Pakistani man sought out assassination targets for Iran, says Germany
January 10, 2017 Leave a comment
 Authorities in Germany have pressed espionage charges against a Pakistani man who allegedly spied for Iran and even compiled lists of potential targets for assassination. The man, who has been identified in media reports only as “Syed Mustafa H.”, is a 31-year-old worker at the German Aerospace Center in the northern German city of Bremen. He is also reportedly a graduate of the Materials Science and Production Engineering department of the Universität Bremen. According to court documents, he is believed to have been spying for Iranian intelligence since the summer of 2015. It appears that the Federal Office for the Protection of the Constitution (BfV), Germany’s domestic intelligence agency, had been aware of the man’s espionage activities for at least a year prior to his arrest.
Authorities in Germany have pressed espionage charges against a Pakistani man who allegedly spied for Iran and even compiled lists of potential targets for assassination. The man, who has been identified in media reports only as “Syed Mustafa H.”, is a 31-year-old worker at the German Aerospace Center in the northern German city of Bremen. He is also reportedly a graduate of the Materials Science and Production Engineering department of the Universität Bremen. According to court documents, he is believed to have been spying for Iranian intelligence since the summer of 2015. It appears that the Federal Office for the Protection of the Constitution (BfV), Germany’s domestic intelligence agency, had been aware of the man’s espionage activities for at least a year prior to his arrest.
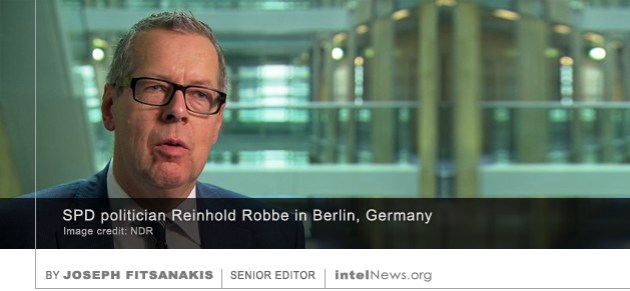
German media, including the newspapers Süddeutsche Zeitung and Die Zeit, as well as public broadcasters Taggesschau, WDR and NDR, report that Syed Mustafa H.’s main task was to compile lists of potential assassination targets. These included prominent Jews or German-Israelis living in northern Germany. Among them was Reinhold Robbe, a politician with the center-left Social Democratic Party (SPD), who served for a number of years as president of the German-Israeli Congress (DIG). According to reports, the Pakistani spy had compiled detailed maps of Robbe’s daily movements, which outlined his travel routines and the routes he took from his home to the DIG headquarters in Berlin. German officials believe that the type of surveillance that Syed Mustafa H. carried out against Robbe indisputably leads to the conclusion that the politician’s assassination was being planned.
Reports in the German media suggest that Syed Mustafa H.’s work was a small part of a much broader operation by Iranian intelligence. The operation aims to identify prominent individuals throughout Europe, who have Israeli connections. These individuals can be targeted during a future conflagration between Israel and Iran, or in retaliation to an Israeli intelligence operation against Tehran. If Syed Mustafa H. is found guilty of targeting Robbe, it will mark the first proven case of a German political figure who has been targeted for possible assassination by an Iranian intelligence agency.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 10 January 2017 | Permalink
 British intelligence agencies gave their United States counterparts an early warning about Russian attempts to influence the outcome of the American presidential election, according to The New York Times. The American newspaper
