North Korea said to have executed senior nuclear negotiators as ‘spies’
June 3, 2019 Leave a comment
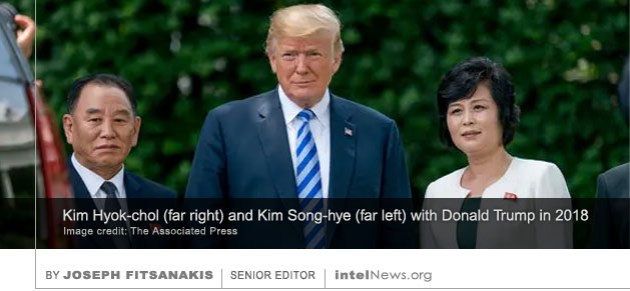 North Korea has executed at least five of its senior nuclear negotiators and imprisoned several others, according to a report in a leading South Korean newspaper. Rumors of executions of North Korean nuclear negotiators have circulated in international diplomatic circles since February, but specific allegations have not surfaced in the news media. That changed on Friday, when Chosun Ilbo, South Korea’s highest-circulation newspaper, said that at least five executions of nuclear negotiators took place in Pyongyang in March.
North Korea has executed at least five of its senior nuclear negotiators and imprisoned several others, according to a report in a leading South Korean newspaper. Rumors of executions of North Korean nuclear negotiators have circulated in international diplomatic circles since February, but specific allegations have not surfaced in the news media. That changed on Friday, when Chosun Ilbo, South Korea’s highest-circulation newspaper, said that at least five executions of nuclear negotiators took place in Pyongyang in March.
According to the paper, the most senior North Korean official to be executed was Kim Hyok-chol (pictured), who led the nuclear negotiations with Washington until February, when the North Korean Supreme Leader Kim Jong-un met US President Donald Trump in Vietnam. Citing an “anonymous source” Chosun Ilbo said on Friday that Kim was executed by a firing squad at the Pyongyang East Airfield in Mirim, a suburb of the North Korean capital. Four other Ministry of Foreign Affairs officials were executed at the same time, allegedly for having been “swayed by American imperialists to betray the Supreme Leader”, said the newspaper. Two more senior North Korean nuclear negotiators, Kim Yong-chol and Kim Song-hye (also pictured), have been stripped of their government posts and sent to labor camps, according to the report. Until recently, Kim Song-hye headed the Bureau of the Committee for the Peaceful Reunification of the Fatherland, Pyongyahg’s main agency for negotiations with South Korea. Kim Yong-chol was one of several vice-chairs of the ruling Workers’ Party of Korea. He visited Washington with Kim Song-hye for negotiations prior to last February’s high-level summit in Vietnam.
There have been no reports in North Korean media about purges of senior officials or executions of alleged spies. However, the three officials named in the Chosun Ilbo report have not been seen in public in nearly a month. Additionally, last week the official Workers’ Party of Korea newspaper, Rodong Sinmun, published an editorial that condemned “counter-party and counter-revolutionary actions” of government officials who “claim to labor for the Supreme Leader […] but clandestinely harbor other machinations behind the back of the Supreme Leader”. The New York Times reached out to the South Korean and American governments about the Chosun Ilbo report, but no-one would comment on record. If the Chosun Ilbo report is accurate, it would support the view that there is exasperation in Pyongyang about the breakdown of its nuclear negotiations with Washington. It would also signify that Kim has radically reshuffled his team of negotiators, but this does not necessarily denote a change in his negotiating stance.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 03 June 2019 | Permalink
 A senior North Korea expert in the United States Central Intelligence Agency, who has been instrumental in the ongoing negotiations between Washington and Pyongyang, has tendered his resignation, according to sources. The official was
A senior North Korea expert in the United States Central Intelligence Agency, who has been instrumental in the ongoing negotiations between Washington and Pyongyang, has tendered his resignation, according to sources. The official was  North Korea offered to stop selling missile technology to Iran and other enemies of Israel in exchange for $1 billion in cash from the Jewish state, according to former senior North Korean diplomat who has now defected. The account of the offer can be read in Password from the Third Floor, a book published earlier this year by Thae Yong Ho. Thae, a member of a prominent North Korean family, defected with his wife and children in 2016, while he was serving as a senior member of the diplomatic staff of the North Korean embassy in London.
North Korea offered to stop selling missile technology to Iran and other enemies of Israel in exchange for $1 billion in cash from the Jewish state, according to former senior North Korean diplomat who has now defected. The account of the offer can be read in Password from the Third Floor, a book published earlier this year by Thae Yong Ho. Thae, a member of a prominent North Korean family, defected with his wife and children in 2016, while he was serving as a senior member of the diplomatic staff of the North Korean embassy in London.  North Korea used its embassy in Berlin to acquire technologies that were almost certainly used to advance its missile and nuclear weapons programs, according to the head of Germany’s counterintelligence agency. For many decades, Pyongyang has used a sophisticated international system of procurement to acquire technologies and material for its conventional and nuclear weapons programs. These secret methods have enabled the country to evade sanctions placed on it by the international community, which wants to foil North Korea’s nuclear aspirations.
North Korea used its embassy in Berlin to acquire technologies that were almost certainly used to advance its missile and nuclear weapons programs, according to the head of Germany’s counterintelligence agency. For many decades, Pyongyang has used a sophisticated international system of procurement to acquire technologies and material for its conventional and nuclear weapons programs. These secret methods have enabled the country to evade sanctions placed on it by the international community, which wants to foil North Korea’s nuclear aspirations. A North Korean nuclear scientist who defected to China but was involuntarily sent back to North Korea in November reportedly killed himself in his North Korean cell hours before he was due to be interrogated. Information about the scientist’s alleged suicide was issued on Thursday by Radio Free Asia (RFA), a multilingual news service based in Washington, DC, which is funded by the United States government. The service said its reporters spoke to an anonymous source in North Hamgyong province, North Korea’s northernmost region that borders China. The source identified the late scientist as Hyun Cheol Huh, but cautioned that this may not be his real name, because the North Korean security services are known to “use […] fake names when referring to important persons” in their custody.
