Analysis: Yemen conflict shows small-drone warfare ‘is here to stay’, say experts
May 30, 2019 Leave a comment
 The current wars in the Middle East, especially the ongoing conflict in Yemen, are proof that the use of small drones in insurgencies is now a permanent phenomenon of irregular warfare, according to experts. Drones have been used in warfare in the Middle East for almost 20 years —including by outside powers like the United States. But National Public Radio’s Geoff Brumfiel reports that the wars in Iraq and Syria, and especially the war between the Yemeni government and Houthi rebels, clearly demonstrate that we have entered “a new era of drone warfare”.
The current wars in the Middle East, especially the ongoing conflict in Yemen, are proof that the use of small drones in insurgencies is now a permanent phenomenon of irregular warfare, according to experts. Drones have been used in warfare in the Middle East for almost 20 years —including by outside powers like the United States. But National Public Radio’s Geoff Brumfiel reports that the wars in Iraq and Syria, and especially the war between the Yemeni government and Houthi rebels, clearly demonstrate that we have entered “a new era of drone warfare”.
The use of off-the-shelf small drones has been increasing since 2010, with the Syrian Civil War having served as a testing ground for military uses of drones by all sides involved in the conflict. Belligerents quickly realized that the use of drones —whether remotely operated from the ground, or guided by GPS coordinates— could provide useful air power “for a fraction of the cost of fighter jets” employed by national militaries, according to Brumfiel. He quotes numerous drone warfare expects who agree that the ongoing Yemeni Civil War provides the clearest sign yet of the proliferation of drones for military and paramilitary purposes. The Houthi rebels have employed drones to attack government targets and targets such as air fields, oil installations and military bases in neighboring Saudi Arabia. Most of these drones, and the knowledge of how to modify them for military use, are given to the Houthis by Iran, according to RAND Corporation expert Ariane Tabatabai, who is quoted in Brumfiel’s article.
Iran has been developing military drone technology since the 1980s, but did not begin to employ drones outside of its airspace until 2015. The change was prompted by the emergence of the Islamic State emerged as a major Sunni threat to Shiite populations in the region. Iranian drones are now everywhere, from Iraq and Syria to Yemen. These drones, including drones used by the Houthis, are major sources of concern for conventional armies, because they are difficult to detect and destroy, according to Center for a New American Security researcher Nicholas Heras. He told Brumfiel that small drones are difficult to locate by radar, and their flight paths are far more flexible than those of airplanes. Additionally, those drones controllers can use GPS systems to “navigate through holes” in air defenses, said Heras.
► Author: Ian Allen | Date: 30 May 2019 | Permalink
 Groups of Venezuelan expatriates are reportedly forming armed militias in Colombia and say they are preparing to launch cross-border attacks to topple the government of President Nicolás Maduro in Caracas. It is
Groups of Venezuelan expatriates are reportedly forming armed militias in Colombia and say they are preparing to launch cross-border attacks to topple the government of President Nicolás Maduro in Caracas. It is 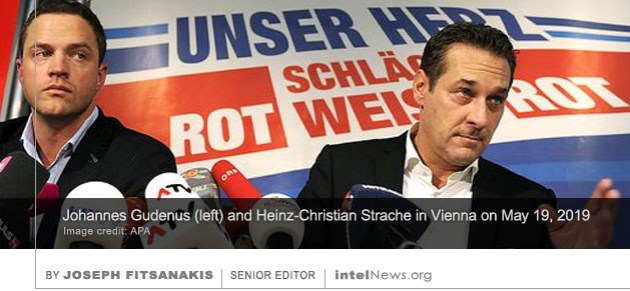 Israeli intelligence was likely behind the leaked video that brought down the far-right governing coalition in Austria on Monday, according to the former deputy director of Germany’s spy agency. The surreptitiously recorded video was
Israeli intelligence was likely behind the leaked video that brought down the far-right governing coalition in Austria on Monday, according to the former deputy director of Germany’s spy agency. The surreptitiously recorded video was  Jonathan Pollard, an American who spied on his country for Israel in the 1980s, and is now free after spending 30 years in prison, has spoken of his frustration with the Israeli government, which it claims has forgotten about him. Pollard, a former intelligence analyst for the United States Navy, was released from an American prison in 2015, after serving a lengthy sentence for selling US government secrets to Israel. Throughout Pollard’s time in prison, the government of Israel
Jonathan Pollard, an American who spied on his country for Israel in the 1980s, and is now free after spending 30 years in prison, has spoken of his frustration with the Israeli government, which it claims has forgotten about him. Pollard, a former intelligence analyst for the United States Navy, was released from an American prison in 2015, after serving a lengthy sentence for selling US government secrets to Israel. Throughout Pollard’s time in prison, the government of Israel  France’s domestic intelligence agency has summoned eight journalists for questioning in relation to two separate investigative reports, prompting concerns about press freedom, according to reports from Paris. Last month, France’s domestic security and counter- intelligence agency, the General Directorate for Internal Security (DGSI), summoned three journalists for questioning. The summonses related to a
France’s domestic intelligence agency has summoned eight journalists for questioning in relation to two separate investigative reports, prompting concerns about press freedom, according to reports from Paris. Last month, France’s domestic security and counter- intelligence agency, the General Directorate for Internal Security (DGSI), summoned three journalists for questioning. The summonses related to a  The West Africa province of the Islamic State has claimed responsibility for the killing 20 Nigerian soldiers and the execution of nine more soldiers that were captured in various operations, according to Reuters. The group behind the attacks emerged in 2002 under the name Boko Haram (“Western education is forbidden”), as part of a growing wave of anti-government sentiment in Nigeria’s Muslim-majority northern regions. In 2014, the group pledged allegiance to Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, leader of the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria —otherwise known as Islamic State. Since that time, Boko Haram has rebranded itself as Islamic State – West Africa Province, while a smaller faction of the group has refused to align itself with the ISIS and continues to operate under the name Boko Haram.
