Alleged third suspect in Skripal poison attack identified by investigative website
February 15, 2019 6 Comments
 An investigative website has linked a graduate of an elite intelligence academy in Moscow with the attempted assassination of a Russian former double spy in Britain last year. Reports last year identified Dr. Alexander Yevgenyevich Mishkin (cover name ‘Alexander Petrov’) and Colonel Anatoliy Chepiga (cover name ‘Ruslan Boshirov’) as the two men that tried to kill Sergei Skripal in the English town of Salisbury in March 2018. Skripal, a former officer in Russia’s military intelligence service, the GRU, was resettled in Salisbury in 2010, after spending several years in a Russian prison for spying on behalf of Britain. But he and his daughter Yulia almost died last March, after they were poisoned with a powerful nerve agent that nearly killed them. The Kremlin denies that Mishkin and Chepiga —believed to be GRU officers— had any role in the attack.
An investigative website has linked a graduate of an elite intelligence academy in Moscow with the attempted assassination of a Russian former double spy in Britain last year. Reports last year identified Dr. Alexander Yevgenyevich Mishkin (cover name ‘Alexander Petrov’) and Colonel Anatoliy Chepiga (cover name ‘Ruslan Boshirov’) as the two men that tried to kill Sergei Skripal in the English town of Salisbury in March 2018. Skripal, a former officer in Russia’s military intelligence service, the GRU, was resettled in Salisbury in 2010, after spending several years in a Russian prison for spying on behalf of Britain. But he and his daughter Yulia almost died last March, after they were poisoned with a powerful nerve agent that nearly killed them. The Kremlin denies that Mishkin and Chepiga —believed to be GRU officers— had any role in the attack.
Last week, the Russian investigative news site Bellingcat alleged that a third man may have been involved in the attempt to assassinate Skripal. The man used the name Sergey Fedotov, said Bellingcat, but added that the name was probably a cover that was concocted by Russia’s intelligence services. On Thursday, the website said it was able to identify the so-called third man as Denis Vyacheslavovich Sergeev, a graduate of the Diplomatic Academy of the Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs. The Diplomatic Academy is one of the most prominent educational institutions in the country and its graduates enter the Foreign Service. However, many of its graduates are elite members of Russian intelligence, said Bellingcat. Earlier this month, the investigative website said that Sergeev traveled extensively in the Middle East, Asia and Europe between 2010 and 2015, using the operational name Sergey Fedotov. It also claimed that Sergeev/Fedotov was in Bulgaria in late April 2015, when Emilian Gebrev, a wealthy local defense industry entrepreneur, fell violently ill. Gebrev was hospitalized for signs of poisoning along with his son and one of his company’s executives for several days. All three made a full recovery.
Bellingcat added that it was able to name the alleged Russian intelligence operative following a four-month investigation that was aided by another Russian news website known as The Russia Insider, Czech newspaper Respekt, and Finland’s Helsingin Sanomat daily. But it also acknowledged that Fedotov’s alleged role in the Skripal assassination remained “unclear” and that authorities in the United Kingdom had not publicly identified a third suspect in the attempted murder. Meanwhile, British newspaper The Guardian said yesterday that it was told by Bulgaria’s Prime Minister Boyko Borisov that a team of British investigators were “on the ground” in Sofia to investigate possible links between the Skripal and Gebrev cases.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 15 February 2019 | Permalink
 New reports from Russian investigative sites claim that a third man using a fake name was involved in the attempted assassination of former double spy Sergei Skripal in England last year. Skripal, a former military intelligence officer, was resettled in the English town of Salisbury in 2010, after spending several years in a Russian prison for spying on behalf of Britain. But he and his daughter Yulia almost died in March 2018, after they were
New reports from Russian investigative sites claim that a third man using a fake name was involved in the attempted assassination of former double spy Sergei Skripal in England last year. Skripal, a former military intelligence officer, was resettled in the English town of Salisbury in 2010, after spending several years in a Russian prison for spying on behalf of Britain. But he and his daughter Yulia almost died in March 2018, after they were  The amount of poison smuggled into Britain for a near-fatal attack on Russian former spy Sergei Skripal was powerful enough to kill “thousands of people”, according those leading the investigation into the incident. Skripal, a former military intelligence officer, was resettled in the English town of Salisbury in 2010, after spending several years in a Russian prison for spying for Britain. But he and his daughter Yulia almost died in March of this year, after being