A North Korean nuclear scientist who defected to China but was involuntarily sent back to North Korea in November reportedly killed himself in his North Korean cell hours before he was due to be interrogated. Information about the scientist’s alleged suicide was issued on Thursday by Radio Free Asia (RFA), a multilingual news service based in Washington, DC, which is funded by the United States government. The service said its reporters spoke to an anonymous source in North Hamgyong province, North Korea’s northernmost region that borders China. The source identified the late scientist as Hyun Cheol Huh, but cautioned that this may not be his real name, because the North Korean security services are known to “use […] fake names when referring to important persons” in their custody.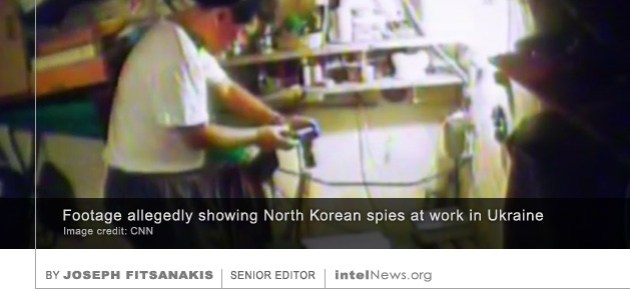 Ukrainian authorities have released rare surveillance footage filmed during a sting operation that ended with the capture of three North Korean spies. The North Koreans, two of whom are now serving prison sentences in Ukraine, had traveled there in 2011 believing they would be given missile technology secrets. Last July, North Korea surprised missile technology experts by successfully testing two intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs). Government-controlled media in Pyongyang claimed that North Korean ICBMs were capable of reaching the United States’ mainland.
Ukrainian authorities have released rare surveillance footage filmed during a sting operation that ended with the capture of three North Korean spies. The North Koreans, two of whom are now serving prison sentences in Ukraine, had traveled there in 2011 believing they would be given missile technology secrets. Last July, North Korea surprised missile technology experts by successfully testing two intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs). Government-controlled media in Pyongyang claimed that North Korean ICBMs were capable of reaching the United States’ mainland. Students who have pledged allegiance to North Korea are being taught advanced courses in nuclear physics and control engineering in Japan, which violates United Nations sanctions, according to human rights campaigners. The students take classes at Korea University, a higher-education institution located in in Kodaira, a western suburb of the Japanese capital Tokyo. The University is funded directly by the government of North Korea through Chongryon, a pro-Pyongyang organization otherwise known as the General Association of Korean Residents in Japan. The group represents tens of thousands of ethnic Koreans living in Japan, who are ideologically affiliated with Pyongyang.
Students who have pledged allegiance to North Korea are being taught advanced courses in nuclear physics and control engineering in Japan, which violates United Nations sanctions, according to human rights campaigners. The students take classes at Korea University, a higher-education institution located in in Kodaira, a western suburb of the Japanese capital Tokyo. The University is funded directly by the government of North Korea through Chongryon, a pro-Pyongyang organization otherwise known as the General Association of Korean Residents in Japan. The group represents tens of thousands of ethnic Koreans living in Japan, who are ideologically affiliated with Pyongyang.










North Korea uses stolen cryptocurrency to fund its missile program, UN report claims
February 7, 2022 by Joseph Fitsanakis Leave a comment
The United Nations imposed sanctions on North Korea in 2006, in response to its announcement that it possessed nuclear weapons. These sanctions have increased over the years, as Pyongyang has continued to advance its nuclear and ballistic missile programs. The sanctions have targeted the communist country’s export industry sectors, including fisheries, textiles, raw materials such as iron, lead and coal, as well as refined energy products.
Now a new report, produced for the United Nations Security Council, suggests that, not only have the sanctions failed to degrade Pyongyang’s nuclear and missile weapons programs, but that the latter actually saw a “marked acceleration” in 2021. The report was delivered last week to the United Nations Security Council by a committee tasked with monitoring the effects of international sanctions on North Korea. According to the Reuters news agency, which accessed the confidential report, it states that North Korea has been able to demonstrate “increased capabilities for rapid deployment, wide mobility (including at sea), and improved resilience of its missile forces”.
Much of this ability comes from funding derived through “cyberattacks, particularly on cryptocurrency assets”, which have now become “an important revenue source” for the North Korean government. These cyberattacks are conducted by North Korean hackers, who regularly target “financial institutions, cryptocurrency firms and exchanges”. According to the report, North Korean hackers were recently able to steal cryptocurrency valued at over $50 million, by attacking just three cryptocurrency exchanges in a period of just 18 months.
The United Nations report comes in the heels of another report, published last month by cybersecurity firm Chainalysis, which alleged that Pyongyang was able to acquire digital assets worth nearly $400 million in 2021 alone. That made 2021 one of the most successful years for North Korean government-sponsored hackers, according to the report. To this one must add cyberattacks that do not target cryptocurrency, which also generate foreign cash supplies for the North Korean government. These generate several hundred million dollars each year, according to research.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 07 February 2022 | Permalink
Filed under Expert news and commentary on intelligence, espionage, spies and spying Tagged with computer hacking, cryptocurrencies, News, North Korea, North Korean nuclear program, United Nations