Cease-fire near collapse after US airstrike kills 62 and injures 100 Syrian troops
September 19, 2016 Leave a comment
 A cease-fire that was launched with much fanfare by the United States and Russia last week appeared in tatters on Sunday night, after Washington acknowledged it mistakenly killed over 60 Syrian troops on Saturday. American officials expressed regret for the alleged error, but Syrian and Russian officials accused Washington of deliberately sabotaging the cease-fire agreement. Russian sources said the US air strike killed 62 and injured over 100 Syrian government troops who were engaged in a battle against Islamic State forces in Syria’s eastern province of Deir al-Zour. American military officials insisted that the pilots, who flew into Syria from bases in Iraq, believed they were targeting Islamic State forces. The operation was allegedly aborted as soon as US forces were notified by the Russian military that Syrian government troops were being targeted.
A cease-fire that was launched with much fanfare by the United States and Russia last week appeared in tatters on Sunday night, after Washington acknowledged it mistakenly killed over 60 Syrian troops on Saturday. American officials expressed regret for the alleged error, but Syrian and Russian officials accused Washington of deliberately sabotaging the cease-fire agreement. Russian sources said the US air strike killed 62 and injured over 100 Syrian government troops who were engaged in a battle against Islamic State forces in Syria’s eastern province of Deir al-Zour. American military officials insisted that the pilots, who flew into Syria from bases in Iraq, believed they were targeting Islamic State forces. The operation was allegedly aborted as soon as US forces were notified by the Russian military that Syrian government troops were being targeted.
According to media reports, the US government has apologized to Damascus though Russian intermediaries for the “unintentional loss of life of Syrian forces”. But the incident has incensed Moscow, as it marks the first known engagement between US and Syrian forces since American military forces began fighting the Islamic State in 2014. The incident was described by The Washington Post late on Saturday as having sparked “one of the most hostile diplomatic exchanges between Washington and Moscow in recent years”. Soon after the US airstrike, Russia called an emergency meeting of the United Nations Security Council, during which the Russian delegation accused the United States of deliberately trying to derail the cease-fire. According to reports, the American delegation stormed out of the closed-door meeting and denounced it as a “stunt” after the Russians openly accused Washington of aiding the Islamic State and al-Qaeda in Syria.
American officials have launched an investigation into Saturday’s incident and are so far refusing to speculate whether it was caused by human error or an intelligence failure. In Washington, a State Department spokesman insisted that “coalition forces would not intentionally strike a known a Syrian military unit”. But in a statement issued on Saturday, Russian Major General Igor Konashenkov said that, if the US air strike was in error, it was a “direct outcome of the US side’s stubborn unwillingness to coordinate its activities in Syria with Russia”.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 19 September 2016 | Permalink
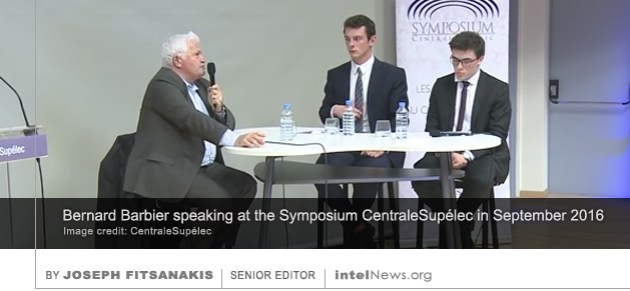 The former director of France’s cyber spy agency has spoken candidly about the recent activities and current state of French cyber espionage, admitting for the first time that France engages in offensive cyber operations. Between 2006 and 2013, Bernard Barbier was director of the technical division of the General Directorate for External Security, France’s external intelligence agency, which is commonly known as DGSE. During his tenure at DGSE, the organization’s technical division witnessed unprecedented financial and administrative growth. Today it is said to employ over 2500 people, nearly half of DGSE’s total personnel.
