German parliament report on NSA spying contains little consensus
July 3, 2017 Leave a comment
 A lengthy parliamentary report on American intelligence activities in Germany was presented last week in Berlin, but was condemned by opposition parties as insufficient and incomplete, prompting calls for a new investigation. The parliamentary probe was initiated in 2013, following a series of revelations by Edward Snowden, a former employee of the United States Central Intelligence Agency and National Security Agency who defected to Russia. Snowden alleged that both agencies spied on Germany, with the NSA going so far as to eavesdrop on the personal telephone communications of German Chancellor Angela Merkel. The allegations shocked German public opinion, and resulted in the unprecedented expulsion of the CIA station chief in Berlin —the most senior US intelligence official in the country. However, the parliamentary probe soon broadened its scope to include subsequent allegations that German intelligence agencies collaborated with the NSA in spying against other Western countries.
A lengthy parliamentary report on American intelligence activities in Germany was presented last week in Berlin, but was condemned by opposition parties as insufficient and incomplete, prompting calls for a new investigation. The parliamentary probe was initiated in 2013, following a series of revelations by Edward Snowden, a former employee of the United States Central Intelligence Agency and National Security Agency who defected to Russia. Snowden alleged that both agencies spied on Germany, with the NSA going so far as to eavesdrop on the personal telephone communications of German Chancellor Angela Merkel. The allegations shocked German public opinion, and resulted in the unprecedented expulsion of the CIA station chief in Berlin —the most senior US intelligence official in the country. However, the parliamentary probe soon broadened its scope to include subsequent allegations that German intelligence agencies collaborated with the NSA in spying against other Western countries.
Last Wednesday, after three years of work, the parliamentary committee, known officially as the “German Parliamentary Committee Investigating the NSA Spying Scandal”, presented its findings to the Bundestag. They consist of thousands of pages of technical details concerning interception methods and capabilities. However, the final report fails to draw concrete conclusions, and its concluding section does not reflect a consensus among the committee’s members. The section begins by noting that, “unfortunately, despite an initial shared conviction by all parliamentary groups about the need for the investigation, substantial disagreements emerged between the governing and opposition groups, concerning the methodology and goals of the committee’s work”. Read more of this post
 One of Saudi Arabia’s most powerful men, who until last week was first in line to the throne, is reportedly under house arrest. If true, this development would reveal a deep and growing division within the ruling House of Saud. Until the early hours of June 21, Crown Prince Mohammed bin Nayef, 57, was the officially appointed successor to the Saudi ruler, King Salman. In addition to running the country’s feared security services, Prince Nayef was close to Washington, and is a trusted friend of numerous American intelligence officials. But on June 21, King Salman announced radical changes to the line of succession to the throne, stunning the Saudi establishment and international observers alike. The announcement, which came shortly after midnight, completely deposed Prince Nayef from the line of succession.
One of Saudi Arabia’s most powerful men, who until last week was first in line to the throne, is reportedly under house arrest. If true, this development would reveal a deep and growing division within the ruling House of Saud. Until the early hours of June 21, Crown Prince Mohammed bin Nayef, 57, was the officially appointed successor to the Saudi ruler, King Salman. In addition to running the country’s feared security services, Prince Nayef was close to Washington, and is a trusted friend of numerous American intelligence officials. But on June 21, King Salman announced radical changes to the line of succession to the throne, stunning the Saudi establishment and international observers alike. The announcement, which came shortly after midnight, completely deposed Prince Nayef from the line of succession.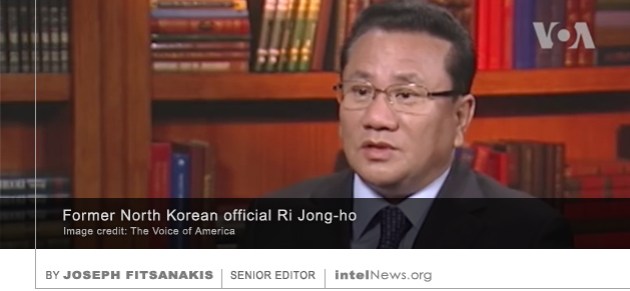 The government of North Korea uses intermediary firms in Singapore to import thousands of tons of Russian oil each year, according to a senior North Korean defector who has spoken publicly for the first time since his defection. Ri Jong-ho was a senior official in the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea under its previous leader, the late Kim Jong-il. He rose through the ranks of the Workers’ Party of Korea and was directly mentored by Kim, who personally appointed him to a post in Bureau 39. The powerful body is in charge of securing much-needed foreign currency for Pyongyang —often through illegal activities— and partly funds the personal accounts of the ruling Kim dynasty.
