British tip helped French police foil ‘imminent’ terrorist attack
April 19, 2017 2 Comments
 A tip from British intelligence helped French counterterrorist officials arrest two men who are thought to have been in the final stages of planning a large-scale terrorist attack, according to French media. Government sources in Paris say officers from the country’s domestic intelligence agency, DGSE, arrested two men on Monday. Both men are reportedly French citizens from France’s northern regions. They were residing in the southern port city of Marseilles, where they were arrested by the DGSE. They were later named as Merabet Mahiedine, 29, and Clement Baur, 23. It is alleged that Mahiedine has North African roots, but that Baur is a Caucasian convert to Islam. Both were allegedly known to French police for having repeatedly stated views in support of radical Islamist policies.
A tip from British intelligence helped French counterterrorist officials arrest two men who are thought to have been in the final stages of planning a large-scale terrorist attack, according to French media. Government sources in Paris say officers from the country’s domestic intelligence agency, DGSE, arrested two men on Monday. Both men are reportedly French citizens from France’s northern regions. They were residing in the southern port city of Marseilles, where they were arrested by the DGSE. They were later named as Merabet Mahiedine, 29, and Clement Baur, 23. It is alleged that Mahiedine has North African roots, but that Baur is a Caucasian convert to Islam. Both were allegedly known to French police for having repeatedly stated views in support of radical Islamist policies.
According to France’s Minister of the Interior, Matthias Fekl, the two men were planning to carry out a large-scale armed attack in Marseilles this week, which is the last before the long-awaited presidential election in the country. Some sources in the French intelligence community claim that the two men planned to kill one of the major candidates in the election. A number of reports suggest that their target was François Fillon, a conservative presidential candidate who served as Prime Minister from 2007 to 2012 under President Nicolas Sarkozy. It is not known why Fillon may have been targeted, though some observers speculate that radical Islamists seek to promote the aspirations of Fillon’s main rival, the far-right candidate Marine LePen, whom they see as someone whose policies would further-radicalize Muslims in France and North Africa.
Reports in the French media state that DGSE officers confiscated several guns and significant quantities of bomb-making material that were found in an apartment belonging to one of the two men. Meanwhile, an aide to Mr. Fillon told the Paris-based newspaper Le Figaro that the primary tip that led to the arrest of the two men in Marseilles came from British intelligence. The subsequent capture of the two men prevented an attack that would have almost certainly taken place “in the next couple of days”, according to sources in Paris.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 19 April 2017 | Permalink
 France’s primary intelligence agency warned the country’s government this week that Russia has launched a secret operation to try to influence the outcome of the upcoming French presidential election in favor of the far right. According to the Paris-based weekly newspaper Le Canard Enchaîné, France’s Directorate-General for External Security (DGSE) has notified the country’s leadership that a covert operation by the Kremlin is already underway, and is expected to intensify in the run-up to April’s election. The spy agency allegedly believes that Russian efforts aim to promote Marine Le Pen, leader of the ultra-right National Front. Le Pen wants to curb immigration to France and remove the country from the European Union.
France’s primary intelligence agency warned the country’s government this week that Russia has launched a secret operation to try to influence the outcome of the upcoming French presidential election in favor of the far right. According to the Paris-based weekly newspaper Le Canard Enchaîné, France’s Directorate-General for External Security (DGSE) has notified the country’s leadership that a covert operation by the Kremlin is already underway, and is expected to intensify in the run-up to April’s election. The spy agency allegedly believes that Russian efforts aim to promote Marine Le Pen, leader of the ultra-right National Front. Le Pen wants to curb immigration to France and remove the country from the European Union.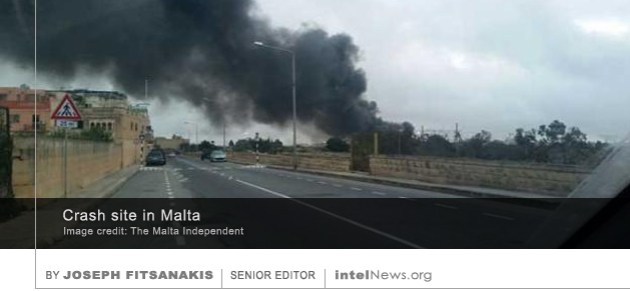 Despite initial denials, it appears that at least three of the five French citizens who were killed in an airplane crash in Malta earlier this week were employees of the country’s external intelligence agency. The crash happened in the early hours of Monday near the village of Luqa in southern Malta. Early reports identified that the plane as a light aircraft and was carrying five French citizens when it crashed, shortly after taking off from the nearby Malta International Airport. Initial statements from Maltese and French government officials said the plane was on a local flight route and had not been scheduled to land outside of the Mediterranean island. The five passengers were identified in press statements as “customs officers” who were conducting a joint project with their Maltese counterparts.