The amount of poison smuggled into Britain for a near-fatal attack on Russian former spy Sergei Skripal was powerful enough to kill “thousands of people”, according those leading the investigation into the incident. Skripal, a former military intelligence officer, was resettled in the English town of Salisbury in 2010, after spending several years in a Russian prison for spying for Britain. But he and his daughter Yulia almost died in March of this year, after being  Intelligence officials in the United States are feverishly reassessing the physical safety of dozens of Russian defectors, in light of the case of Russian double spy Sergei Skripal, who was poisoned in England last March. Skripal, a former military intelligence officer who spied for Britain, was resettled in the English town of Salisbury in 2010 by the British Secret Intelligence Service (MI6). But he and his daughter Yulia made international headlines in March, after they were
Intelligence officials in the United States are feverishly reassessing the physical safety of dozens of Russian defectors, in light of the case of Russian double spy Sergei Skripal, who was poisoned in England last March. Skripal, a former military intelligence officer who spied for Britain, was resettled in the English town of Salisbury in 2010 by the British Secret Intelligence Service (MI6). But he and his daughter Yulia made international headlines in March, after they were  Sergei Skripal, the Russian double agent who was poisoned with a military-grade nerve agent in England earlier this year, worked with Spanish intelligence after his defection to the United Kingdom, according to sources. Skripal, a former military intelligence officer who spied for Britain in the early 2000s, had kept a low profile while living in the English town of Salisbury. He was resettled there in 2010 by the British Secret Intelligence Service (MI6), after he was released from a Russian prison. But he and his daughter Yulia made international headlines in March, after they were
Sergei Skripal, the Russian double agent who was poisoned with a military-grade nerve agent in England earlier this year, worked with Spanish intelligence after his defection to the United Kingdom, according to sources. Skripal, a former military intelligence officer who spied for Britain in the early 2000s, had kept a low profile while living in the English town of Salisbury. He was resettled there in 2010 by the British Secret Intelligence Service (MI6), after he was released from a Russian prison. But he and his daughter Yulia made international headlines in March, after they were  Some North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) member states obtained access to the Soviet Union’s so-called ‘Novichok’ nerve agents in the 1990s, through an informant recruited by German intelligence, according to reports. NATO countries refer to ‘Novichok-class’ nerve agents to describe a series of weaponized substances that were developed by the Soviet Union and post-Soviet Russia from the early 1970s to at least 1993. They are believed to be the deadliest nerve agents ever produced, but Moscow denies their very existence. A type of Novichok agent, described by British scientists as A234, is said to have been used in March of this year by the person or persons who
Some North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) member states obtained access to the Soviet Union’s so-called ‘Novichok’ nerve agents in the 1990s, through an informant recruited by German intelligence, according to reports. NATO countries refer to ‘Novichok-class’ nerve agents to describe a series of weaponized substances that were developed by the Soviet Union and post-Soviet Russia from the early 1970s to at least 1993. They are believed to be the deadliest nerve agents ever produced, but Moscow denies their very existence. A type of Novichok agent, described by British scientists as A234, is said to have been used in March of this year by the person or persons who  A former officer in the Soviet KGB, who now lives in the United Kingdom, is to be questioned by British police after alleging that there is a link between the recent poisoning of Sergei Skripal and the mysterious death of a British intelligence officer in 2010. There has been extensive media coverage in the past month of the poisoning of Sergei Skripal, a Russian former military intelligence officer who spied for Britain in the early 2000s and has been living in England since 2010. Nearly every European country, as well as Canada, Australia and the United States,