The former director of France’s cyber spy agency has spoken candidly about the recent activities and current state of French cyber espionage, admitting for the first time that France engages in offensive cyber operations. Between 2006 and 2013, Bernard Barbier was director of the technical division of the General Directorate for External Security, France’s external intelligence agency, which is commonly known as DGSE. During his tenure at DGSE, the organization’s technical division witnessed unprecedented financial and administrative growth. Today it is said to employ over 2500 people, nearly half of DGSE’s total personnel. American intelligence agencies are diverting counterterrorist resources to Russian accounts, prompting some commentators to describe the move as the greatest expansion of spy operations against Russia since the Cold War. In a leading
American intelligence agencies are diverting counterterrorist resources to Russian accounts, prompting some commentators to describe the move as the greatest expansion of spy operations against Russia since the Cold War. In a leading  The recently discovered memoirs of a former director of the Soviet KGB suggest that a senior Swedish diplomat, who disappeared mysteriously in the closing stages of World War II, was killed on the orders of Joseph Stalin. The fate of Swedish diplomat Raoul Wallenberg is one of the 20th century’s unsolved espionage mysteries. In 1944 and 1945, the 33-year-old Wallenberg was Sweden’s ambassador to Budapest, the capital of German-allied Hungary. During his time there, Wallenberg is said to have saved over 20,000 Hungarian Jews from the Nazi concentration camps, by supplying them with Swedish travel documents, or smuggling them out of the country through a network of safe houses. He also reportedly dissuaded German military commanders from launching an all-out armed attack on Budapest’s Jewish ghetto.
The recently discovered memoirs of a former director of the Soviet KGB suggest that a senior Swedish diplomat, who disappeared mysteriously in the closing stages of World War II, was killed on the orders of Joseph Stalin. The fate of Swedish diplomat Raoul Wallenberg is one of the 20th century’s unsolved espionage mysteries. In 1944 and 1945, the 33-year-old Wallenberg was Sweden’s ambassador to Budapest, the capital of German-allied Hungary. During his time there, Wallenberg is said to have saved over 20,000 Hungarian Jews from the Nazi concentration camps, by supplying them with Swedish travel documents, or smuggling them out of the country through a network of safe houses. He also reportedly dissuaded German military commanders from launching an all-out armed attack on Budapest’s Jewish ghetto. The transfer of foreign fighters into Iraq and Syria to join the Islamic State and other Sunni militant groups has been all but eliminated in countries across the world, according to intelligence assessments. In previous years, it has been estimated that nearly as many as 2,000 foreign recruits, both men and women, crossed into Syria each month, mainly from Turkey, with the intention of joining armed Sunni groups. By the end of 2015, it was believed that over 30,000 foreign nationals from close to 90 countries had entered Syria and Iraq to fight for one of the Sunni-inspired opposition groups taking part in the Syrian civil war. Most of these foreign recruits joined the Islamic State, which is also known as the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS).
The transfer of foreign fighters into Iraq and Syria to join the Islamic State and other Sunni militant groups has been all but eliminated in countries across the world, according to intelligence assessments. In previous years, it has been estimated that nearly as many as 2,000 foreign recruits, both men and women, crossed into Syria each month, mainly from Turkey, with the intention of joining armed Sunni groups. By the end of 2015, it was believed that over 30,000 foreign nationals from close to 90 countries had entered Syria and Iraq to fight for one of the Sunni-inspired opposition groups taking part in the Syrian civil war. Most of these foreign recruits joined the Islamic State, which is also known as the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS). Two more members of a computer hacker group that targeted senior United States intelligence officials, including the director of the Central Intelligence Agency, have been arrested by the Federal Bureau of Investigation. The arrests of Justin Liverman, 24, and Andrew Boggs, 22, took place on Thursday in Morehead City and North Wilkesboro, in the US state of North Carolina. They are
Two more members of a computer hacker group that targeted senior United States intelligence officials, including the director of the Central Intelligence Agency, have been arrested by the Federal Bureau of Investigation. The arrests of Justin Liverman, 24, and Andrew Boggs, 22, took place on Thursday in Morehead City and North Wilkesboro, in the US state of North Carolina. They are 
 The Federal Bureau of Investigation is among several intelligence agencies in the United States that have expressed concerns about an alleged Russian campaign to destabilize November’s presidential elections. The Washington Post, which
The Federal Bureau of Investigation is among several intelligence agencies in the United States that have expressed concerns about an alleged Russian campaign to destabilize November’s presidential elections. The Washington Post, which  The intelligence agency of the Czech Republic has accused Russian spy services of waging a “war of information” aimed at destabilizing the eastern European country. The agency has also warned that Russia continues to maintain a large intelligence presence in the Czech Republic, 25 years after the country, which was formerly known as Czechoslovakia, exited the Soviet sphere of influence and joined the European Union (EU) and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO).