Despite initial denials, it appears that at least three of the five French citizens who were killed in an airplane crash in Malta earlier this week were employees of the country’s external intelligence agency. The crash happened in the early hours of Monday near the village of Luqa in southern Malta. Early reports identified that the plane as a light aircraft and was carrying five French citizens when it crashed, shortly after taking off from the nearby Malta International Airport. Initial statements from Maltese and French government officials said the plane was on a local flight route and had not been scheduled to land outside of the Mediterranean island. The five passengers were identified in press statements as “customs officers” who were conducting a joint project with their Maltese counterparts.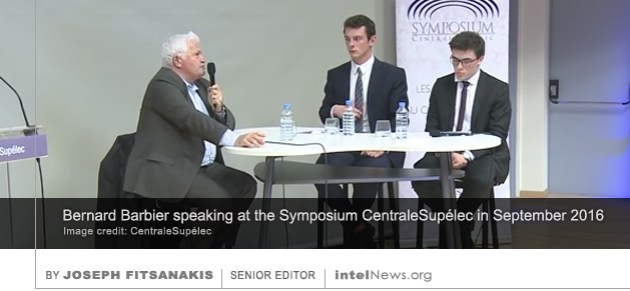 The former director of France’s cyber spy agency has spoken candidly about the recent activities and current state of French cyber espionage, admitting for the first time that France engages in offensive cyber operations. Between 2006 and 2013, Bernard Barbier was director of the technical division of the General Directorate for External Security, France’s external intelligence agency, which is commonly known as DGSE. During his tenure at DGSE, the organization’s technical division witnessed unprecedented financial and administrative growth. Today it is said to employ over 2500 people, nearly half of DGSE’s total personnel.
The former director of France’s cyber spy agency has spoken candidly about the recent activities and current state of French cyber espionage, admitting for the first time that France engages in offensive cyber operations. Between 2006 and 2013, Bernard Barbier was director of the technical division of the General Directorate for External Security, France’s external intelligence agency, which is commonly known as DGSE. During his tenure at DGSE, the organization’s technical division witnessed unprecedented financial and administrative growth. Today it is said to employ over 2500 people, nearly half of DGSE’s total personnel. The death of three French Special Forces soldiers in Libya has prompted the first public acknowledgement by France that its troops are involved in “dangerous intelligence operations” in the North African country. The acknowledgement was made on Wednesday in an official statement issued by Jean-Yves Le Drian, France’s Minister of Defense. In the statement, Le Drian said he “regretted the loss of three French officers who expired while on mission in Libya”. The
The death of three French Special Forces soldiers in Libya has prompted the first public acknowledgement by France that its troops are involved in “dangerous intelligence operations” in the North African country. The acknowledgement was made on Wednesday in an official statement issued by Jean-Yves Le Drian, France’s Minister of Defense. In the statement, Le Drian said he “regretted the loss of three French officers who expired while on mission in Libya”. The 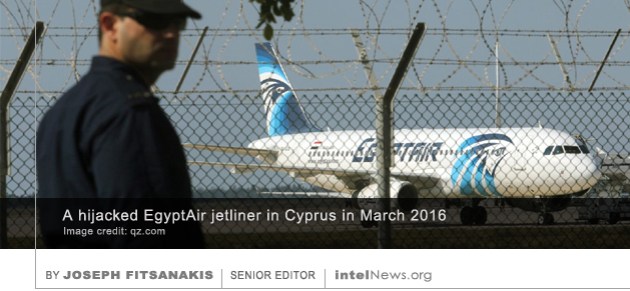 Egypt’s aviation minister has joined the head of Russia’s domestic security service, unnamed US intelligence sources, as well as a host of aviation security experts, in seeing terrorism as the most likely cause behind the EgyptAir MS804 air disaster. That is despite the absence of a clear ‘smoking gun’ and silence from the Islamic State, which leads many to still caution that the possibility of an accident should not be ruled out. The regularly scheduled flight departed Paris, France, late on Wednesday, heading for Cairo, Egypt. But it disappeared from radar screens just minutes after entering Egyptian airspace and is now believed to have crashed into the Mediterranean Sea.
