How Did Israel Miss This Attack? Some Likely Explanations
October 9, 2023 7 Comments
 THE HAMAS-LED OPERATION al-Aqsa Flood, which began on October 7, marked the first large-scale conflict within the borders of Israel since the 1948 Arab-Israeli War. However, unlike the coalition of Arab armies it faced in 1948, Israel now confronts an alliance of sub-state groups. Led by Hamas’ military wing, the al-Qassam Brigades, this alliance includes the Syrian- and Iranian-backed Palestinian Islamic Jihad and a number of secular groups, such as the Fatah-aligned al-Aqsa Martyrs’ Brigades, the Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine (PFLP) and the Democratic Front for the Liberation of Palestine (DFLP).
THE HAMAS-LED OPERATION al-Aqsa Flood, which began on October 7, marked the first large-scale conflict within the borders of Israel since the 1948 Arab-Israeli War. However, unlike the coalition of Arab armies it faced in 1948, Israel now confronts an alliance of sub-state groups. Led by Hamas’ military wing, the al-Qassam Brigades, this alliance includes the Syrian- and Iranian-backed Palestinian Islamic Jihad and a number of secular groups, such as the Fatah-aligned al-Aqsa Martyrs’ Brigades, the Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine (PFLP) and the Democratic Front for the Liberation of Palestine (DFLP).
Such groups are lesser-known than Hamas; however, they often bring with them expertise in niche areas, such as handling networks of informants inside Israel, building sophisticated explosives, employing unmanned combat drones, or procuring specialized weaponry. They are therefore likely to have contributed greatly to the outcome of Operation al-Aqsa Flood. Their participation also enabled Hamas to launch what essentially amounted to a combined arms assault on Israel. The latter included coordinated land, sea and air elements, which were purposefully low-tech. That may explain why the assailants were able to short-circuit and overwhelm the purportedly impregnable security perimeter that Israel maintains around the Gaza Strip.
Iranian and Lebanese Coaching
Putting aside the individual low-tech elements of the operation, its overall level of tactical organization almost certainly points to considerable support from actors beyond the Gaza Strip. Such actors likely include networks of informants within Israel, as well as possibly Iran and its Lebanese proxy, Hezbollah. Both are well-versed in hybrid warfare and have studied Israeli defense systems more extensively than any other regional actor. Additionally, Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) and Hezbollah’s Lebanese Resistance Brigades are seasoned practitioners of deception operations. They likely coached Hamas, not only on how to carry out Operation al-Aqsa Flood, but more importantly on how to prevent Israel and its allies from gathering intelligence about it.
There is no question that an operation of such a magnitude must have taken months —possibly even years— to conceive, develop and organize. Such a complex process would have taken place under the watchful eyes and ears of Israeli and Egyptian intelligence agencies, who have historically faced little resistance in penetrating Palestinian militant groups, including Hamas. Yet none seem to have collected enough intelligence to anticipate the attack. It is equally stunning that the meticulous planning of Operation al-Aqsa Flood appears to have escaped the attention of American intelligence agencies, whose presence in the Middle East is significant. How was that even possible? Read more of this post
 LAST WEEK, TWO SENIOR UNITED States intelligence officials shared rare insights on artificial intelligence, as they discussed some of the opportunities and threats of this new technological paradigm for their agencies. On Wednesday, Lakshmi Raman, Director of Artificial Intelligence at the Central Intelligence Agency, addressed the topic during an on-stage interview at Politico’s AI & Tech Summit in Washington, DC. On Thursday, the National Security Agency’s outgoing director, Army General Paul Nakasone, discussed the same subject at the National Press Club’s Headliners Luncheon in the US capital.