A former officer in the Soviet KGB, who now lives in the United Kingdom, is to be questioned by British police after alleging that there is a link between the recent poisoning of Sergei Skripal and the mysterious death of a British intelligence officer in 2010. There has been extensive media coverage in the past month of the poisoning of Sergei Skripal, a Russian former military intelligence officer who spied for Britain in the early 2000s and has been living in England since 2010. Nearly every European country, as well as Canada, Australia and the United States,  Though unprecedented in size, the recent expulsions of over 150 diplomats by nearly 30 countries and organizations around the world have hardly made a dent on Russia’s huge diplomatic footprint. The
Though unprecedented in size, the recent expulsions of over 150 diplomats by nearly 30 countries and organizations around the world have hardly made a dent on Russia’s huge diplomatic footprint. The  Britain secured the largest expulsion of Russian diplomats in history by sharing “unprecedented degrees of intelligence” with dozens of foreign countries about the attempted killing of former spy Sergei Skripal. Nearly 30 countries and international organizations, including the European Union and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, have expelled or refused to accredit over
Britain secured the largest expulsion of Russian diplomats in history by sharing “unprecedented degrees of intelligence” with dozens of foreign countries about the attempted killing of former spy Sergei Skripal. Nearly 30 countries and international organizations, including the European Union and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, have expelled or refused to accredit over  Relations between Russia and much of the West reached a new low on Monday, with the expulsion of over 100 Russian diplomats from two dozen countries around the world. The unprecedented expulsions were publicized on Monday with a series of coordinated announcements issued from nearly every European capital, as well as from Washington, Ottawa and Canberra. By the early hours of Tuesday, the number of Russian diplomatic expulsions had reached 118 —not counting the 23 Russian so-called “undeclared intelligence officers” that were expelled from Britain last week. Further expulsions of Russian diplomats are expected in the coming days.
Relations between Russia and much of the West reached a new low on Monday, with the expulsion of over 100 Russian diplomats from two dozen countries around the world. The unprecedented expulsions were publicized on Monday with a series of coordinated announcements issued from nearly every European capital, as well as from Washington, Ottawa and Canberra. By the early hours of Tuesday, the number of Russian diplomatic expulsions had reached 118 —not counting the 23 Russian so-called “undeclared intelligence officers” that were expelled from Britain last week. Further expulsions of Russian diplomats are expected in the coming days. predecessor, Barack Obama, and his Secretary of State Hillary Clinton, who is known for her hardline anti-Russian stance. In Europe, the move to expel dozens of Russian envoys from 23 different countries —most of them European Union members— was a rare act of unity that surprised European observers as much as it did the Russians.
predecessor, Barack Obama, and his Secretary of State Hillary Clinton, who is known for her hardline anti-Russian stance. In Europe, the move to expel dozens of Russian envoys from 23 different countries —most of them European Union members— was a rare act of unity that surprised European observers as much as it did the Russians. Sergei Skripal, the Russian double agent who was poisoned with a military-grade nerve agent in England earlier this month, wrote to the Kremlin asking to return to Russia, according to one of his old school friends. Skripal, 66, and his daughter Yulia, 33, remain in critical condition in hospital, three weeks after being
Sergei Skripal, the Russian double agent who was poisoned with a military-grade nerve agent in England earlier this month, wrote to the Kremlin asking to return to Russia, according to one of his old school friends. Skripal, 66, and his daughter Yulia, 33, remain in critical condition in hospital, three weeks after being 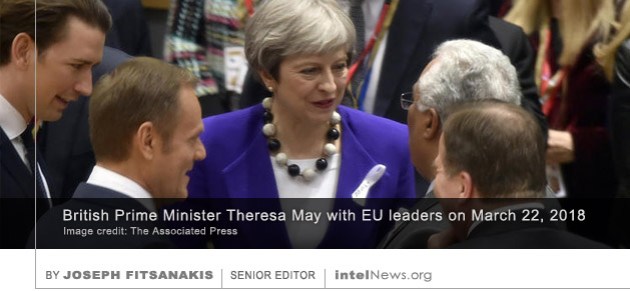 The European Union has recalled its ambassador to Moscow in an apparent response to the poisoning of Sergei Skripal, a Russian double agent, who was attacked with a nerve agent in England earlier this month. Skripal, 66, and his daughter Yulia, 33, remain in critical condition in hospital, nearly three weeks after being poisoned with a nerve agent that British scientists say belongs to Russia’s Cold-War-era chemical stockpiles. Moscow has angrily rejected claims that Skripal, who spied for Britain in the early 2000s, was on a Kremlin-approved hit-list of defectors. But British Prime Minister Theresa May traveled to Brussels on Thursday to brief European Union heads of state about the attack on Skripal.
