German spy agency tapped Finnish phone lines in early 2000s
January 20, 2016 1 Comment
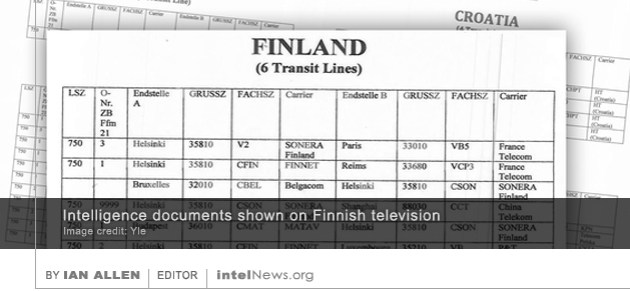 German intelligence, possibly with the collaboration of the United States, monitored communications lines connecting Finland with at least five countries in the early 2000s, according to leaked documents. The documents, aired this week by Yle Uutiset, the main news program of the Finnish Broadcasting Company (Yle), is based on information contained in “leaked German intelligence documents” that were first made public in May 2015. As intelNews reported at the time, the intelligence collection was described as a secret collaboration between Germany’s BND (Bundesnachrichtendienst) and America’s National Security Agency (NSA). According to Austrian politician Peter Pilz, who made the initial allegations, the BND-NSA collaboration was codenamed EIKONAL and was active from 2005 to 2008. Pilz said at the time that many European phone carriers and Internet service providers were targeted by the two agencies. Belgium and Switzerland have already launched investigations into EIKONAL.
German intelligence, possibly with the collaboration of the United States, monitored communications lines connecting Finland with at least five countries in the early 2000s, according to leaked documents. The documents, aired this week by Yle Uutiset, the main news program of the Finnish Broadcasting Company (Yle), is based on information contained in “leaked German intelligence documents” that were first made public in May 2015. As intelNews reported at the time, the intelligence collection was described as a secret collaboration between Germany’s BND (Bundesnachrichtendienst) and America’s National Security Agency (NSA). According to Austrian politician Peter Pilz, who made the initial allegations, the BND-NSA collaboration was codenamed EIKONAL and was active from 2005 to 2008. Pilz said at the time that many European phone carriers and Internet service providers were targeted by the two agencies. Belgium and Switzerland have already launched investigations into EIKONAL.
Now new information provided by Yle seems to show that the secret BND-NSA collaboration targeted Finnish communications as well, focusing on at least six separate communications transit lines. The lines are believed to carry telephone call and possibly Internet traffic from Finnish capital Helsinki to a number of cities in France, Belgium, Hungary, Luxemburg, and China, said Yle Uutiset. Although the targeted lines are known to carry telephone and Internet traffic, it is unknown at this time whether EIKONAL targeted both kinds. But Yle said the interception lasted for most of the first part of the 2000s and involved large amounts of communications data.
The station contacted Tuomas Portaankorva, Inspector General of SUPO, the Finnish Security Intelligence Service. He told Yle that, speaking broadly, he was not surprised to be told that Finnish telecommunications lines had been monitored by foreign intelligence agencies, Western or otherwise. He went on to caution that, even though Finnish lines had been targeted, it was not possible to conclude that Finland was indeed the target of the surveillance operation. Yle also spoke to Vesa Häkkinen, spokesman for the from Finland’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs, who told the station that SUPO, and not the ministry, was the proper official body to be consulted about EIKONAL. “If there is reason to suspect that these actions were directed at the Finnish state”, said Häkkinen, “we would undertake appropriate action”.
► Author: Ian Allen| Date: 20 January 2016 | Permalink | News tip: Matthew Aid
 A court in Portugal has ruled to extradite a former officer of the United States Central Intelligence Agency to Italy, where she faces charges of kidnapping a man as part of a secret operation. Sabrina De Sousa, 59, was an accredited diplomat stationed at the US consulate in Milan, Italy, in 2003, when a CIA team kidnapped Hassan Mustafa Osama Nasr from a Milan street in broad daylight. Nasr, who goes by the nickname Abu Omar, is a former member of Egyptian militant group al-Gama’a al-Islamiyya, and was believed by the CIA to have links to al-Qaeda. Soon after his abduction, Nasr was renditioned to Egypt, where he says he was brutally tortured, raped, and held illegally for years before being released without charge.
