Britain knew of Saudi plan to target journalist, warned Saudis against it
October 29, 2018 9 Comments
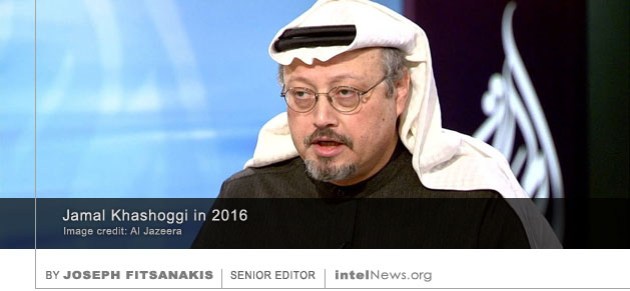 British intelligence had prior knowledge of a plot by the Saudi government to target Jamal Khashoggi, the dissident journalist who was killed in the hands of Saudi intelligence officers in Istanbul on October 2, and allegedly warned Riyadh not to proceed with the plan, according to a report. Khashoggi was a former Saudi government adviser who became critical of the kingdom’s style of governance. He is believed to have been killed by a 15-member Saudi hit squad while visiting the Saudi consulate in Istanbul. He went there for a scheduled appointment in order to be issued a document certifying his divorce from his former wife in Saudi Arabia. After vehemently denying any role in Khashoggi’s killing, the Saudi government admitted last week that the journalist was killed while inside the Saudi consulate in Istanbul. It has pledged to punish those responsible and reform the Kingdom’s intelligence services. But critics accuse Riyadh of ordering the dissident’s murder.
British intelligence had prior knowledge of a plot by the Saudi government to target Jamal Khashoggi, the dissident journalist who was killed in the hands of Saudi intelligence officers in Istanbul on October 2, and allegedly warned Riyadh not to proceed with the plan, according to a report. Khashoggi was a former Saudi government adviser who became critical of the kingdom’s style of governance. He is believed to have been killed by a 15-member Saudi hit squad while visiting the Saudi consulate in Istanbul. He went there for a scheduled appointment in order to be issued a document certifying his divorce from his former wife in Saudi Arabia. After vehemently denying any role in Khashoggi’s killing, the Saudi government admitted last week that the journalist was killed while inside the Saudi consulate in Istanbul. It has pledged to punish those responsible and reform the Kingdom’s intelligence services. But critics accuse Riyadh of ordering the dissident’s murder.
Now a new report claims that Britain’s external intelligence agency, the Secret Intelligence Service (MI6), was aware of a plot by the Saudi government to kidnap Khashoggi in order to silence him. British newspaper The Sunday Express says it has evidence from “high ranking intelligence sources” that MI6 was in possession of communications intercepts containing conversations about Khashoggi. The conversations were between Saudi government officials and officers of the General Intelligence Directorate (GID), the Kingdom’s primary spy agency. In the intercepts, a member of the Saudi royal family is allegedly heard giving orders for the GID to kidnap Khashoggi from Turkey sometime in early September. He also instructs the GID to secretly transport the dissident journalist to Saudi soil where he could be interrogated. During the conversation, a discussion took place about the possibility that Khashoggi would physically resist his abductors. At that point in the conversation, the high ranking intelligence source told The Express, the royal family member “left the door open for alternative remedies […] should Khashoggi be troublesome”.