British intelligence agencies gave their United States counterparts an early warning about Russian attempts to influence the outcome of the American presidential election, according to The New York Times. The American newspaper 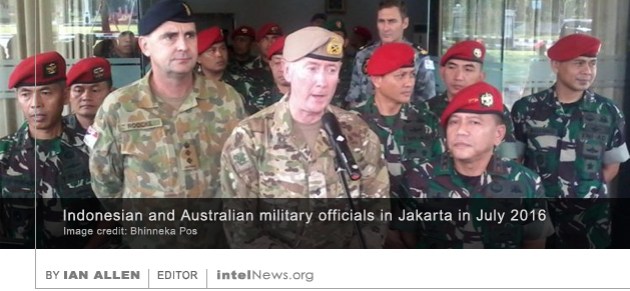 The Indonesian military has halted all forms of cooperation with the armed forces of Australia, with some media reports suggesting that the decision was prompted by fears of espionage. Indonesia and Australia have held joined military training sessions for many decades. In recent weeks, members of the Kopassus, the elite special forces of the Indonesian military, were training on a base in Perth, Australia, with their counterparts in the Australian Special Air Service. On Wednesday, however, the Indonesian government
The Indonesian military has halted all forms of cooperation with the armed forces of Australia, with some media reports suggesting that the decision was prompted by fears of espionage. Indonesia and Australia have held joined military training sessions for many decades. In recent weeks, members of the Kopassus, the elite special forces of the Indonesian military, were training on a base in Perth, Australia, with their counterparts in the Australian Special Air Service. On Wednesday, however, the Indonesian government 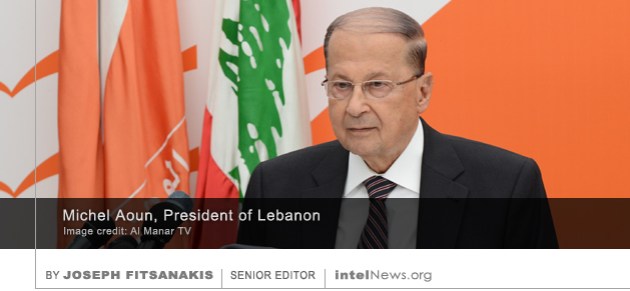 The president of Lebanon said on Wednesday that Israeli intelligence was behind the killing of a Lebanese businessman who was shot dead by a team of assailants last weekend in southwestern Africa. Amine Bakri, 54, who was from southern Lebanon, had lived and worked in Angola since his mid-20s. He was a well-known businessman in the Angola capital Luanda, where he owned a number of factories that make furniture and various medical equipment. On Sunday, Bakri was driving on an unpaved road in the Angolan capital, when his vehicle was ambushed by a group of three armed assailants. According to media reports, one of the men shot the windshield of Bakri’s car and then proceeded to shoot him in the head at close range. The men fled the scene and Bakri was transported to a local hospital, where he soon died from his wounds.
The president of Lebanon said on Wednesday that Israeli intelligence was behind the killing of a Lebanese businessman who was shot dead by a team of assailants last weekend in southwestern Africa. Amine Bakri, 54, who was from southern Lebanon, had lived and worked in Angola since his mid-20s. He was a well-known businessman in the Angola capital Luanda, where he owned a number of factories that make furniture and various medical equipment. On Sunday, Bakri was driving on an unpaved road in the Angolan capital, when his vehicle was ambushed by a group of three armed assailants. According to media reports, one of the men shot the windshield of Bakri’s car and then proceeded to shoot him in the head at close range. The men fled the scene and Bakri was transported to a local hospital, where he soon died from his wounds. A man at the center of the first case of Chinese nuclear espionage in United States history will be pleading guilty on Friday, according to court documents. This could mean that the alleged spy has decided to give the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) details of Chinese nuclear espionage in the US. The accused man is Szuhsiung ‘Allen’ Ho, a Taiwanese-born engineer and naturalized American citizen. Ho was arrested by the FBI in April on charges of sharing American nuclear secrets with the government of China.