LAST WEEK, TWO SENIOR UNITED States intelligence officials shared rare insights on artificial intelligence, as they discussed some of the opportunities and threats of this new technological paradigm for their agencies. On Wednesday, Lakshmi Raman, Director of Artificial Intelligence at the Central Intelligence Agency, addressed the topic during an on-stage interview at Politico’s AI & Tech Summit in Washington, DC. On Thursday, the National Security Agency’s outgoing director, Army General Paul Nakasone, discussed the same subject at the National Press Club’s Headliners Luncheon in the US capital. THE GOVERNMENT OF CANADA expelled a senior Indian diplomat on Monday, after accusing “agents of the government of India” of having perpetrated the assassination of a Canadian citizen on Canadian soil last June. Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau released information about the alleged assassination during a rare emergency statement to parliament on Monday morning. He also warned India that Canada would continue to work with its allies around the world, including the United Kingdom, to unearth further intelligence about the alleged assassination.
THE GOVERNMENT OF CANADA expelled a senior Indian diplomat on Monday, after accusing “agents of the government of India” of having perpetrated the assassination of a Canadian citizen on Canadian soil last June. Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau released information about the alleged assassination during a rare emergency statement to parliament on Monday morning. He also warned India that Canada would continue to work with its allies around the world, including the United Kingdom, to unearth further intelligence about the alleged assassination. GERMANY HAS CHARGED TWO men, among them a German intelligence officer, with spying for Russia, in a case that has shocked German public opinion and
GERMANY HAS CHARGED TWO men, among them a German intelligence officer, with spying for Russia, in a case that has shocked German public opinion and  ONE OF GERMANY’S LEADING universities has suspended researchers funded by the Chinese government, citing concerns about academic freedom and industrial espionage. The Friedrich Alexander University of Erlangen-Nuremberg (FAU) announced the suspension of Chinese government-funded researchers in June of this year. In announcing the measure, the university stated that the move was designed to protect academic freedom and freedom of expression among its faculty and staff. Earlier this week, however, German media reported the contents of an internal FAU email, which expressed concerns that the Chinese state could be utilizing government-funded researches as spies.
ONE OF GERMANY’S LEADING universities has suspended researchers funded by the Chinese government, citing concerns about academic freedom and industrial espionage. The Friedrich Alexander University of Erlangen-Nuremberg (FAU) announced the suspension of Chinese government-funded researchers in June of this year. In announcing the measure, the university stated that the move was designed to protect academic freedom and freedom of expression among its faculty and staff. Earlier this week, however, German media reported the contents of an internal FAU email, which expressed concerns that the Chinese state could be utilizing government-funded researches as spies. A DANISH CITIZEN IS suing two Danish spy agencies, claiming that he was wrongly jailed for being a member of the Islamic State, when in fact he had been asked by his handlers to join the group as an undercover informant. The lawsuit has been brought in Copenhagen by Ahmed Samsam, a 34-year-old Danish citizen of Syrian origin. Samsam’s father, Jihad Samsam, fled to Denmark from Syria following the 1982 Hama massacre, when the Syrian military violently quelled an anti-government uprising by members of the Muslim Brotherhood.
A DANISH CITIZEN IS suing two Danish spy agencies, claiming that he was wrongly jailed for being a member of the Islamic State, when in fact he had been asked by his handlers to join the group as an undercover informant. The lawsuit has been brought in Copenhagen by Ahmed Samsam, a 34-year-old Danish citizen of Syrian origin. Samsam’s father, Jihad Samsam, fled to Denmark from Syria following the 1982 Hama massacre, when the Syrian military violently quelled an anti-government uprising by members of the Muslim Brotherhood. FOR THE SECOND TIME in 10 days, the government of China has announced the arrest of a Chinese government employee on suspicion of spying for the United States Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). In a statement issued on Monday, China’s civilian intelligence agency, the Ministry of State Security (MSS), said it had launched an investigation into an official of a government ministry, who was allegedly caught conducting espionage on behalf of the CIA.
