Moscow names intersection after Kim Philby, British spy for the USSR
November 9, 2018 1 Comment
 In a sign of worsening relations between the United Kingdom and Russia, a busy intersection in Moscow has been named after Kim Philby, the British senior intelligence officer who secretly spied for the Soviet Union. While working as a senior member of British intelligence, Harold Adrian Russell Philby, known as ‘Kim’ to his friends, spied on behalf of the Soviet NKVD and KGB. His espionage activities lasted from about 1933 until 1963, when he secretly defected to the USSR from his home in Beirut, Lebanon. Philby’s defection sent ripples of shock across Western intelligence and is often seen as one of the most dramatic incidents of the Cold War. He was part of a wider ring of upper-class British spies, known collectively as ‘the Cambridge spies’ because they were recruited by Soviet intelligence during their student days at the University of Cambridge in England.
In a sign of worsening relations between the United Kingdom and Russia, a busy intersection in Moscow has been named after Kim Philby, the British senior intelligence officer who secretly spied for the Soviet Union. While working as a senior member of British intelligence, Harold Adrian Russell Philby, known as ‘Kim’ to his friends, spied on behalf of the Soviet NKVD and KGB. His espionage activities lasted from about 1933 until 1963, when he secretly defected to the USSR from his home in Beirut, Lebanon. Philby’s defection sent ripples of shock across Western intelligence and is often seen as one of the most dramatic incidents of the Cold War. He was part of a wider ring of upper-class British spies, known collectively as ‘the Cambridge spies’ because they were recruited by Soviet intelligence during their student days at the University of Cambridge in England.
Following his sensational defection, Philby lived in the Soviet capital until his death in 1988 at the age of 76. On Tuesday, a statement published on the website of the Moscow City Council announced that a busy intersection in the city’s southeast would be renamed to ‘Kim Philby Square’ in honor of the British defector. The statement said that the name change had been agreed upon by the city council and decreed by Moscow Mayor Sergei Sbyanin, a close associate of Russian President Vladimir Putin. Interestingly, Philby lived nowhere near the intersection named after him. His apartment —provided to him by the Soviet state in exchange for services rendered during his 30 years of spying— was located in a residential area of central Moscow. However, the intersection in question is situated near the headquarters of the SVR, Russia’s Foreign Intelligence Service, which is the primary successor agency to the Soviet-era KGB. In September of last year, SVR Director Sergei Naryshkin attended an exhibition in Moscow entitled “Kim Philby: His Intelligence Work and Personal Life”, organized by the Russian Historical Society. While there, Naryshkin was told by veterans of the KGB that Philby liked to take long walks through the streets of Moscow and that a street should be named after him in his honor.
French news agency Agence France Presse reported that it contacted the Moscow City Council but a spokeswoman said she was not in a position to comment on the Kim Philby Square renaming. The move comes a few months after a small pedestrian thoroughfare located across from the front entrance of the Russian embassy in Washington DC was symbolically named ‘Boris Nemtsov’, after a Russian opposition leader who was gunned down in downtown Moscow in February of 2015.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 09 November 2018 | Permalink
 A new book reveals for the first time the name of a former intelligence officer of the Soviet KGB who helped American authorities arrest Robert Hanssen, an American spy for the Soviet Union and Russia. The son of a Chicago police officer, Hanssen joined the Federal Bureau of Investigation in 1976 and was eventually transferred to the Bureau’s Soviet analytical unit, where he held senior counterintelligence posts. It wasn’t until 2000, however, that the FBI realized Hanssen had spied for Moscow since 1979. Following Hanssen’s arrest in 2001, it emerged that he had betrayed the names of 50 FBI and CIA assets or informants, many of whom perished in the hands of the Russian intelligence services.