The paper reports that MI6 “became aware” of the arrival of a 15-member Saudi hit squad in Istanbul on October 1, a day before Khashoggi went missing. According to the paper’s source “it was pretty clear what their aim was”, so MI6 contacted the GID directly and warned the Saudi spy agency to “cancel the mission”, said the source. However, the source added, “this request was ignored”. On October 10, The Washington Post, the newspaper that employed Khashoggi, said that American intelligence agencies had evidence that the Saudi royal family tried to lure The Washington Post journalist Jamal Khashoggi back to Saudi Arabia, in order to capture him.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 29 October 2018 | Permalink
 Sergei Skripal, the Russian double agent who was poisoned with a military-grade nerve agent in England earlier this year, worked with Spanish intelligence after his defection to the United Kingdom, according to sources. Skripal, a former military intelligence officer who spied for Britain in the early 2000s, had kept a low profile while living in the English town of Salisbury. He was resettled there in 2010 by the British Secret Intelligence Service (MI6), after he was released from a Russian prison. But he and his daughter Yulia made international headlines in March, after they were
Sergei Skripal, the Russian double agent who was poisoned with a military-grade nerve agent in England earlier this year, worked with Spanish intelligence after his defection to the United Kingdom, according to sources. Skripal, a former military intelligence officer who spied for Britain in the early 2000s, had kept a low profile while living in the English town of Salisbury. He was resettled there in 2010 by the British Secret Intelligence Service (MI6), after he was released from a Russian prison. But he and his daughter Yulia made international headlines in March, after they were  Relations between the European Union and the United Kingdom hit a new low on Thursday, as the European Council refused to comment on claims that British spy agencies have spied on Brexit negotiators in Brussels. Consultations between the two sides have progressed at an alarmingly slow pace ever since June 23, 2016, when voters in the island nation elected to leave the EU during a nationwide referendum. In March of 2017, London officially invoked Article 50 of the EU Treaty, which requires that Britain’s withdrawal from the multinational body be completed within two calendar years. But there are many who think that a mutual agreement will not be reached between the two sides.
Relations between the European Union and the United Kingdom hit a new low on Thursday, as the European Council refused to comment on claims that British spy agencies have spied on Brexit negotiators in Brussels. Consultations between the two sides have progressed at an alarmingly slow pace ever since June 23, 2016, when voters in the island nation elected to leave the EU during a nationwide referendum. In March of 2017, London officially invoked Article 50 of the EU Treaty, which requires that Britain’s withdrawal from the multinational body be completed within two calendar years. But there are many who think that a mutual agreement will not be reached between the two sides.
 The British government may relocate Sergei Skripal, the Russian double spy who appears to have survived an assassination attempt in England, to the United States, in an effort to protect him from further attacks. The BBC
The British government may relocate Sergei Skripal, the Russian double spy who appears to have survived an assassination attempt in England, to the United States, in an effort to protect him from further attacks. The BBC  The British secret services have begun tightening the physical security of dozens of Russian defectors living in Britain, a week after the attempted murder of former KGB Colonel Sergei Skripal in southern England. The 66-year-old double spy and his daughter, Yulia, were found in a catatonic state in the town of Salisbury on March 4. It was later determined that they had been attacked with a nerve agent. Russian officials have vehemently denied that the Kremlin had any involvement with the brazen attempt to kill Skripal. But,
The British secret services have begun tightening the physical security of dozens of Russian defectors living in Britain, a week after the attempted murder of former KGB Colonel Sergei Skripal in southern England. The 66-year-old double spy and his daughter, Yulia, were found in a catatonic state in the town of Salisbury on March 4. It was later determined that they had been attacked with a nerve agent. Russian officials have vehemently denied that the Kremlin had any involvement with the brazen attempt to kill Skripal. But,  Successive directors of the Secret Intelligence Service used a secret slush fund to finance spy operations without British government oversight after World War II, according to a top-secret document unearthed in London. The document was found in a collection belonging to the personal archive of the secretary of the British cabinet, which was released by the United Kingdom’s National Archives. It was discovered earlier this year by Dr Rory Cormac, Associate Professor of International Relations in the Faculty of Social Sciences of the University of Nottingham in England. It forms the basis of an episode of BBC Radio 4’s investigative history program, Document, which
Successive directors of the Secret Intelligence Service used a secret slush fund to finance spy operations without British government oversight after World War II, according to a top-secret document unearthed in London. The document was found in a collection belonging to the personal archive of the secretary of the British cabinet, which was released by the United Kingdom’s National Archives. It was discovered earlier this year by Dr Rory Cormac, Associate Professor of International Relations in the Faculty of Social Sciences of the University of Nottingham in England. It forms the basis of an episode of BBC Radio 4’s investigative history program, Document, which  One of the Cold War’s most recognizable spy figures, George Blake, who escaped to the Soviet Union after betraying British intelligence, issued a rare statement last week, praising the successor agency to Soviet-era KGB. Blake was born George Behar in Rotterdam, Holland, to a Dutch mother and a British father. Having fought with the Dutch resistance against the Nazis, he escaped to Britain, where he joined the Secret Intelligence Service, known as MI6, in 1944. He was serving in a British diplomatic post in Korea in 1950, when he was captured by advancing North Korean troops and spent time in a prisoner of war camp. He was eventually freed, but, unbeknownst to MI6, had become a communist and come in contact with the Soviet KGB while in captivity. Blake remained in the service of the KGB as a defector-in-place until 1961, when he was arrested and tried for espionage.