Egypt’s aviation minister has joined the head of Russia’s domestic security service, unnamed US intelligence sources, as well as a host of aviation security experts, in seeing terrorism as the most likely cause behind the EgyptAir MS804 air disaster. That is despite the absence of a clear ‘smoking gun’ and silence from the Islamic State, which leads many to still caution that the possibility of an accident should not be ruled out. The regularly scheduled flight departed Paris, France, late on Wednesday, heading for Cairo, Egypt. But it disappeared from radar screens just minutes after entering Egyptian airspace and is now believed to have crashed into the Mediterranean Sea. In the early hours of Thursday, May 19, EgyptAir, Egypt’s national airline carrier,
In the early hours of Thursday, May 19, EgyptAir, Egypt’s national airline carrier,  efforts. The group has remained silent since early this morning, when EgyptAir announced the disappearance of flight MS804. However, it typically waits for several hours, and sometimes days, before assuming responsibility for high-profile attacks.
efforts. The group has remained silent since early this morning, when EgyptAir announced the disappearance of flight MS804. However, it typically waits for several hours, and sometimes days, before assuming responsibility for high-profile attacks. The United States says a ship carrying hundreds of weapons, which was captured by the French Navy in the Indian Ocean, originated from Iran, and that the cargo was destined for Yemeni rebels through Somalia. The ship was seized on March 20 by a French warship patrolling the Indian Ocean as part of the Combined Maritime Forces (CMF). The CMF is a multinational naval fleet that aims to implement United Nations sanctions on Somalia. The sanctions are designed to frustrate the activities of al-Shabaab, an al-Qaeda-linked Somali militant group, and to put an end to maritime piracy in the Horn of Africa.
The United States says a ship carrying hundreds of weapons, which was captured by the French Navy in the Indian Ocean, originated from Iran, and that the cargo was destined for Yemeni rebels through Somalia. The ship was seized on March 20 by a French warship patrolling the Indian Ocean as part of the Combined Maritime Forces (CMF). The CMF is a multinational naval fleet that aims to implement United Nations sanctions on Somalia. The sanctions are designed to frustrate the activities of al-Shabaab, an al-Qaeda-linked Somali militant group, and to put an end to maritime piracy in the Horn of Africa. French troops have reportedly killed a Spanish citizen who was a senior commander of al-Qaeda in the Islamic Maghreb (AQIM), one of the most prolific al-Qaeda-linked groups in Africa. The Spaniard, Abu al-Nur al-Andalusi, 35, was from Melilla, a coastal Spanish enclave in northern Africa, which borders Morocco. Since 2014, al-Nur had operated as a military leader of AQIM, an armed Islamist group that aims to create a caliphate in northern Africa. AQIM emerged in the 1990s out of the brutal Algerian Civil War, which pitted the country’s secular but authoritarian government against a host of Islamist groups, including the Armed Islamic Group, known as GIA. In 1998 a band of GIA members left the group in protest against its indiscriminate killing of civilians, and formed a separate organization, which called itself Salafist Group for Preaching and Combat. In2007 the group renamed itself AQIM and pledged allegiance to al-Qaeda’s co-founder Osama bin Laden.