A new book reveals for the first time the name of a former intelligence officer of the Soviet KGB who helped American authorities arrest Robert Hanssen, an American spy for the Soviet Union and Russia. The son of a Chicago police officer, Hanssen joined the Federal Bureau of Investigation in 1976 and was eventually transferred to the Bureau’s Soviet analytical unit, where he held senior counterintelligence posts. It wasn’t until 2000, however, that the FBI realized Hanssen had spied for Moscow since 1979. Following Hanssen’s arrest in 2001, it emerged that he had betrayed the names of 50 FBI and CIA assets or informants, many of whom perished in the hands of the Russian intelligence services.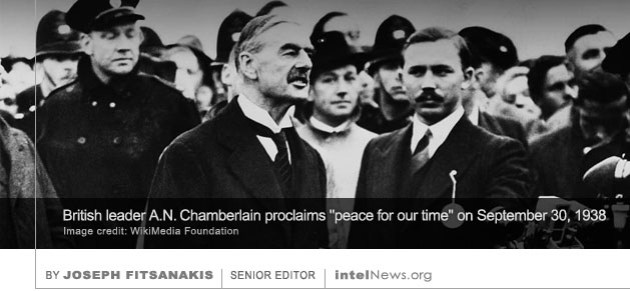 Nearly 2,000 missing British intelligence files relating to the so-called Munich Agreement, a failed attempt by Britain, France and Italy to appease Adolf Hitler in 1938, may not have been destroyed, according to historians. On September 30, 1938, the leaders of France, Britain and Italy signed a peace treaty with the Nazi government of German Chancellor Adolf Hitler. The treaty, which became known as the Munich Agreement, gave Hitler de facto control of Czechoslovakia’s German-speaking areas, in return for him promising to resign from territorial claims against other countries, such as Poland and Hungary. Hours after the treaty was formalized, British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain arrived by airplane at an airport near London, and boldly proclaimed that he had secured “peace for our time” (pictured above). Contrary to Chamberlain’s expectations, however, the German government was emboldened by what it saw as attempts to appease it, and promptly proceeded to invade Poland, thus firing the opening shots of World War II in Europe.
Nearly 2,000 missing British intelligence files relating to the so-called Munich Agreement, a failed attempt by Britain, France and Italy to appease Adolf Hitler in 1938, may not have been destroyed, according to historians. On September 30, 1938, the leaders of France, Britain and Italy signed a peace treaty with the Nazi government of German Chancellor Adolf Hitler. The treaty, which became known as the Munich Agreement, gave Hitler de facto control of Czechoslovakia’s German-speaking areas, in return for him promising to resign from territorial claims against other countries, such as Poland and Hungary. Hours after the treaty was formalized, British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain arrived by airplane at an airport near London, and boldly proclaimed that he had secured “peace for our time” (pictured above). Contrary to Chamberlain’s expectations, however, the German government was emboldened by what it saw as attempts to appease it, and promptly proceeded to invade Poland, thus firing the opening shots of World War II in Europe. The leadership of the Labour Party in Britain has reacted with disdain after a new book by a leading author and columnist claimed that Michael Foot, who led the Party in the early 1980s was paid agent of the Soviet KGB. Foot, a staunch and vocal representative of the postwar British left, was a member of parliament for over 40 years, eventually serving as leader of the House of Commons. He rose to the post of deputy leader of the Labour Party and in 1980 succeeded Jim Callahan as head of the Party. But he stepped down in 1983 in the aftermath of Labour’s largest electoral defeat in over half a century.
The leadership of the Labour Party in Britain has reacted with disdain after a new book by a leading author and columnist claimed that Michael Foot, who led the Party in the early 1980s was paid agent of the Soviet KGB. Foot, a staunch and vocal representative of the postwar British left, was a member of parliament for over 40 years, eventually serving as leader of the House of Commons. He rose to the post of deputy leader of the Labour Party and in 1980 succeeded Jim Callahan as head of the Party. But he stepped down in 1983 in the aftermath of Labour’s largest electoral defeat in over half a century. A group of German radicals planned to assassinate Soviet Premier Mikhail Gorbachev in East Germany in 1989, thus triggering a Soviet military invasion of the country, according to a new book written by a former British spy. The
A group of German radicals planned to assassinate Soviet Premier Mikhail Gorbachev in East Germany in 1989, thus triggering a Soviet military invasion of the country, according to a new book written by a former British spy. The  Japan has released secret documents from 1942 relating to the Tokyo spy ring led by Richard Sorge, a German who spied for the USSR and is often credited with helping Moscow win World War II. The documents detail efforts by the wartime Japanese government to trivialize the discovery of the
Japan has released secret documents from 1942 relating to the Tokyo spy ring led by Richard Sorge, a German who spied for the USSR and is often credited with helping Moscow win World War II. The documents detail efforts by the wartime Japanese government to trivialize the discovery of the  A man has been arrested by British counter-terrorism police in Northern Ireland, reportedly in connection with the assassination of a Seychelles exiled political leader in London in 1985. No-one has ever been charged with the murder of Gérard Hoarau, who was gunned down with a Sterling submachine gun in Edgware, London, on November 29, 1985. At the time of his killing, the 35-year-old Hoarau led the Mouvement Pour La Resistance (MPR), which was outlawed by the Seychelles government but was supported by Western governments and their allies in Africa. The reason was that the MPR challenged the president of the Seychelles, France-Albert René, leader of the leftwing Seychelles People’s United Party —known today as the Seychelles People’s United Party. The British-educated René assumed the presidency via a coup d’etat in 1977, which was supported by neighboring Tanzania, and remained in power in the island-country until 2004.