One of the Cold War’s most recognizable spy figures, George Blake, who escaped to the Soviet Union after betraying British intelligence, issued a rare statement last week, praising the successor agency to Soviet-era KGB. Blake was born George Behar in Rotterdam, Holland, to a Dutch mother and a British father. Having fought with the Dutch resistance against the Nazis, he escaped to Britain, where he joined the Secret Intelligence Service, known as MI6, in 1944. He was serving in a British diplomatic post in Korea in 1950, when he was captured by advancing North Korean troops and spent time in a prisoner of war camp. He was eventually freed, but, unbeknownst to MI6, had become a communist and come in contact with the Soviet KGB while in captivity. Blake remained in the service of the KGB as a defector-in-place until 1961, when he was arrested and tried for espionage. The life of Kim Philby, one of the Cold War’s most recognizable espionage figures, is the subject of a new exhibition that opened last week in Moscow. Items displayed at the exhibition include secret documents stolen by Philby and passed to his Soviet handlers during his three decades in the service of Soviet intelligence. While working as a senior member of British intelligence, Harold Adrian Russell Philby, known as ‘Kim’ to his friends, spied on behalf of the Soviet NKVD and KGB. His espionage lasted from about 1933 until 1963, when he secretly defected to the USSR from his home in Beirut, Lebanon. Philby’s defection sent ripples of shock across Western intelligence and is often seen as one of the most dramatic incidents of the Cold War.
The life of Kim Philby, one of the Cold War’s most recognizable espionage figures, is the subject of a new exhibition that opened last week in Moscow. Items displayed at the exhibition include secret documents stolen by Philby and passed to his Soviet handlers during his three decades in the service of Soviet intelligence. While working as a senior member of British intelligence, Harold Adrian Russell Philby, known as ‘Kim’ to his friends, spied on behalf of the Soviet NKVD and KGB. His espionage lasted from about 1933 until 1963, when he secretly defected to the USSR from his home in Beirut, Lebanon. Philby’s defection sent ripples of shock across Western intelligence and is often seen as one of the most dramatic incidents of the Cold War. Britain’s primary external-intelligence agency will revert to old-fashioned ways of recruiting employees, including the co-called “tap on the shoulder” method, according to its director. Known informally as MI6, the Secret Intelligence Service (SIS) was founded in 1908 to protect Britain’s national security by collecting intelligence from foreign sources. However, the agency has had difficulty recruiting a diverse group of people, and many still view it as a professional destination for a small wealthy elite, drawn primarily from Britain’s most prestigious universities such as Oxford and Cambridge.
Britain’s primary external-intelligence agency will revert to old-fashioned ways of recruiting employees, including the co-called “tap on the shoulder” method, according to its director. Known informally as MI6, the Secret Intelligence Service (SIS) was founded in 1908 to protect Britain’s national security by collecting intelligence from foreign sources. However, the agency has had difficulty recruiting a diverse group of people, and many still view it as a professional destination for a small wealthy elite, drawn primarily from Britain’s most prestigious universities such as Oxford and Cambridge. Iranian officials have confirmed reports from earlier this month that a member of the country’s team of nuclear negotiators has been arrested for engaging in espionage for a foreign country. But there are conflicting details about the case in Iranian media reports. Rumors about the identity of the individual began to circulate on August 16, after the office of the Iranian prosecutor announced that a dual national with Iranian citizenship had been arrested for spying on Tehran for a foreign intelligence service. The individual was not named, but some reports connected him with Britain’s Secret Intelligence Service, known as MI6.