A court in Portugal has ruled to extradite a former officer of the United States Central Intelligence Agency to Italy, where she faces charges of kidnapping a man as part of a secret operation. Sabrina De Sousa, 59, was an accredited diplomat stationed at the US consulate in Milan, Italy, in 2003, when a CIA team kidnapped Hassan Mustafa Osama Nasr from a Milan street in broad daylight. Nasr, who goes by the nickname Abu Omar, is a former member of Egyptian militant group al-Gama’a al-Islamiyya, and was believed by the CIA to have links to al-Qaeda. Soon after his abduction, Nasr was renditioned to Egypt, where he says he was brutally tortured, raped, and held illegally for years before being released without charge. Police in Germany caught Anders Breivik with ammunition and weapon parts in 2009, two years before he killed nearly 80 people in Norway, but did not arrest him and failed to notify Norwegian police, according to a new documentary. Breivik is a jailed far-right terrorist, who in 2011 single-handedly perpetrated two terrorist attacks that killed 8 people in Norwegian capital Oslo and another 69 on the island of Utøya. During his trial, he said he killed his victims, most of whom were participants at a Norwegian Labor Party summer camp, in order to protest against “multi-culturalism” and “Islamization” in Norway. The attack, which included the use of a car bomb and semi-automatic weapons, is considered the deadliest terrorist incident in Norway’s history since World War II.
Police in Germany caught Anders Breivik with ammunition and weapon parts in 2009, two years before he killed nearly 80 people in Norway, but did not arrest him and failed to notify Norwegian police, according to a new documentary. Breivik is a jailed far-right terrorist, who in 2011 single-handedly perpetrated two terrorist attacks that killed 8 people in Norwegian capital Oslo and another 69 on the island of Utøya. During his trial, he said he killed his victims, most of whom were participants at a Norwegian Labor Party summer camp, in order to protest against “multi-culturalism” and “Islamization” in Norway. The attack, which included the use of a car bomb and semi-automatic weapons, is considered the deadliest terrorist incident in Norway’s history since World War II. A member of a hacker group that took responsibility for breaking into the personal email account of the director of the Central Intelligence Agency last year has now hacked the email of the most senior intelligence official in the United States. In October 2015, the hacker group referred to by its members as “Crackas With Attitude” —CWA for short—
A member of a hacker group that took responsibility for breaking into the personal email account of the director of the Central Intelligence Agency last year has now hacked the email of the most senior intelligence official in the United States. In October 2015, the hacker group referred to by its members as “Crackas With Attitude” —CWA for short—  Poland’s first post-communist president, Lech Wałęsa, has denied allegations that he was secretly a communist spy and has called for a public debate so he can respond to his critics. In 1980, when Poland was still under communist rule, Wałęsa was among the founders of Solidarność (Solidarity), the communist bloc’s first independent trade union. After winning the Nobel Peace Prize in 1983, Wałęsa intensified his criticism of Poland’s communist government. In 1990, following the end of communist rule, Wałęsa, was elected Poland’s president by receiving nearly 75% of the vote in a nationwide election. After stepping down from the presidency, in 1995, Wałęsa officially retired from politics and is today considered a major Polish and Eastern European statesman.
Poland’s first post-communist president, Lech Wałęsa, has denied allegations that he was secretly a communist spy and has called for a public debate so he can respond to his critics. In 1980, when Poland was still under communist rule, Wałęsa was among the founders of Solidarność (Solidarity), the communist bloc’s first independent trade union. After winning the Nobel Peace Prize in 1983, Wałęsa intensified his criticism of Poland’s communist government. In 1990, following the end of communist rule, Wałęsa, was elected Poland’s president by receiving nearly 75% of the vote in a nationwide election. After stepping down from the presidency, in 1995, Wałęsa officially retired from politics and is today considered a major Polish and Eastern European statesman. Russia’s official envoy to Afghanistan has said that Moscow is now working with the Afghan Taliban in order to stop the growth of the Islamic State in the region. Many Taliban fighters are direct descendants of the Afghan and Pakistani Pashtuns who fought the Soviet Red Army in the 1980s, when the USSR invaded Afghanistan and fought a bloody decade-long war there. But the militant group, which today continues to control much of Afghanistan, despite a prolonged American-led military effort to defeat it, is now being challenged by the Islamic State. Known also as the Islamic State in Iraq and Syria (ISIS), the group enjoys growing popularity in Afghanistan, and some tribal warlords have already declared their allegiance to it. In contrast, the leadership of the Taliban has rejected the legitimacy of ISIS and refused to recognize its leader, Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, as the caliph of all Sunni Muslims. According to Sunni doctrine, a caliph is the recognized political and religious successor to Muhammad, Islam’s prophet, and thus commands the Muslim ummah, or community.