A man has been arrested by British counter-terrorism police in Northern Ireland, reportedly in connection with the assassination of a Seychelles exiled political leader in London in 1985. No-one has ever been charged with the murder of Gérard Hoarau, who was gunned down with a Sterling submachine gun in Edgware, London, on November 29, 1985. At the time of his killing, the 35-year-old Hoarau led the Mouvement Pour La Resistance (MPR), which was outlawed by the Seychelles government but was supported by Western governments and their allies in Africa. The reason was that the MPR challenged the president of the Seychelles, France-Albert René, leader of the leftwing Seychelles People’s United Party —known today as the Seychelles People’s United Party. The British-educated René assumed the presidency via a coup d’etat in 1977, which was supported by neighboring Tanzania, and remained in power in the island-country until 2004. The daughter of Heinrich Himmler, who was second in command in the German Nazi Party until the end of World War II, worked for West German intelligence in the 1960s, it has been confirmed. Gudrun Burwitz was born Gudrun Himmler in 1929. During the reign of Adolf Hitler, her father, Heinrich Himmler, commanded the feared Schutzstaffel, known more commonly as the SS. Under his command, the SS played a central part in administering the Holocaust, and carried out a systematic campaign of extermination of millions of civilians in Nazi-occupied Europe. But the Nazi regime collapsed under the weight of the Allied military advance, and on May 20, 1945, Himmler was captured alive by Soviet troops. Shortly thereafter he was transferred to a British-administered prison, where, just days later, he committed suicide with a cyanide capsule that he had with him. Gudrun, who by that time was nearly 16 years old, managed to escape to Italy with her mother, where she was captured by American forces. She testified in the Nuremberg Trials and was eventually released in 1948. She settled with her mother in northern West Germany and lived away from the limelight of publicity until her death on May 24 of this year, aged 88.
The daughter of Heinrich Himmler, who was second in command in the German Nazi Party until the end of World War II, worked for West German intelligence in the 1960s, it has been confirmed. Gudrun Burwitz was born Gudrun Himmler in 1929. During the reign of Adolf Hitler, her father, Heinrich Himmler, commanded the feared Schutzstaffel, known more commonly as the SS. Under his command, the SS played a central part in administering the Holocaust, and carried out a systematic campaign of extermination of millions of civilians in Nazi-occupied Europe. But the Nazi regime collapsed under the weight of the Allied military advance, and on May 20, 1945, Himmler was captured alive by Soviet troops. Shortly thereafter he was transferred to a British-administered prison, where, just days later, he committed suicide with a cyanide capsule that he had with him. Gudrun, who by that time was nearly 16 years old, managed to escape to Italy with her mother, where she was captured by American forces. She testified in the Nuremberg Trials and was eventually released in 1948. She settled with her mother in northern West Germany and lived away from the limelight of publicity until her death on May 24 of this year, aged 88. A lengthy exposé by a leading American newsmagazine has claimed that Israel and the United Arab Emirates, two countries that officially have no relations, have been secretly collaborating for more than two decades. Their secret cooperation has been extremely tight and has included clandestine weapons sales and intelligence-sharing, according to the exposé, which was published on the website of The New Yorker on Monday and will feature in the magazine’s print edition on June 18. The lengthy piece, which deals with the changing geopolitics of the Middle East, is written by Adam Entous, national security correspondent for The Washington Post, who has previously reported for more than two decades for Reuters and The Wall Street Journal.