Iranian officials have confirmed reports from earlier this month that a member of the country’s team of nuclear negotiators has been arrested for engaging in espionage for a foreign country. But there are conflicting details about the case in Iranian media reports. Rumors about the identity of the individual began to circulate on August 16, after the office of the Iranian prosecutor announced that a dual national with Iranian citizenship had been arrested for spying on Tehran for a foreign intelligence service. The individual was not named, but some reports connected him with Britain’s Secret Intelligence Service, known as MI6. Relations between two of Britain’s most powerful intelligence agencies, MI5 and MI6, suffered a “serious and prolonged breakdown” during the American-led war on terrorism. Citing sources in the British government, the London-based Guardian newspaper said on Tuesday that the two agencies entered an extensive row over Britain’s support for extraordinary rendition. The policy refers to the government-sponsored abduction of individuals and their extrajudicial transfer across national borders. It was widely practiced by the administration of US President George W. Bush, despite its connection to documented cases of torture of terrorism detainees, in countries like Egypt, Libya, and Jordan.
Relations between two of Britain’s most powerful intelligence agencies, MI5 and MI6, suffered a “serious and prolonged breakdown” during the American-led war on terrorism. Citing sources in the British government, the London-based Guardian newspaper said on Tuesday that the two agencies entered an extensive row over Britain’s support for extraordinary rendition. The policy refers to the government-sponsored abduction of individuals and their extrajudicial transfer across national borders. It was widely practiced by the administration of US President George W. Bush, despite its connection to documented cases of torture of terrorism detainees, in countries like Egypt, Libya, and Jordan. A videotaped lecture by Kim Philby, one of the Cold War’s most recognizable espionage figures, has been unearthed in the archives of the Stasi, the Ministry of State Security of the former East Germany. During the one-hour lecture, filmed in 1981, Philby addresses a select audience of Stasi operations officers and offers them advice on espionage, drawn from his own career. While working as a senior member of British intelligence, Harold Adrian Russell Philby, known as ‘Kim’ to his friends, spied on behalf of the Soviet NKVD and KGB from the early 1930s until 1963, when he secretly defected to the USSR from his home in Beirut, Lebanon. Philby’s defection sent ripples of shock across Western intelligence and is often seen as one of the most dramatic moments of the Cold War.
A videotaped lecture by Kim Philby, one of the Cold War’s most recognizable espionage figures, has been unearthed in the archives of the Stasi, the Ministry of State Security of the former East Germany. During the one-hour lecture, filmed in 1981, Philby addresses a select audience of Stasi operations officers and offers them advice on espionage, drawn from his own career. While working as a senior member of British intelligence, Harold Adrian Russell Philby, known as ‘Kim’ to his friends, spied on behalf of the Soviet NKVD and KGB from the early 1930s until 1963, when he secretly defected to the USSR from his home in Beirut, Lebanon. Philby’s defection sent ripples of shock across Western intelligence and is often seen as one of the most dramatic moments of the Cold War.






Moscow names intersection after Kim Philby, British spy for the USSR
November 9, 2018 by Joseph Fitsanakis 1 Comment
Following his sensational defection, Philby lived in the Soviet capital until his death in 1988 at the age of 76. On Tuesday, a statement published on the website of the Moscow City Council announced that a busy intersection in the city’s southeast would be renamed to ‘Kim Philby Square’ in honor of the British defector. The statement said that the name change had been agreed upon by the city council and decreed by Moscow Mayor Sergei Sbyanin, a close associate of Russian President Vladimir Putin. Interestingly, Philby lived nowhere near the intersection named after him. His apartment —provided to him by the Soviet state in exchange for services rendered during his 30 years of spying— was located in a residential area of central Moscow. However, the intersection in question is situated near the headquarters of the SVR, Russia’s Foreign Intelligence Service, which is the primary successor agency to the Soviet-era KGB. In September of last year, SVR Director Sergei Naryshkin attended an exhibition in Moscow entitled “Kim Philby: His Intelligence Work and Personal Life”, organized by the Russian Historical Society. While there, Naryshkin was told by veterans of the KGB that Philby liked to take long walks through the streets of Moscow and that a street should be named after him in his honor.
French news agency Agence France Presse reported that it contacted the Moscow City Council but a spokeswoman said she was not in a position to comment on the Kim Philby Square renaming. The move comes a few months after a small pedestrian thoroughfare located across from the front entrance of the Russian embassy in Washington DC was symbolically named ‘Boris Nemtsov’, after a Russian opposition leader who was gunned down in downtown Moscow in February of 2015.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 09 November 2018 | Permalink
Filed under Expert news and commentary on intelligence, espionage, spies and spying Tagged with Cold War, defectors, H.A.R. "Kim" Philby, history, MI6, News, SVR (Russia), UK