The West Africa province of the Islamic State has claimed responsibility for the killing 20 Nigerian soldiers and the execution of nine more soldiers that were captured in various operations, according to Reuters. The group behind the attacks emerged in 2002 under the name Boko Haram (“Western education is forbidden”), as part of a growing wave of anti-government sentiment in Nigeria’s Muslim-majority northern regions. In 2014, the group pledged allegiance to Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, leader of the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria —otherwise known as Islamic State. Since that time, Boko Haram has rebranded itself as Islamic State – West Africa Province, while a smaller faction of the group has refused to align itself with the ISIS and continues to operate under the name Boko Haram.
 A new star that was recently added to the United States Central Intelligence Agency’s memorial wall is seen by some as a way to draw attention to the mental pressures that come with the job, while others view it as disrespectful to the Agency’s mission. The specially designated wall is located at the main entrance lobby of the CIA’s headquarters in Langley, Virginia. It was created in 1974 and displays a star for each of the CIA’s personnel who have perished in the line of duty while working for the Agency. Today it displays nearly 130 stars, which span the CIA’s 72-year history.
A new star that was recently added to the United States Central Intelligence Agency’s memorial wall is seen by some as a way to draw attention to the mental pressures that come with the job, while others view it as disrespectful to the Agency’s mission. The specially designated wall is located at the main entrance lobby of the CIA’s headquarters in Langley, Virginia. It was created in 1974 and displays a star for each of the CIA’s personnel who have perished in the line of duty while working for the Agency. Today it displays nearly 130 stars, which span the CIA’s 72-year history. A day after Austria’s political system was thrown into a disarray by a covert video featuring the country’s vice chancellor and a woman posing as a Russian investor, German intelligence sources have raised fears that Russia may have penetrated the Austrian government with informants. Heinz-Christian Strache, who heads Austria’s far-right Freedom Party, stepped down from the post of vice chancellor on Saturday. His resignation came a day after two German media outlets aired a
A day after Austria’s political system was thrown into a disarray by a covert video featuring the country’s vice chancellor and a woman posing as a Russian investor, German intelligence sources have raised fears that Russia may have penetrated the Austrian government with informants. Heinz-Christian Strache, who heads Austria’s far-right Freedom Party, stepped down from the post of vice chancellor on Saturday. His resignation came a day after two German media outlets aired a  The escalating tension between the United States and Iran, and the ensuing military buildup in the Persian Gulf, may have resulted from a misreading of intelligence by both sides, according to a new report in The Wall Street Journal. Reports from the Middle East continue to describe the situation there as tense, while the political rhetoric by both Washington and Tehran remains heightened. Last week, the White House ordered the USS Abraham Lincoln carrier strike group to sail to Middle Eastern waters, following intelligence
The escalating tension between the United States and Iran, and the ensuing military buildup in the Persian Gulf, may have resulted from a misreading of intelligence by both sides, according to a new report in The Wall Street Journal. Reports from the Middle East continue to describe the situation there as tense, while the political rhetoric by both Washington and Tehran remains heightened. Last week, the White House ordered the USS Abraham Lincoln carrier strike group to sail to Middle Eastern waters, following intelligence  The group calling itself the Islamic State has announced the establishment of a new overseas province in Pakistan, just days after proclaiming another new overseas province in northern India. Until recently, the Islamic State’s operations in Asia were conducted under the banner of the Islamic State – Khorasan Province, or IS-KP. The shadowy group was founded in early 2015 and was led by former Taliban warlords who pledged allegiance to Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, the spiritual leader and self-proclaimed emir of the Islamic State. Since that time, at least two of IS-KP’s leaders have been killed by United States forces, while the group has been engaged in a war against rival militant groups in Afghanistan and Pakistan, notably the Taliban.