A lengthy exposé by a leading American newsmagazine has claimed that Israel and the United Arab Emirates, two countries that officially have no relations, have been secretly collaborating for more than two decades. Their secret cooperation has been extremely tight and has included clandestine weapons sales and intelligence-sharing, according to the exposé, which was published on the website of The New Yorker on Monday and will feature in the magazine’s print edition on June 18. The lengthy piece, which deals with the changing geopolitics of the Middle East, is written by Adam Entous, national security correspondent for The Washington Post, who has previously reported for more than two decades for Reuters and The Wall Street Journal. Files released on Monday by the British government reveal new evidence about one of the most prolific Soviet spy rings that operated in the West after World War II, which became known as the Portland Spy Ring. Some of the members of the Portland Spy Ring were Soviet operatives who, at the time of their arrest, posed as citizens of third countries. All were non-official-cover intelligence officers, or NOCs, as they are known in Western intelligence parlance. Their Soviet —and nowadays Russian— equivalents are known as illegals. NOCs are high-level principal agents or officers of an intelligence agency, who operate without official connection to the authorities of the country that employs them. During much of the Cold War, NOCs posed as business executives, students, academics, journalists, or non-profit agency workers. Unlike official-cover officers, who are protected by diplomatic immunity, NOCs have no such protection. If arrested by authorities of their host country, they can be tried and convicted for engaging in espionage.
Files released on Monday by the British government reveal new evidence about one of the most prolific Soviet spy rings that operated in the West after World War II, which became known as the Portland Spy Ring. Some of the members of the Portland Spy Ring were Soviet operatives who, at the time of their arrest, posed as citizens of third countries. All were non-official-cover intelligence officers, or NOCs, as they are known in Western intelligence parlance. Their Soviet —and nowadays Russian— equivalents are known as illegals. NOCs are high-level principal agents or officers of an intelligence agency, who operate without official connection to the authorities of the country that employs them. During much of the Cold War, NOCs posed as business executives, students, academics, journalists, or non-profit agency workers. Unlike official-cover officers, who are protected by diplomatic immunity, NOCs have no such protection. If arrested by authorities of their host country, they can be tried and convicted for engaging in espionage. The United States Central Intelligence Agency believed that Yugoslavia was on the brink of becoming a nuclear-armed state in 1975, due partly to assistance from Washington, according to newly declassified documents. The documents, which date from 1957 to 1986, were
The United States Central Intelligence Agency believed that Yugoslavia was on the brink of becoming a nuclear-armed state in 1975, due partly to assistance from Washington, according to newly declassified documents. The documents, which date from 1957 to 1986, were  Successive directors of the Secret Intelligence Service used a secret slush fund to finance spy operations without British government oversight after World War II, according to a top-secret document unearthed in London. The document was found in a collection belonging to the personal archive of the secretary of the British cabinet, which was released by the United Kingdom’s National Archives. It was discovered earlier this year by Dr Rory Cormac, Associate Professor of International Relations in the Faculty of Social Sciences of the University of Nottingham in England. It forms the basis of an episode of BBC Radio 4’s investigative history program, Document, which
Successive directors of the Secret Intelligence Service used a secret slush fund to finance spy operations without British government oversight after World War II, according to a top-secret document unearthed in London. The document was found in a collection belonging to the personal archive of the secretary of the British cabinet, which was released by the United Kingdom’s National Archives. It was discovered earlier this year by Dr Rory Cormac, Associate Professor of International Relations in the Faculty of Social Sciences of the University of Nottingham in England. It forms the basis of an episode of BBC Radio 4’s investigative history program, Document, which  One of the Cold War’s most recognizable spy figures, George Blake, who escaped to the Soviet Union after betraying British intelligence, issued a rare statement last week, praising the successor agency to Soviet-era KGB. Blake was born George Behar in Rotterdam, Holland, to a Dutch mother and a British father. Having fought with the Dutch resistance against the Nazis, he escaped to Britain, where he joined the Secret Intelligence Service, known as MI6, in 1944. He was serving in a British diplomatic post in Korea in 1950, when he was captured by advancing North Korean troops and spent time in a prisoner of war camp. He was eventually freed, but, unbeknownst to MI6, had become a communist and come in contact with the Soviet KGB while in captivity. Blake remained in the service of the KGB as a defector-in-place until 1961, when he was arrested and tried for espionage.