FOR THE SECOND TIME in 10 days, the government of China has announced the arrest of a Chinese government employee on suspicion of spying for the United States Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). In a statement issued on Monday, China’s civilian intelligence agency, the Ministry of State Security (MSS), said it had launched an investigation into an official of a government ministry, who was allegedly caught conducting espionage on behalf of the CIA. A SEVENTH PERSON HAS been detained in Taiwan as a result of a broadening investigation into a Chinese spy ring that allegedly provided Beijing with sensitive military intelligence. The existence of the investigation was
A SEVENTH PERSON HAS been detained in Taiwan as a result of a broadening investigation into a Chinese spy ring that allegedly provided Beijing with sensitive military intelligence. The existence of the investigation was 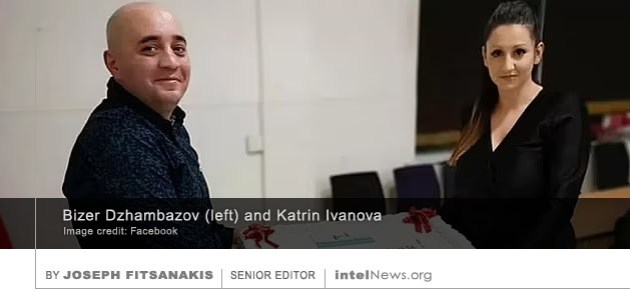 AUTHORITIES IN BRITAIN HAVE charged three Bulgarian nationals with spying for Russia, as part of “a major national security investigation” that led to at least five arrests as early as last February. Two of the Bulgarians appear to be legally married. They have been identified as Bizer Dzhambazov, 41, and Katrin Ivanova, 31, who live in Harrow, a northwestern borrow of Greater London. The third Bulgarian, Orlin Roussev, 45, was arrested in Great Yarmouth, a seaside town in the east coast identity dof England. None of the suspect appears to have a formal diplomatic connection to either Bulgaria or Russia.
AUTHORITIES IN BRITAIN HAVE charged three Bulgarian nationals with spying for Russia, as part of “a major national security investigation” that led to at least five arrests as early as last February. Two of the Bulgarians appear to be legally married. They have been identified as Bizer Dzhambazov, 41, and Katrin Ivanova, 31, who live in Harrow, a northwestern borrow of Greater London. The third Bulgarian, Orlin Roussev, 45, was arrested in Great Yarmouth, a seaside town in the east coast identity dof England. None of the suspect appears to have a formal diplomatic connection to either Bulgaria or Russia. A CHINESE GOVERNMENT EMPLOYEE gave “core information” about China’s military to the United States, after he was recruited by a Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) officer in Italy, a Chinese state agency has said. The allegation was made in a statement that was issued on Friday by China’s civilian intelligence agency, the Ministry of State Security (MSS), on its WeChat social media account.
A CHINESE GOVERNMENT EMPLOYEE gave “core information” about China’s military to the United States, after he was recruited by a Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) officer in Italy, a Chinese state agency has said. The allegation was made in a statement that was issued on Friday by China’s civilian intelligence agency, the Ministry of State Security (MSS), on its WeChat social media account. MEMBERS OF A PROLIFIC hacker group that many associate with Russian intelligence impersonated Microsoft technicians in order to compromise nearly 40 government agencies and companies around the world. Microsoft security researchers
MEMBERS OF A PROLIFIC hacker group that many associate with Russian intelligence impersonated Microsoft technicians in order to compromise nearly 40 government agencies and companies around the world. Microsoft security researchers  THE BRAZILIAN GOVERNMENT IS blocking requests from the United States and Russia to extradite an alleged Russian deep-cover spy, whose forged Brazilian identity papers were discovered by Dutch counterintelligence. Sergey Cherkasov was
THE BRAZILIAN GOVERNMENT IS blocking requests from the United States and Russia to extradite an alleged Russian deep-cover spy, whose forged Brazilian identity papers were discovered by Dutch counterintelligence. Sergey Cherkasov was  AN INVESTIGATIVE REPORT BY the Wall Street Journal discusses a little-known Russian counterintelligence unit that targets foreign diplomats in ways that often “blur the lines between spycraft and harassment”. Among other activities, this secretive unit is likely behind a string of operations targeting American citizens, which have led to the arrest of at least three of them since 2018. These include the Wall Street Journal correspondent Evan Gershkovich, who earlier this year became the first American reporter to be held in Russia on espionage charges since the Cold War.