The intelligence agency of the Czech Republic has accused Russian spy services of waging a “war of information” aimed at destabilizing the eastern European country. The agency has also warned that Russia continues to maintain a large intelligence presence in the Czech Republic, 25 years after the country, which was formerly known as Czechoslovakia, exited the Soviet sphere of influence and joined the European Union (EU) and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO).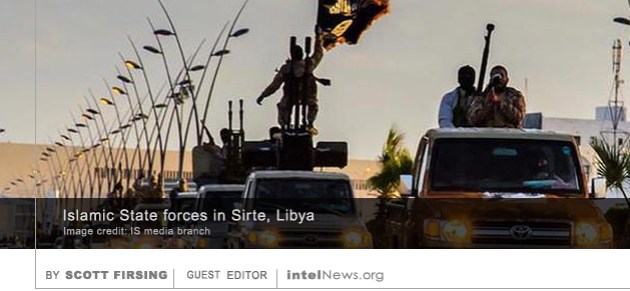 As United States air strikes and special-forces operations
As United States air strikes and special-forces operations  One of the men caught burglarizing the offices of the United States Democratic Party in 1972, a ploy that led to the resignation of President Richard Nixon, was an agent of the Central Intelligence Agency, according to a newly declassified document. The revelation is included in a narrative history of the Watergate scandal, produced over 40 years ago by the CIA to assess its own role in the affair. It recounts the events of the early morning hours of June 17, 1972, when a security guard saw five men dressed in black breaking into the headquarters of the Democratic National Committee at the Watergate office complex in Washington, DC. When the five men were arrested by police, it was discovered that one of them was connected with the Committee for the Re-Election of the President, a fundraising organization set up by US President Richard Nixon. The remaining four burglars had CIA contacts. They included E. Howard Hunt, a retired CIA operations officer who in 1961 had played a leading role in the failed Bay of Pigs invasion. It was eventually discovered that the burglary had been authorized by President Nixon himself, as part of a broader program to sabotage his political opponents.
One of the men caught burglarizing the offices of the United States Democratic Party in 1972, a ploy that led to the resignation of President Richard Nixon, was an agent of the Central Intelligence Agency, according to a newly declassified document. The revelation is included in a narrative history of the Watergate scandal, produced over 40 years ago by the CIA to assess its own role in the affair. It recounts the events of the early morning hours of June 17, 1972, when a security guard saw five men dressed in black breaking into the headquarters of the Democratic National Committee at the Watergate office complex in Washington, DC. When the five men were arrested by police, it was discovered that one of them was connected with the Committee for the Re-Election of the President, a fundraising organization set up by US President Richard Nixon. The remaining four burglars had CIA contacts. They included E. Howard Hunt, a retired CIA operations officer who in 1961 had played a leading role in the failed Bay of Pigs invasion. It was eventually discovered that the burglary had been authorized by President Nixon himself, as part of a broader program to sabotage his political opponents.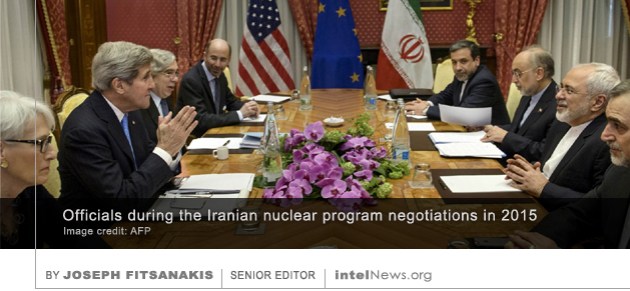 Iranian officials have confirmed reports from earlier this month that a member of the country’s team of nuclear negotiators has been arrested for engaging in espionage for a foreign country. But there are conflicting details about the case in Iranian media reports. Rumors about the identity of the individual began to circulate on August 16, after the office of the Iranian prosecutor announced that a dual national with Iranian citizenship had been arrested for spying on Tehran for a foreign intelligence service. The individual was not named, but some reports connected him with Britain’s Secret Intelligence Service, known as MI6.