French troops have reportedly killed a Spanish citizen who was a senior commander of al-Qaeda in the Islamic Maghreb (AQIM), one of the most prolific al-Qaeda-linked groups in Africa. The Spaniard, Abu al-Nur al-Andalusi, 35, was from Melilla, a coastal Spanish enclave in northern Africa, which borders Morocco. Since 2014, al-Nur had operated as a military leader of AQIM, an armed Islamist group that aims to create a caliphate in northern Africa. AQIM emerged in the 1990s out of the brutal Algerian Civil War, which pitted the country’s secular but authoritarian government against a host of Islamist groups, including the Armed Islamic Group, known as GIA. In 1998 a band of GIA members left the group in protest against its indiscriminate killing of civilians, and formed a separate organization, which called itself Salafist Group for Preaching and Combat. In2007 the group renamed itself AQIM and pledged allegiance to al-Qaeda’s co-founder Osama bin Laden. One of the guns used by Islamist militants to attack locations in downtown Paris on November 13 was purchased legally through a dealer in the United States, according to a report by the Associated Press. Investigators have confirmed that several of the weapons used in the attack, which killed 130 and injured hundreds more, were manufactured in Serbia. Most are slightly modified versions of the Soviet-era AK-47, known in the West as “shortened Kalashnikov”. All were produced in a weapons factory called Zastava, which is located in the city of Kragujevac, in central Serbia. They were made in the 1980s and sold within the former Yugoslavia.
One of the guns used by Islamist militants to attack locations in downtown Paris on November 13 was purchased legally through a dealer in the United States, according to a report by the Associated Press. Investigators have confirmed that several of the weapons used in the attack, which killed 130 and injured hundreds more, were manufactured in Serbia. Most are slightly modified versions of the Soviet-era AK-47, known in the West as “shortened Kalashnikov”. All were produced in a weapons factory called Zastava, which is located in the city of Kragujevac, in central Serbia. They were made in the 1980s and sold within the former Yugoslavia. The man who masterminded November’s Islamist attacks in Paris was based in Athens, and last January managed to escape arrest during a joint Greek-Belgian police operation aimed at capturing him. Moroccan-born Abdelhamid Abaaoud, who had lived in Brussels for years, died in a gun battle with French police on November 18, just days after the multiple attacks in Paris that killed 130 people and injured hundreds. It is believed that the perpetrators of the attacks, who were based in Belgium, were guided and directed by Abaaoud. He, however, was not based in Belgium, but in Athens, Greece. It was from there that he directed the Islamist cells, mostly by phone, according to the BBC.
The man who masterminded November’s Islamist attacks in Paris was based in Athens, and last January managed to escape arrest during a joint Greek-Belgian police operation aimed at capturing him. Moroccan-born Abdelhamid Abaaoud, who had lived in Brussels for years, died in a gun battle with French police on November 18, just days after the multiple attacks in Paris that killed 130 people and injured hundreds. It is believed that the perpetrators of the attacks, who were based in Belgium, were guided and directed by Abaaoud. He, however, was not based in Belgium, but in Athens, Greece. It was from there that he directed the Islamist cells, mostly by phone, according to the BBC. The United States and Russia, which have traditionally been cautious about sharing Middle East-related intelligence with France, have both announced that they will begin giving classified information to Paris. On Wednesday, France’s Defense Minister Jean-Yves Le Drian
The United States and Russia, which have traditionally been cautious about sharing Middle East-related intelligence with France, have both announced that they will begin giving classified information to Paris. On Wednesday, France’s Defense Minister Jean-Yves Le Drian  The recent attacks by Islamic State militants in Paris continue to dominate the world’s headlines. But the double suicide blasts that struck Beirut three days earlier are far more significant for the future of the Syrian Civil War. The outpouring of grief that followed the attacks of November 15 in the French capital prompted
The recent attacks by Islamic State militants in Paris continue to dominate the world’s headlines. But the double suicide blasts that struck Beirut three days earlier are far more significant for the future of the Syrian Civil War. The outpouring of grief that followed the attacks of November 15 in the French capital prompted  there, and even the Mossad, Israel’s feared spy service, rarely ventures in the Hezbollah-controlled neighborhoods.
