Did US DEA forces pose as Mexican troops to capture drug kingpin?
July 24, 2015 3 Comments
 The notorious drug lord Joaquín ‘El Chapo’ Guzmán captured the attention of the world’s media a few weeks ago, when he escaped from a maximum security prison in Mexico through a secret tunnel. But his cinematic prison breakout may have overshadowed the story of his arrest, which, according to recent reports, may be as interesting as that of his latest escape from prison.
The notorious drug lord Joaquín ‘El Chapo’ Guzmán captured the attention of the world’s media a few weeks ago, when he escaped from a maximum security prison in Mexico through a secret tunnel. But his cinematic prison breakout may have overshadowed the story of his arrest, which, according to recent reports, may be as interesting as that of his latest escape from prison.
Guzmán was arrested in a pre-dawn raid on February 22, 2014. He was reportedly captured in Mazatlán, a resort town in Mexico’s west-coast state of Sinaloa, by an elite squad of Mexican marines. The marines, we were told at the time, were receiving crucial intelligence support from a several United States government agencies. Or at least that is the official story of the drug kingpin’s arrest. On July 18, however, Mexico’s leading investigative newsmagazine, Proceso, published a lead article alleging that Guzmán was not arrested by Mexican marines, but by American operatives disguised as Mexican marines.
The article was written by J. Jesús Esquivel, a longtime reporter on intelligence and security affairs, who has authored two books on the history of operations conducted by the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA), the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) and other American security and intelligence agencies in Mexico. In his July 18 article, Esquivel says he was told by two American officials —who he does not name— that Mexican marines had little to do with Guzmán’s capture. The drug lord was tracked down by the US Marshals Service and the DEA through a web of informants and electronic tracking devices. Once they knew they had him, he two agencies, supported by a third American agency, which Esquivel does not identify, raided Guzmán’s hotel suite in Mazatlán, dressed in Mexican marine uniforms and driving vehicles bearing Mexican navy insignia.
The Intercept, which covered Proceso’s story on Thursday, correctly stated that, if the newsmagazine’s allegations are true, they would not mark the first time that American government agents posing as Mexican troops have conducted counternarcotics operations in Mexico. The practice has been revealed before, most recently by The Wall Street Journal. But, if true, Proceso’s allegations would seem to indicate an unprecedented degree of operational activity by US intelligence and security agencies south of the border. Additionally, it is alleged that the American agencies deliberately chose to keep their Mexican counterparts in the dark until after Guzmán had been captured, because they feared that the drug kingpin would be notified by informants inside the Mexican government. If this information is accurate, it would indicate that the line separating the Mexican drug cartels from the country’s government remains markedly blurry.
► Author: Ian Allen | Date: 24 July 2015 | Permalink: https://intelnews.org/2015/07/24/01-1742/
 Officials in China think that United States spy agencies are using casinos in Macau to entrap Chinese government employees, according to a report produced on behalf of an American-owned casino chain in the former Portuguese colony. The report was produced by a private investigator and was commissioned by Sands China, the Macau branch of a casino venture owned by American gambling magnate Sheldon Adelson. Its goal was to investigate why the Chinese-appointed authorities in Macau were hostile to the gambling industry in general and Sands China in particular.
Officials in China think that United States spy agencies are using casinos in Macau to entrap Chinese government employees, according to a report produced on behalf of an American-owned casino chain in the former Portuguese colony. The report was produced by a private investigator and was commissioned by Sands China, the Macau branch of a casino venture owned by American gambling magnate Sheldon Adelson. Its goal was to investigate why the Chinese-appointed authorities in Macau were hostile to the gambling industry in general and Sands China in particular. A government prosecutor in France has urged that a probe looking into whether the late Palestinian leader Yasser Arafat was poisoned with a radioactive substance should be dropped, because evidence shows he died of natural causes. Arafat was the founder of Palestinian nationalist group Fatah and led the Palestine Liberation Organization for over three decades before becoming the first president of the Palestinian Authority. He died in November 2004 at the Percy military hospital in Paris, France, weeks after being transferred there from his headquarters in Ramallah, West Bank. His official records indicate that he died from a stroke, which he suffered as a result of a blood disorder known as disseminated intravascular coagulation.
