurred less than two weeks after a coup d’état, led by General Augusto Pinochet, toppled the democratically elected government of Salvador Allende, a Marxist who was a close friend of Neruda.






British judge denies request to name alleged new member of Cambridge spy ring
September 20, 2016 by Joseph Fitsanakis 7 Comments
Over the years, more individuals have been suggested by historians as potential members of the group, including intelligence officers Leo Long and Guy Liddell, academics Ludwig Wittgenstein and Andrew Gow, and physicist Wilfrid Mann. But according to British newspaper The Daily Mail, another individual may be identified in a classified document as a possible member of the Cambridge spy ring. The document was allegedly traced by Andrew Lownie, who authored the recently published Stalin’s Englishman: The Lives of Guy Burgess. Lownie filed a Freedom of Information request to have the document, which is held at the National Archives in London, released. But the request was denied, and a judge has now upheld the decision.
In denying the request, the judge argued that the man named in the document is still alive and that a possible release of the document could “jeopardize […] personal relationships”. He also contended that the case is too old to warrant immediate public interest, and thus there was “no pressing need” to declassify the file. The Mail speculates that the individual named in the document could have cooperated with the British government in the past in return for protection, or that the file in question may contain details that could embarrass the British government.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 20 September 2016 | Permalink
Filed under Expert news and commentary on intelligence, espionage, spies and spying Tagged with Andrew Lownie, Cambridge Five, Cold War, declassification, espionage, history, News, UK, UK National Archives