The government of North Korea uses intermediary firms in Singapore to import thousands of tons of Russian oil each year, according to a senior North Korean defector who has spoken publicly for the first time since his defection. Ri Jong-ho was a senior official in the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea under its previous leader, the late Kim Jong-il. He rose through the ranks of the Workers’ Party of Korea and was directly mentored by Kim, who personally appointed him to a post in Bureau 39. The powerful body is in charge of securing much-needed foreign currency for Pyongyang —often through illegal activities— and partly funds the personal accounts of the ruling Kim dynasty. A senior military intelligence officer, who commanded a Ukrainian special-forces unit that fought against the Russians in eastern Ukraine, was killed on Monday when his car exploded in broad daylight in Kiev. Initially, the Ukrainian government sources simply said that the dead driver of the car was a member of the Ministry of Defense’s Main Directorate of Intelligence. Later, the casualty was
A senior military intelligence officer, who commanded a Ukrainian special-forces unit that fought against the Russians in eastern Ukraine, was killed on Monday when his car exploded in broad daylight in Kiev. Initially, the Ukrainian government sources simply said that the dead driver of the car was a member of the Ministry of Defense’s Main Directorate of Intelligence. Later, the casualty was  American intelligence services have made use of a little-known confidentiality exception to spy on the financial activities of foreign banks who have accounts with the United States Federal Reserve, according to Reuters. Established in 1913, the Federal Reserve System is the central banking structure of the US. It oversees and regulates the nation’s financial institutions, and is tasked with —among other things— maintaining the stability of the American financial system. Additionally, however, the Federal Reserve offers a host of financial services to official (government-owned or sanctioned) foreign institutions. Thus, over 250 foreign banks (typically central banks) from dozens of countries have deposited nearly $3.3 trillion in assets at the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, one of 12 Federal Reserve Banks in the US. Depositing assets at a US Federal Reserve Bank, allows these foreign ‘depository institutions’ to use the US Federal Reserve as a ‘custodial institution’. Through it, they get direct and immediate access to American debt markets, where they can trade directly in dollars — the reserve currency of the global economy.
American intelligence services have made use of a little-known confidentiality exception to spy on the financial activities of foreign banks who have accounts with the United States Federal Reserve, according to Reuters. Established in 1913, the Federal Reserve System is the central banking structure of the US. It oversees and regulates the nation’s financial institutions, and is tasked with —among other things— maintaining the stability of the American financial system. Additionally, however, the Federal Reserve offers a host of financial services to official (government-owned or sanctioned) foreign institutions. Thus, over 250 foreign banks (typically central banks) from dozens of countries have deposited nearly $3.3 trillion in assets at the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, one of 12 Federal Reserve Banks in the US. Depositing assets at a US Federal Reserve Bank, allows these foreign ‘depository institutions’ to use the US Federal Reserve as a ‘custodial institution’. Through it, they get direct and immediate access to American debt markets, where they can trade directly in dollars — the reserve currency of the global economy. General Yuri Ivanovich Drozdov, who held senior positions in the Soviet KGB for 35 years, and handled a global network of Soviet undercover officers from 1979 until 1991,
General Yuri Ivanovich Drozdov, who held senior positions in the Soviet KGB for 35 years, and handled a global network of Soviet undercover officers from 1979 until 1991,  The foreign intelligence service of Germany spied on at least 4,000 targets in the United States from 1998 until 2006, according to a leaked document published yesterday by leading German newsmagazine Der Spiegel. The German investigative weekly said that the surveillance was carried out by the German Federal Intelligence Service, known as BND. The Hamburg-based magazine claimed to have in its possession a list of approximately 4,000 “selector keywords”, unique distinguishing terms, addresses or numbers that identify individual targets for surveillance. The list allegedly includes names, telephone or fax numbers, and email addresses of people that the BND had identified as worthy of individual attention between 1998 and 2006.