A man at the center of the first case of Chinese nuclear espionage in United States history will be pleading guilty on Friday, according to court documents. This could mean that the alleged spy has decided to give the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) details of Chinese nuclear espionage in the US. The accused man is Szuhsiung ‘Allen’ Ho, a Taiwanese-born engineer and naturalized American citizen. Ho was arrested by the FBI in April on charges of sharing American nuclear secrets with the government of China. Since 2008, when we launched intelNews, it has been our end-of-the-year tradition to take a look back and highlight what we think were the most important intelligence-related stories of the past 12 months. In anticipation of what 2017 may bring in this highly volatile field, we present you with our selection of the top spy stories of 2016. They are listed below in reverse order of significance. This is part two in a two-part series; you can access part one
Since 2008, when we launched intelNews, it has been our end-of-the-year tradition to take a look back and highlight what we think were the most important intelligence-related stories of the past 12 months. In anticipation of what 2017 may bring in this highly volatile field, we present you with our selection of the top spy stories of 2016. They are listed below in reverse order of significance. This is part two in a two-part series; you can access part one  There had been rumors for some time about a possible expulsion of Russian diplomats from the United States, in response to alleged Russian interference in the 2016 US Presidential election. The White House confirmed the rumors on Thursday morning, by
There had been rumors for some time about a possible expulsion of Russian diplomats from the United States, in response to alleged Russian interference in the 2016 US Presidential election. The White House confirmed the rumors on Thursday morning, by  Since 2008, when we launched intelNews, it has been our end-of-the-year tradition to take a look back and highlight what we think were the most important intelligence-related stories of the past 12 months. In anticipation of what 2017 may bring in this highly volatile field, we present you with our selection of the top spy stories of 2016. They are listed below in reverse order of significance. This is part one in a two-part series; part two is
Since 2008, when we launched intelNews, it has been our end-of-the-year tradition to take a look back and highlight what we think were the most important intelligence-related stories of the past 12 months. In anticipation of what 2017 may bring in this highly volatile field, we present you with our selection of the top spy stories of 2016. They are listed below in reverse order of significance. This is part one in a two-part series; part two is  United States President Barack Obama has signed a new law that designates $160 million to set up a government center for “countering foreign propaganda and disinformation”. The law authorizes the US departments of State and Defense to work with other federal agencies in establishing the new body. Its precise tasks are not yet known, nor is the role in it —if any— of intelligence agencies, though the Director of National Intelligence is mentioned in the
United States President Barack Obama has signed a new law that designates $160 million to set up a government center for “countering foreign propaganda and disinformation”. The law authorizes the US departments of State and Defense to work with other federal agencies in establishing the new body. Its precise tasks are not yet known, nor is the role in it —if any— of intelligence agencies, though the Director of National Intelligence is mentioned in the  On Saturday, Nigerian President Muhammadu Buhari made a
On Saturday, Nigerian President Muhammadu Buhari made a  Students who have pledged allegiance to North Korea are being taught advanced courses in nuclear physics and control engineering in Japan, which violates United Nations sanctions, according to human rights campaigners. The students take classes at Korea University, a higher-education institution located in in Kodaira, a western suburb of the Japanese capital Tokyo. The University is funded directly by the government of North Korea through Chongryon, a pro-Pyongyang organization otherwise known as the General Association of Korean Residents in Japan. The group represents tens of thousands of ethnic Koreans living in Japan, who are ideologically affiliated with Pyongyang.
Students who have pledged allegiance to North Korea are being taught advanced courses in nuclear physics and control engineering in Japan, which violates United Nations sanctions, according to human rights campaigners. The students take classes at Korea University, a higher-education institution located in in Kodaira, a western suburb of the Japanese capital Tokyo. The University is funded directly by the government of North Korea through Chongryon, a pro-Pyongyang organization otherwise known as the General Association of Korean Residents in Japan. The group represents tens of thousands of ethnic Koreans living in Japan, who are ideologically affiliated with Pyongyang.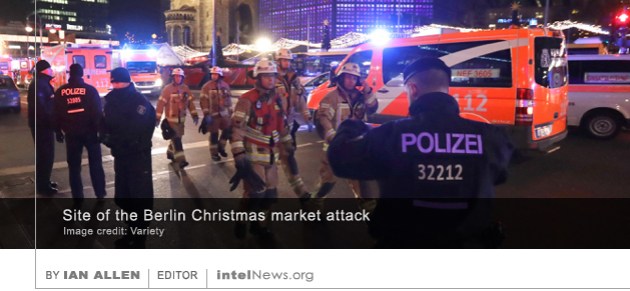 The central suspect in the Berlin Christmas market attack had been on the radar of German security agencies since January of this year, because he had links with radical Islamists and sought to buy guns for a terrorist attack. Anis Amiri, 23, left his native Tunisia in 2011, soon after the outbreak of the so-called Arab Spring there. He lived in Italy for three years before arriving in Germany in July 2015. In April of this year, he applied for an asylum in Germany. According to German authorities, Amiri was arrested multiple times in Tunisia for drug-related offenses. He is also believed to have used at least six different aliases since moving to Europe, and to have claimed to be a citizen of Lebanon and Egypt at different times.