The group calling itself the Islamic State has announced the establishment of a new overseas province in Pakistan, just days after proclaiming another new overseas province in northern India. Until recently, the Islamic State’s operations in Asia were conducted under the banner of the Islamic State – Khorasan Province, or IS-KP. The shadowy group was founded in early 2015 and was led by former Taliban warlords who pledged allegiance to Abu Bakr al-Baghdadi, the spiritual leader and self-proclaimed emir of the Islamic State. Since that time, at least two of IS-KP’s leaders have been killed by United States forces, while the group has been engaged in a war against rival militant groups in Afghanistan and Pakistan, notably the Taliban. The most senior British military officer in the war against the Islamic State contradicted American assessments of a heightened threat from Iran, prompting an unusually strong rebuke from Washington. Last week, the White House ordered the USS Abraham Lincoln carrier strike group to sail to Middle Eastern waters, following intelligence
The most senior British military officer in the war against the Islamic State contradicted American assessments of a heightened threat from Iran, prompting an unusually strong rebuke from Washington. Last week, the White House ordered the USS Abraham Lincoln carrier strike group to sail to Middle Eastern waters, following intelligence 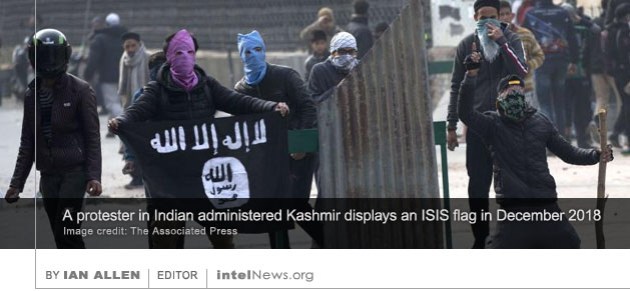 The group calling itself the Islamic State has announced the establishment of a new overseas province in India’s Jammu and Kashmir state. The announcement was made over the weekend by Amaq, which serves as the news agency of the Islamic State. According to the news release, the Islamic State (known also as the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria) has named the new province “wilayah al-Hind” (province of Hind), and said it is based in the Muslim-majority Kashmir Valley, which is located in one of the three administrative divisions of the Indian administered state of Jammu and Kashmir.
The group calling itself the Islamic State has announced the establishment of a new overseas province in India’s Jammu and Kashmir state. The announcement was made over the weekend by Amaq, which serves as the news agency of the Islamic State. According to the news release, the Islamic State (known also as the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria) has named the new province “wilayah al-Hind” (province of Hind), and said it is based in the Muslim-majority Kashmir Valley, which is located in one of the three administrative divisions of the Indian administered state of Jammu and Kashmir. Authorities in the United Arab Emirates said on Sunday that four commercial ships were targeted by “sabotage operations”, but did not point to possible culprits. The announcement came hours after false reports circulated in Iranian and Lebanese media stating that explosions had been witnessed at the port of Fujairah, a major Emirati commercial shipping facility that borders the Sultanate of Oman and is visible from the coast of Iran. The alleged explosions were first
Authorities in the United Arab Emirates said on Sunday that four commercial ships were targeted by “sabotage operations”, but did not point to possible culprits. The announcement came hours after false reports circulated in Iranian and Lebanese media stating that explosions had been witnessed at the port of Fujairah, a major Emirati commercial shipping facility that borders the Sultanate of Oman and is visible from the coast of Iran. The alleged explosions were first 






Pakistan sentences two, including senior military officer, to death for espionage
May 31, 2019 by Joseph Fitsanakis Leave a comment
The three men were identified as Lieutenant General Javed Iqbal, Brigadier (ret.) Raja Rizwan, and Dr. Wasim Akram, who was reportedly “employed at [an unidentified] sensitive organization”. Iqbal and Akram were sentenced to death, while Rizwan was sentenced to 14 years of “vigorous imprisonment”, according to ISPR. Reports in local media said that General Qamar Javed Bajwa, the Pakistani Army’s Chief of Staff, had approved the sentences handed to the men by the military judges. This means that the sentences will be carried out unless Pakistan’s President, Arif Alvi, pardons them. Interestingly, the ISPR statement noted that the three men were tried in separate military courts for separate cases. No further information was provided. As intelNews reported in February, Pakistani media claimed at the time that those arrested included a Pakistani official with diplomatic credentials who was serving in a Pakistani embassy “in a European capital”.
No information has emerged about the country or countries to which the alleged spies gave sensitive information. Back in February, Pakistan’s leading conservative daily, The News International, claimed that the spies’ handlers belonged to an intelligence agency of one of “the world’s most powerful countries”. The paper also hinted that the alleged spy network may have been working for the United States Central Intelligence Agency, but provided no information to support this claim. It added that the network had been “completely dismantled” following a counterintelligence operation that an unnamed source described to the paper as “remarkable”.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 31 May | Permalink
Filed under Expert news and commentary on intelligence, espionage, spies and spying Tagged with counterintelligence, espionage, Inter-Services Public Relations (Pakistan), Javed Iqbal, News, Pakistan, Raja Rizwan, Wasim Akram