The European Union has recalled its ambassador to Moscow in an apparent response to the poisoning of Sergei Skripal, a Russian double agent, who was attacked with a nerve agent in England earlier this month. Skripal, 66, and his daughter Yulia, 33, remain in critical condition in hospital, nearly three weeks after being poisoned with a nerve agent that British scientists say belongs to Russia’s Cold-War-era chemical stockpiles. Moscow has angrily rejected claims that Skripal, who spied for Britain in the early 2000s, was on a Kremlin-approved hit-list of defectors. But British Prime Minister Theresa May traveled to Brussels on Thursday to brief European Union heads of state about the attack on Skripal.






Veil of secrecy may soon be lifted on Novichok nerve agent used to attack Skripal
October 24, 2019 by Joseph Fitsanakis 5 Comments
The first public discussion about the existence of these agents took place in the early 1990s, when Vil Mirzayanov, a chemical warfare expert working for the Soviet military, revealed their existence. However, Western intelligence agencies have discouraged public scientific research on these nerve agents, fearing that such activities could reveal their chemical structure and mechanism of action. That could in turn facilitate the proliferation of novichok nerve agents worldwide.
But this attitude shifted drastically after March 2018, when —according to British intelligence— Russian spies used novichok in an attempt to kill Sergei Skripal, a Russian defector to Britain. The British government claims that Russians spies smuggled novichok into Britain by hiding it inside an imitation perfume bottle.
The attempt on Skripal’s life failed, but it prompted the United States, Canada and the Netherlands to propose that two categories of novichoks be chemically identified and added to the CWC list of Schedule 1 chemical weapons. If that were to happen, members of the OPCW —including Russia— would be required to declare and promptly destroy any stockpiles of novichoks in their possession.
Russia’s initial reaction was to oppose the proposal by the United States, Canada and the Netherlands. The Russian OPCW delegation questioned the proposal’s scientific validity and dismissed it as politically motivated. However, according to a report published yesterday in the leading scientific journal Science, Moscow has now agreed with the proposal to list two classes of novichoks in the CWC list, and even proposed adding a third class of the obscure nerve agent to the list. Russia also proposed the inclusion into the CWC list of two families of carbamates —organic compounds with insecticide properties, which the United States is reputed to have included in its chemical weapons arsenal during the Cold War.
According to the Science report, the OPCW Executive Council has already approved Russia’s proposal, which means that the organization is now close to classifying novichoks as Schedule 1 nerve agents. If this happens, academic researchers in the West and elsewhere will be able for the first time to collaborate with defense laboratories in order to research the chemical structure, as well as the mechanism of action, of novichoks. This is likely to produce computer models that will shed unprecedented light on the symptoms of novichoks and the various methods of treating them. But they will also provide information about the chemical structure of the nerve agent, which may eventually lead to proliferation concerns.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 24 October 2019 | Permalink
Filed under Expert news and commentary on intelligence, espionage, spies and spying Tagged with chemical weapons, Chemical Weapons Convention, nerve agents, novichok, Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons, poisoning, Russia, scientific intelligence, Sergei Skripal, UK