AN INVESTIGATIVE REPORT BY the Wall Street Journal discusses a little-known Russian counterintelligence unit that targets foreign diplomats in ways that often “blur the lines between spycraft and harassment”. Among other activities, this secretive unit is likely behind a string of operations targeting American citizens, which have led to the arrest of at least three of them since 2018. These include the Wall Street Journal correspondent Evan Gershkovich, who earlier this year became the first American reporter to be held in Russia on espionage charges since the Cold War.






In entering Gaza, the IDF will be facing not just Hamas, but Iran’s ‘Axis of Resistance’
October 23, 2023 1 Comment
The PMF belongs to what Iranian leaders refer to as the ‘Axis of Resistance’ (mehvar–e moqâvemat in Farsi), a term that denotes the extraordinary expansion of Iran’s influence in the Middle East and Central Asia in recent years. In addition to the PMF in Iraq, the Axis of Resistance incorporates an international coalition of dozens of armed groups, militant factions, Shia tribes, and political parties. They range from the Houthis in Yemen and the Hezbollah in Lebanon, to entire branches of the Syrian Armed Forces, and even Shia militias in Afghanistan, Azerbaijan, and Bahrain. The coalition also includes a complex mosaic of armed Palestinian groups, such as Palestinian Islamic Jihad and —increasingly after 2018— Hamas.
These actors are certainly disparate, and often contrast with each other. For instance, relations between Hamas and the Syrians have been strained for years. All of them, however, are united in their common anti-Western stance and contempt for pro-Western states in the Middle East, including Saudi Arabia and Israel. Moreover, their ties under the Axis of Resistance umbrella remain informal and relatively loose. However, they all receive support —including funding and training— from Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guards Corps (IRGC), a branch of the Iranian Armed Forces that protects and promotes the ideological inheritance of the 1979 Islamic Revolution.
branch of the Iranian Armed Forces that protects and promotes the ideological inheritance of the 1979 Islamic Revolution.
Since 2011, the IRGC has viewed the Axis of Resistance as a vital element of its asymmetric military strategy. Its purpose is to help Iran successfully confront its much stronger adversaries, two of which —the United States and Israel— are nuclear-armed. That is precisely why Tehran has invested nothing short of a fortune to transform Hezbollah into what experts describe as “a force multiplier” that can give Israel a run for its money. In 2014, Tehran launched a similar effort in the Gaza Strip, initially with Palestinian Islamic Jihad —a group that, very much like Hamas, emerged out of the Egyptian Islamic Brotherhood in the 1980s.
The financial arrangement between Palestinian Islamic Jihad and Iran alarmed Hamas, which has controlled Gaza since 2008. Over time, however, Hamas too began to flirt with Iran’s Axis of Resistance, enticed by the lucrative funding and training opportunities offered by Tehran. By 2020, Hamas was actively engaging with the IRGC under the Axis of Resistance umbrella. To a significant extent, the operational sophistication of the October 7 attack on Israel, which was jointly led by Hamas and Palestinian Islamic Jihad, provided clear evidence of Iran’s patronage of these two militant groups. Because of Iran, the Palestinian armed factions in Gaza are today better-armed and better-trained than at any time in the past. They will likely demonstrate that in the coming days or weeks, as the Israel Defense Forces (IDF) begin their ground offensive on Gaza.
The big question, however, is how the other components of the Axis of Resistance will respond to the impending IDF attack. Read more of this post
Filed under Expert news and commentary on intelligence, espionage, spies and spying Tagged with 2023 Israel-Hamas War, Analysis, Hamas, Iran, Israel, Joseph Fitsanakis, Newstex, Palestine