The foreign intelligence service of Germany spied on at least 4,000 targets in the United States from 1998 until 2006, according to a leaked document published yesterday by leading German newsmagazine Der Spiegel. The German investigative weekly said that the surveillance was carried out by the German Federal Intelligence Service, known as BND. The Hamburg-based magazine claimed to have in its possession a list of approximately 4,000 “selector keywords”, unique distinguishing terms, addresses or numbers that identify individual targets for surveillance. The list allegedly includes names, telephone or fax numbers, and email addresses of people that the BND had identified as worthy of individual attention between 1998 and 2006. A British court has convicted a lone-wolf female dissident Irish republican, who plotted attacks against police officers after using Facebook to lure two men into joining a fictitious militant organization. Her two male accomplices took their own lives in recent months. The rare case centers on Christine Connor, a 31-year-old resident of Northern Ireland and self-described dissident republican.
A British court has convicted a lone-wolf female dissident Irish republican, who plotted attacks against police officers after using Facebook to lure two men into joining a fictitious militant organization. Her two male accomplices took their own lives in recent months. The rare case centers on Christine Connor, a 31-year-old resident of Northern Ireland and self-described dissident republican. The global reach of the Islamic State through the use of the internet remains “largely intact” despite relentless efforts by some of America’s most advanced cyber warfare experts to neutralize the group’s online presence. It is now over a year since the United States Department of Defense announced that it had launched a cyber war against the Islamic State —the militant Sunni Muslim group that today controls large parts of Syria and Iraq.
The global reach of the Islamic State through the use of the internet remains “largely intact” despite relentless efforts by some of America’s most advanced cyber warfare experts to neutralize the group’s online presence. It is now over a year since the United States Department of Defense announced that it had launched a cyber war against the Islamic State —the militant Sunni Muslim group that today controls large parts of Syria and Iraq.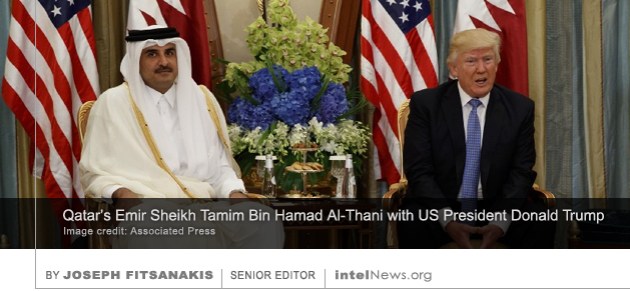 A former director of Qatar’s intelligence agency broke ranks with the government of Qatar and accused Doha of supporting terrorism. He also warned that the United States, which has a base in Qatar, would not allow the presence of foreign troops there.
A former director of Qatar’s intelligence agency broke ranks with the government of Qatar and accused Doha of supporting terrorism. He also warned that the United States, which has a base in Qatar, would not allow the presence of foreign troops there. Secret military assistance from the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia, which violates United Nations sanctions, is helping Libya’s eastern-based rebels prevail in the civil war there, according to a new report. Libya has remained in a state of anarchy since 2011, when a popular uprising backed by the West and its allies led to the demise of the country’s dictator, Muammar Gaddafi. Currently the strongest faction in the post-2011 Libyan Civil War is the eastern-based Tobruk-led Government, which is affiliated with the Libyan National Army (LNA). The commander of the LNA is Field Marshal Khalifa Haftar, an old adversary of Colonel Gaddafi, who lived in the US under Washington’s protection for several decades before returning to Libya in 2011.