One of the Cold War’s most recognizable spy figures, George Blake, who escaped to the Soviet Union after betraying British intelligence, issued a rare statement last week, praising the successor agency to Soviet-era KGB. Blake was born George Behar in Rotterdam, Holland, to a Dutch mother and a British father. Having fought with the Dutch resistance against the Nazis, he escaped to Britain, where he joined the Secret Intelligence Service, known as MI6, in 1944. He was serving in a British diplomatic post in Korea in 1950, when he was captured by advancing North Korean troops and spent time in a prisoner of war camp. He was eventually freed, but, unbeknownst to MI6, had become a communist and come in contact with the Soviet KGB while in captivity. Blake remained in the service of the KGB as a defector-in-place until 1961, when he was arrested and tried for espionage. A symposium about the life, activities and legacy of World War I-era double spy Mata Hari is to take place in London this month, on the 100th anniversary of her death by execution. Mata Hari was born Margaretha Geertruida Zelle in Holland in 1876. In 1895 she married Rudolf MacLeod, a Dutch Army Captain of Scottish descent serving the Dutch colonial administration of what is now Indonesia. She eventually divorced the alcoholic and abusive MacLeod, who was 20 years her senior, and joined the circus in Paris. Eventually she became wildly popular as an exotic dancer, a position that placed her in direct and close contact with several influential men in France, including the millionaire industrialist Émile Étienne Guimet, who became her longtime lover. Several of her male devotees came from military backgrounds from various European countries. Most historians agree that by 1916 Mata Hari was working for French intelligence, gathering information from her German lovers. However, in February of the following year she was arrested by French counterintelligence officers in Paris and accused of spying on behalf of the German Empire. French prosecutors accused her of having provided Germany with tactical intelligence that cost the Triple Entente the lives of over 50,000 soldiers.
A symposium about the life, activities and legacy of World War I-era double spy Mata Hari is to take place in London this month, on the 100th anniversary of her death by execution. Mata Hari was born Margaretha Geertruida Zelle in Holland in 1876. In 1895 she married Rudolf MacLeod, a Dutch Army Captain of Scottish descent serving the Dutch colonial administration of what is now Indonesia. She eventually divorced the alcoholic and abusive MacLeod, who was 20 years her senior, and joined the circus in Paris. Eventually she became wildly popular as an exotic dancer, a position that placed her in direct and close contact with several influential men in France, including the millionaire industrialist Émile Étienne Guimet, who became her longtime lover. Several of her male devotees came from military backgrounds from various European countries. Most historians agree that by 1916 Mata Hari was working for French intelligence, gathering information from her German lovers. However, in February of the following year she was arrested by French counterintelligence officers in Paris and accused of spying on behalf of the German Empire. French prosecutors accused her of having provided Germany with tactical intelligence that cost the Triple Entente the lives of over 50,000 soldiers.






Morton Sobell, convicted of conspiracy in the Rosenberg espionage case, dies at 101
January 31, 2019 by Joseph Fitsanakis 1 Comment
Sobell was born in New York’s Manhattan Island in 1917 and worked on radar tracking systems for defense contractors. During college, he and several of his friends, including fellow-engineer Julius Rosenberg, joined the United States Communist Party, partly in reaction to the Great Depression. When the Federal Bureau of Investigation began to arrest members of what the United States government claimed was a Soviet atomic spy ring led by Rosenberg, Sobell escaped with his family to Mexico, where he used a fake identity to evade the authorities. But he was dramatically abducted by a paramilitary force and surrendered to the FBI.
He was then tried alongside Rosenberg and his wife Ethel for conspiracy to commit acts of espionage. The Rosenbergs refused to cooperate with the FBI and were sentenced to death. Both were executed in 1953 and remain to this day the only American citizens to have been executed for espionage after the Civil War. Sobel was found guilty of the lesser charge of conspiracy and no evidence was presented in court that connected him to atomic espionage. He was therefore sentenced to 30 years in prison and served 18 of those, following a successful public-relations campaign organized by his wife, Hellen. He was released from prison in 1969 and continued to insist that he had never been a spy and had been wrongly convicted of conspiracy.
But in 2008, at the age of 91, Sobell spoke to The New York Times and publicly admitted for the first time that he had been a spy for the Soviet Union. He said that he had worked systematically to provide Moscow with information on weapons systems and other classified technologies. However, he had “never thought of it” as spying, he said. He also told The Times that he had developed a favorable impression of Soviet communism during the Great Depression, when he and many others saw the Soviet economic system as an antidote to crisis-ridden capitalism. “Now I know it was an illusion”, he told the paper.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 31 January 2019 | Permalink
Filed under Expert news and commentary on intelligence, espionage, spies and spying Tagged with Cold War, espionage, history, Morton Sobell, News, obituaries, Rosenberg nuclear spy ring, United States, USSR