The central suspect in the Berlin Christmas market attack had been on the radar of German security agencies since January of this year, because he had links with radical Islamists and sought to buy guns for a terrorist attack. Anis Amiri, 23, left his native Tunisia in 2011, soon after the outbreak of the so-called Arab Spring there. He lived in Italy for three years before arriving in Germany in July 2015. In April of this year, he applied for an asylum in Germany. According to German authorities, Amiri was arrested multiple times in Tunisia for drug-related offenses. He is also believed to have used at least six different aliases since moving to Europe, and to have claimed to be a citizen of Lebanon and Egypt at different times. Despite persistent silence from Tel Aviv, commentators there seem increasingly convinced that Israeli spies were behind last week’s killing of an aviation engineer who worked for the Palestinian militant group Hamas. The man, Mohamed Zaouari, 49, was a Tunisian national who had spent over a decade creating an innovative aerial drone program for the Palestinian group that controls the Gaza Strip. He was
Despite persistent silence from Tel Aviv, commentators there seem increasingly convinced that Israeli spies were behind last week’s killing of an aviation engineer who worked for the Palestinian militant group Hamas. The man, Mohamed Zaouari, 49, was a Tunisian national who had spent over a decade creating an innovative aerial drone program for the Palestinian group that controls the Gaza Strip. He was  A senior aviation engineer who headed the unmanned aerial vehicle program of the Palestinian militant group Hamas, has been shot dead outside his home in Tunisia by a group of assailants using gun silencers. Mohamed Zaouari, 49, was a Tunisian national who had spent over a decade creating an innovative aerial drone program for Hamas, the Palestinian group that today controls the Gaza Strip. He had lived outside of Tunisia for much of his life, most recently in Syria, where he is believed to have worked as an engineer in a private firm, while also consulting with the Palestinian group. He had returned to Tunisia in 2011, following the upheaval in the country that sparked the so-called Arab Spring.
A senior aviation engineer who headed the unmanned aerial vehicle program of the Palestinian militant group Hamas, has been shot dead outside his home in Tunisia by a group of assailants using gun silencers. Mohamed Zaouari, 49, was a Tunisian national who had spent over a decade creating an innovative aerial drone program for Hamas, the Palestinian group that today controls the Gaza Strip. He had lived outside of Tunisia for much of his life, most recently in Syria, where he is believed to have worked as an engineer in a private firm, while also consulting with the Palestinian group. He had returned to Tunisia in 2011, following the upheaval in the country that sparked the so-called Arab Spring.






Israeli military says Hamas lured its soldiers using online profiles of women
January 12, 2017 by Joseph Fitsanakis Leave a comment
The anonymous IDF spokesman said that, if the soldiers continued to show interest, they were eventually asked by the hackers posing as women to download an application on their mobile telephones that would allow them to converse using video. Once the soldiers downloaded the application, the ‘women’ would find excuses to delay using the application, or the relationships would abruptly end. But the soldiers would leave the application on their telephones. It would then be used by the Hamas hackers to take control of the camera and microphones on the soldiers’ mobile devices. According to the IDF spokesman, dozens of Israeli soldiers were lured by the Hamas scam. No precise number was given.
Media reports suggest that the Hamas hackers were primarily interested in finding out information about IDF maneuvers around the Gaza Strip, the narrow plot of densely inhabited territory that is controlled by the Palestinian militant group. They were also interested in collecting information about the size and weaponry of the Israeli forces around Gaza. Media representatives were told on Wednesday that the operation “had potential for great damage”. But the IDF claims that the harm to its operations was “minimal”, because it primarily targeted low-ranking soldiers. Consequently, according to the Israeli military, the hackers were not able to acquire highly sensitive information.
In 2009, dozens of members of Sweden’s armed forces serving with NATO’s International Security Assistance Force in Afghanistan were found to have been approached via Facebook, and asked to provide details on NATO’s military presence in the country. The Afghan Taliban are believed to have carried out the operation.
Hamas has not commented on the allegations by the IDF.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 12 January 2017 | Permalink
Filed under Expert news and commentary on intelligence, espionage, spies and spying Tagged with cellular telephony, Facebook, Gaza Strip, Hamas, honey traps, IDF, Israel, News, Palestine, social networking