Russia’s official envoy to Afghanistan has said that Moscow is now working with the Afghan Taliban in order to stop the growth of the Islamic State in the region. Many Taliban fighters are direct descendants of the Afghan and Pakistani Pashtuns who fought the Soviet Red Army in the 1980s, when the USSR invaded Afghanistan and fought a bloody decade-long war there. But the militant group, which today continues to control much of Afghanistan, despite a prolonged American-led military effort to defeat it, is now being challenged by the Islamic State. Known also as the Islamic State in Iraq and Syria (ISIS), the group enjoys growing popularity in Afghanistan, and some tribal warlords have already declared their allegiance to it. In contrast, the leadership of the Taliban has rejected the legitimacy of ISIS and refused to recognize its leader, Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, as the caliph of all Sunni Muslims. According to Sunni doctrine, a caliph is the recognized political and religious successor to Muhammad, Islam’s prophet, and thus commands the Muslim ummah, or community. Intelligence agencies outside North Korea, including those of South Korea and the United States, are skeptical of Pyongyang’s claims that it conducted a successful test of a hydrogen bomb. On the surface, North Korea’s
Intelligence agencies outside North Korea, including those of South Korea and the United States, are skeptical of Pyongyang’s claims that it conducted a successful test of a hydrogen bomb. On the surface, North Korea’s  A tightly knit group of Dutch technical experts helped American spies bug foreign embassies at the height of the Cold War, new research has shown. The research, carried out by Dutch intelligence expert Cees Wiebes and journalist Maurits Martijn, has brought to light a previously unknown operation, codenamed EASY CHAIR. Initiated in secret in 1952, the operation was a collaboration between the United States Central Intelligence Agency and a small Dutch technology company called the Nederlands Radar Proefstation (Dutch Radar Research Station).
A tightly knit group of Dutch technical experts helped American spies bug foreign embassies at the height of the Cold War, new research has shown. The research, carried out by Dutch intelligence expert Cees Wiebes and journalist Maurits Martijn, has brought to light a previously unknown operation, codenamed EASY CHAIR. Initiated in secret in 1952, the operation was a collaboration between the United States Central Intelligence Agency and a small Dutch technology company called the Nederlands Radar Proefstation (Dutch Radar Research Station). The director of Russia’s powerful military intelligence agency has died unexpectedly at 58, according to the Kremlin, which has yet to release precise information about the circumstances of his death. General Igor Sergun had led the Main Intelligence Directorate, known as GRU, since 2011, when he replaced his predecessor, Colonel General Aleksandr Shlyakhturov, in a Kremlin-instigated reshuffle. The Russian government
The director of Russia’s powerful military intelligence agency has died unexpectedly at 58, according to the Kremlin, which has yet to release precise information about the circumstances of his death. General Igor Sergun had led the Main Intelligence Directorate, known as GRU, since 2011, when he replaced his predecessor, Colonel General Aleksandr Shlyakhturov, in a Kremlin-instigated reshuffle. The Russian government  American intelligence agencies spied on Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu during the negotiations between the United States and Iran over the Islamic Republic’s nuclear program, according to officials. Tehran entered a deal, referred to as ‘the Geneva pact’, following drawn-out negotiations with a group of nations that came to be known as P5+1, representing the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council plus Germany. The government of Israel, however, strongly criticized the negotiations. Prime Minister Netanyahu called the pact a “historic mistake” that would enable “the most dangerous regime in the world” to get closer to “attaining the most dangerous weapon in the world”. Israel’s strong reaction, which included open criticism of US President Barack Obama, caused some in the US to
American intelligence agencies spied on Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu during the negotiations between the United States and Iran over the Islamic Republic’s nuclear program, according to officials. Tehran entered a deal, referred to as ‘the Geneva pact’, following drawn-out negotiations with a group of nations that came to be known as P5+1, representing the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council plus Germany. The government of Israel, however, strongly criticized the negotiations. Prime Minister Netanyahu called the pact a “historic mistake” that would enable “the most dangerous regime in the world” to get closer to “attaining the most dangerous weapon in the world”. Israel’s strong reaction, which included open criticism of US President Barack Obama, caused some in the US to  A senior Central Intelligence Agency official, who led the agency as its acting director before retiring in 2013, has said that not having sources in the Iraqi government’s upper echelons led to the intelligence failure of 2003. Michael Morell retired as deputy director of the CIA, after having served twice as its acting director, in 2011 and from 2012 to 2013. A Georgetown University graduate, Morell joined the agency in 1980 and rose through the ranks to lead the Asia, Pacific and Latin America divisions. In May 2015, Morell published his book, The Great War of Our Time: The CIA’s Fight against Terrorism from al Qa’ida to ISIS, which he has been promoting while working as a consultant in the private sector.