Secret military assistance from the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia, which violates United Nations sanctions, is helping Libya’s eastern-based rebels prevail in the civil war there, according to a new report. Libya has remained in a state of anarchy since 2011, when a popular uprising backed by the West and its allies led to the demise of the country’s dictator, Muammar Gaddafi. Currently the strongest faction in the post-2011 Libyan Civil War is the eastern-based Tobruk-led Government, which is affiliated with the Libyan National Army (LNA). The commander of the LNA is Field Marshal Khalifa Haftar, an old adversary of Colonel Gaddafi, who lived in the US under Washington’s protection for several decades before returning to Libya in 2011. New information about carefully targeted attempts by Russian operatives to compromise the November 2016 presidential elections in the United States have emerged in a newly published intelligence document. The document, which dates from May of this year, was produced by the US National Security Agency and
New information about carefully targeted attempts by Russian operatives to compromise the November 2016 presidential elections in the United States have emerged in a newly published intelligence document. The document, which dates from May of this year, was produced by the US National Security Agency and 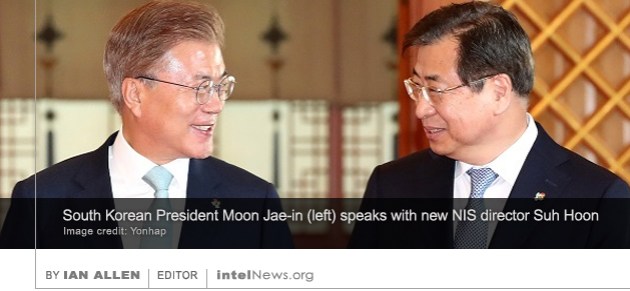 The new president of South Korea has officially banned the country’s spy agency from engaging in domestic intelligence gathering, in a move that some say signals an era of sweeping security reforms in the country. South Korea’s intelligence agency, the National Intelligence Service (NIS) fell into disrepute in recent years, after many of its officers were found to have secretly sided with conservative political candidates for public office. In 2015, the NIS’ former director, Won Sei-hoon, was
The new president of South Korea has officially banned the country’s spy agency from engaging in domestic intelligence gathering, in a move that some say signals an era of sweeping security reforms in the country. South Korea’s intelligence agency, the National Intelligence Service (NIS) fell into disrepute in recent years, after many of its officers were found to have secretly sided with conservative political candidates for public office. In 2015, the NIS’ former director, Won Sei-hoon, was  Russian espionage in the United States has become increasingly sophisticated and brazen, and American counterintelligence professionals are finding it difficult to contain it “after years’ worth of inattention” according to sources.
Russian espionage in the United States has become increasingly sophisticated and brazen, and American counterintelligence professionals are finding it difficult to contain it “after years’ worth of inattention” according to sources. 






Ex-CIA contractor says Pakistan’s leaders helped him escape murder charges
July 4, 2017 by Joseph Fitsanakis 1 Comment
On January 27, 2011, while driving in downtown Lahore, Davis opened fire against two men riding on a motorcycle, killing them instantly. Soon after the incident, Davis appears to have contacted the US consulate in Lahore, which rapidly dispatched a consular vehicle to remove him from the scene of the shooting. However, the vehicle was unable to reach Davis, who was surrounded by an angry crowd. Unable to pick up Davis, the car then returned to the consulate after running down and killing a motorcyclist who was unconnected with the earlier incident. Eventually Davis was arrested and charged with double murder and illegal possession of a firearm. The Pakistani government dismissed Washington’s assertion that Davis was an accredited diplomat, and was thus not subject to Pakistan’s legal system because of his diplomatic immunity. With public opinion in Pakistan heavily against Davis, the case sparked a diplomatic crisis between Washington and Islamabad. Unexpectedly, however, Davis was released in March of the same year, after the families of the two men he killed appeared in court and said they forgave him and wanted him to be pardoned. It later emerged that the families of the murdered men had been given a total of $2.4 million as compensation for their deaths.
Read more of this post
Filed under Expert news and commentary on intelligence, espionage, spies and spying Tagged with book news and reviews, CIA, diplomacy, ISI, News, Pakistan, Raymond Allen Davis, United States