Iranian officials have confirmed reports from earlier this month that a member of the country’s team of nuclear negotiators has been arrested for engaging in espionage for a foreign country. But there are conflicting details about the case in Iranian media reports. Rumors about the identity of the individual began to circulate on August 16, after the office of the Iranian prosecutor announced that a dual national with Iranian citizenship had been arrested for spying on Tehran for a foreign intelligence service. The individual was not named, but some reports connected him with Britain’s Secret Intelligence Service, known as MI6. The White House has no plans to release an American former military analyst who spied for the government of Cuba, according to an official letter sent to a member of the United States Congress. The denial came weeks after some media reports in Miami and Cuba suggested that Washington was examining a request by Havana to release
The White House has no plans to release an American former military analyst who spied for the government of Cuba, according to an official letter sent to a member of the United States Congress. The denial came weeks after some media reports in Miami and Cuba suggested that Washington was examining a request by Havana to release  The Turkish intelligence service currently employs more operatives in Germany than the East German spy agency did at the height of the Cold War, according to a German expert on espionage. The comment was made following the disclosure that Turkey maintains close to 6,000 informants and other intelligence operatives in Germany. An unnamed German security official told German newspaper Die Welt on Monday that the informants are operational throughout Germany and are handled by Turkey’s National Intelligence Organization, known as MİT.
The Turkish intelligence service currently employs more operatives in Germany than the East German spy agency did at the height of the Cold War, according to a German expert on espionage. The comment was made following the disclosure that Turkey maintains close to 6,000 informants and other intelligence operatives in Germany. An unnamed German security official told German newspaper Die Welt on Monday that the informants are operational throughout Germany and are handled by Turkey’s National Intelligence Organization, known as MİT.






British judge denies request to name alleged new member of Cambridge spy ring
September 20, 2016 by Joseph Fitsanakis 7 Comments
Over the years, more individuals have been suggested by historians as potential members of the group, including intelligence officers Leo Long and Guy Liddell, academics Ludwig Wittgenstein and Andrew Gow, and physicist Wilfrid Mann. But according to British newspaper The Daily Mail, another individual may be identified in a classified document as a possible member of the Cambridge spy ring. The document was allegedly traced by Andrew Lownie, who authored the recently published Stalin’s Englishman: The Lives of Guy Burgess. Lownie filed a Freedom of Information request to have the document, which is held at the National Archives in London, released. But the request was denied, and a judge has now upheld the decision.
In denying the request, the judge argued that the man named in the document is still alive and that a possible release of the document could “jeopardize […] personal relationships”. He also contended that the case is too old to warrant immediate public interest, and thus there was “no pressing need” to declassify the file. The Mail speculates that the individual named in the document could have cooperated with the British government in the past in return for protection, or that the file in question may contain details that could embarrass the British government.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 20 September 2016 | Permalink
Filed under Expert news and commentary on intelligence, espionage, spies and spying Tagged with Andrew Lownie, Cambridge Five, Cold War, declassification, espionage, history, News, UK, UK National Archives