A senior Central Intelligence Agency official, who led the agency as its acting director before retiring in 2013, has said that not having sources in the Iraqi government’s upper echelons led to the intelligence failure of 2003. Michael Morell retired as deputy director of the CIA, after having served twice as its acting director, in 2011 and from 2012 to 2013. A Georgetown University graduate, Morell joined the agency in 1980 and rose through the ranks to lead the Asia, Pacific and Latin America divisions. In May 2015, Morell published his book, The Great War of Our Time: The CIA’s Fight against Terrorism from al Qa’ida to ISIS, which he has been promoting while working as a consultant in the private sector. Much emphasis has been given to the Islamic State’s Western recruits, but there is almost nothing known about Westerners fighting against the Islamic State in Iraq and Syria. Last week, an investigative website published the first substantial study on the subject, focusing on volunteers who are citizens of the United States. Entitled “The Other Foreign Fighters”, the study focuses on those Americans who have voluntarily traveled to the Middle East to take up arms against the group, which is also known as the Islamic State in Iraq and Syria (ISIS). It was authored by Nathan Patin, an independent researcher who often publishes his work through Bellingcat, a website specializing in open-source investigations.
Much emphasis has been given to the Islamic State’s Western recruits, but there is almost nothing known about Westerners fighting against the Islamic State in Iraq and Syria. Last week, an investigative website published the first substantial study on the subject, focusing on volunteers who are citizens of the United States. Entitled “The Other Foreign Fighters”, the study focuses on those Americans who have voluntarily traveled to the Middle East to take up arms against the group, which is also known as the Islamic State in Iraq and Syria (ISIS). It was authored by Nathan Patin, an independent researcher who often publishes his work through Bellingcat, a website specializing in open-source investigations. The United States Department of Defense has been secretly sharing intelligence with the Syrian government of President Bashar al-Assad without authorization by the White House, according to an American journalist. Officially, the US government is opposed to the Assad regime in Damascus and has repeatedly stated that peace in Syria can only be achieved if the Assad family leaves power. But in a report published yesterday in The London Review of Books, the veteran American investigative journalist Seymour Hersh claims that America’s military leadership has been secretly aiding the Assad family’s efforts to defeat Islamist groups in Syria.
The United States Department of Defense has been secretly sharing intelligence with the Syrian government of President Bashar al-Assad without authorization by the White House, according to an American journalist. Officially, the US government is opposed to the Assad regime in Damascus and has repeatedly stated that peace in Syria can only be achieved if the Assad family leaves power. But in a report published yesterday in The London Review of Books, the veteran American investigative journalist Seymour Hersh claims that America’s military leadership has been secretly aiding the Assad family’s efforts to defeat Islamist groups in Syria. Following a request from the White House, the United States Department of Defense is putting together options to launch offensive cyber operations of an unprecedented scale against the Islamic State. The White House
Following a request from the White House, the United States Department of Defense is putting together options to launch offensive cyber operations of an unprecedented scale against the Islamic State. The White House 






Long-awaited British report to blame Kremlin for ex-KGB spy’s death
January 21, 2016 by Joseph Fitsanakis 2 Comments
A public inquiry into the death of Litvinenko, ordered by the British state, has taken over six months to conclude. In the process, the judge in charge, Sir Robert Owen, has heard from 62 witnesses. The latter include members of the Secret Intelligence Service, known commonly as MI6, for which the late Russian former spy worked after his arrival in Britain. The release of the inquiry’s report is expected this week. But British media have quoted unnamed “government sources” as saying that the long-awaited document will point to the Russian state as the instigator, planner and execution of Litvinenko’s death. One source was quoted as saying that the report will identify “a clear line of command” and that “it will be very clear that the orders came from the Kremlin”.
It is not believed, however, that the report will point to Russian President Vladimir Putin as having had a role in the former spy’s murder. Nevertheless, there is speculation in London and Moscow about the British government’s possible response to the inquiry’s report. One unnamed source told the British press that the report’s findings would place Whitehall “in a difficult position”, given London’s current cooperation with Russia in Syria. However, the government of British Prime Minister David Cameron is expected to face renewed pressure from the public and from opposition parties to take action against Russia, should it be confirmed this week that the Kremlin was indeed behind Litvinenko’s killing.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 21 January 2016 | Permalink
Filed under Expert news and commentary on intelligence, espionage, spies and spying Tagged with Alexander Litvinenko, KGB, News, poisoning, Russia, Sir Robert Owen, suspicious deaths, UK