there, and even the Mossad, Israel’s feared spy service, rarely ventures in the Hezbollah-controlled neighborhoods. Paris is still reeling from Friday’s unprecedented carnage, which left at least 130 people dead and over 350 wounded. The six separate incidents included the first known suicide bombings in the country’s history and marked the deadliest coordinated attacks on French soil since World War II. The magnitude of the attacks prompted the French government to close the country’s borders and declare a nationwide state of emergency —the first since 1961. The shock from the mass killings is today reverberating throughout Europe, a continent that had not seen such a deadly incident since the Madrid train bombings of 2004, when a group of al-Qaeda-inspired militants killed 191 people in the Spanish capital. A response from France and its Western allies is to be expected. However, the West should pause and think very carefully before deepening its engagement in a chaotic and unpredictable war that is like nothing it has ever experienced. Specifically, Western leaders should consider the following:
Paris is still reeling from Friday’s unprecedented carnage, which left at least 130 people dead and over 350 wounded. The six separate incidents included the first known suicide bombings in the country’s history and marked the deadliest coordinated attacks on French soil since World War II. The magnitude of the attacks prompted the French government to close the country’s borders and declare a nationwide state of emergency —the first since 1961. The shock from the mass killings is today reverberating throughout Europe, a continent that had not seen such a deadly incident since the Madrid train bombings of 2004, when a group of al-Qaeda-inspired militants killed 191 people in the Spanish capital. A response from France and its Western allies is to be expected. However, the West should pause and think very carefully before deepening its engagement in a chaotic and unpredictable war that is like nothing it has ever experienced. Specifically, Western leaders should consider the following: a venue where “a party of perversity” was taking place. Europe’s response to this phenomenon is dismissal and indifference. Most Westerners are still at a loss trying to understand the basic differences between Sunni and Shia Islam, let alone the ideological and spiritual underpinnings of groups like the Islamic State, Jabhat al-Nusra, and others. The idea that radical Islam can be defeated before it is understood is naïve and dangerous.
a venue where “a party of perversity” was taking place. Europe’s response to this phenomenon is dismissal and indifference. Most Westerners are still at a loss trying to understand the basic differences between Sunni and Shia Islam, let alone the ideological and spiritual underpinnings of groups like the Islamic State, Jabhat al-Nusra, and others. The idea that radical Islam can be defeated before it is understood is naïve and dangerous.






Same hacker group is targeting French and German elections, says report
April 26, 2017 by Ian Allen Leave a comment
The Trend Micro report focuses on a mysterious group that cyber-security experts have dubbed Pawn Storm —otherwise known as Sednit, Fancy Bear, APT28, Sofacy, and STRONTIUM. It says that the group has launched an aggressive phishing campaign against German political institutions, which has intensified in the past two months. The group allegedly set up fake computer servers in Germany and the Ukraine, and used them to try to infiltrate the computer networks of two elite German think-tanks, the Konrad Adenauer Foundation (KAF) and the Friedrich Ebert Foundation (FEF). The KAF is connected with the Christian Democratic Union party, which is led by Germany’s Chancellor, Angela Merkel. The FEF has strong ties with the centrist Social Democratic Party, which is part of Germany’s governing alliance.
The report’s leading author, cyber-security expert Feike Hacquebord, told the Reuters news agency that the hackers were possibly seeking to infiltrate the two think-tanks as a means of gaining access to the two political parties that are connected with them. Some cyber-security experts in Europe and the United States have said that the Russian Main Intelligence Directorate, the country’s military intelligence agency, known as GRU, is behind the cyber-attacks on France, Germany and the United States. But the Trend Micro report did not attempt to place blame on Moscow or any other country for the cyber-attacks. The Kremlin has denied involvement with the alleged hacking operations.
► Author: Ian Allen | Date: 26 April 2017 | Permalink
Filed under Expert news and commentary on intelligence, espionage, spies and spying Tagged with APT28, computer hacking, cyberespionage, cybersecurity, Fancy Bear, Feike Hacquebord, France, Germany, GRU, News, Russia, Sednit, Sofacy, STRONTIUM, Trend Micro