A government prosecutor in France has urged that a probe looking into whether the late Palestinian leader Yasser Arafat was poisoned with a radioactive substance should be dropped, because evidence shows he died of natural causes. Arafat was the founder of Palestinian nationalist group Fatah and led the Palestine Liberation Organization for over three decades before becoming the first president of the Palestinian Authority. He died in November 2004 at the Percy military hospital in Paris, France, weeks after being transferred there from his headquarters in Ramallah, West Bank. His official records indicate that he died from a stroke, which he suffered as a result of a blood disorder known as disseminated intravascular coagulation. A former deputy prime minister of New Zealand, who is heading a major review of intelligence practices in the country, has said in an interview that spy agencies hurt their mission by practicing excessive secrecy. Sir Michael Cullen served as finance minister, education minister and attorney-General before serving as deputy prime minister of New Zealand, from 2002 to 2008. He was recently appointed by the government to co-chair a broad review of state intelligence agencies, with particular focus on updating the applicable legislative framework and evaluating the oversight exercised by lawmakers and the executive. The review is expected to affect the work of New Zealand’s two most visible intelligence agencies, the Security Intelligence Service and the Government Communications and Security Bureau.
A former deputy prime minister of New Zealand, who is heading a major review of intelligence practices in the country, has said in an interview that spy agencies hurt their mission by practicing excessive secrecy. Sir Michael Cullen served as finance minister, education minister and attorney-General before serving as deputy prime minister of New Zealand, from 2002 to 2008. He was recently appointed by the government to co-chair a broad review of state intelligence agencies, with particular focus on updating the applicable legislative framework and evaluating the oversight exercised by lawmakers and the executive. The review is expected to affect the work of New Zealand’s two most visible intelligence agencies, the Security Intelligence Service and the Government Communications and Security Bureau. A suicide note found next to the body of a South Korean intelligence officer mentions a phone hacking scandal that has caused controversy in the country. The 45-year-old man, identified only as “Lim” by South Korean authorities, worked for the country’s primary intelligence organization, the National Intelligence Service (NIS). He was found dead late on Saturday morning inside his car, which had been parked on a deserted rural road on the outskirts of South Korean capital Seoul. According to local reports, authorities found a metal plate with burnt-out coal inside his car, which had been locked from the inside. Finding no apparent marks on his body, the police have ruled his death a suicide.
A suicide note found next to the body of a South Korean intelligence officer mentions a phone hacking scandal that has caused controversy in the country. The 45-year-old man, identified only as “Lim” by South Korean authorities, worked for the country’s primary intelligence organization, the National Intelligence Service (NIS). He was found dead late on Saturday morning inside his car, which had been parked on a deserted rural road on the outskirts of South Korean capital Seoul. According to local reports, authorities found a metal plate with burnt-out coal inside his car, which had been locked from the inside. Finding no apparent marks on his body, the police have ruled his death a suicide. The final piece of sealed testimony in one of the most important espionage cases of the Cold War has been released, 64 years after it was given. The case led to the execution in 1953 of Julius and Ethel Rosenberg, an American couple who were convicted of spying for the Soviet Union. The Rosenbergs were arrested in 1950 for being members of a larger Soviet-handled spy ring, which included Ethel’s brother, David Greenglass. Greenglass agreed to testify for the US government in order to save his life, as well as the life of his wife, Ruth, who was also involved in the spy ring. He subsequently fingered Julius Rosenberg as a courier and recruiter for the Soviets, and Ethel as the person who retyped the content of classified documents before they were surrendered to their handlers. That piece of testimony from Greenglass the primary evidence used to convict and execute the Rosenbergs.
The final piece of sealed testimony in one of the most important espionage cases of the Cold War has been released, 64 years after it was given. The case led to the execution in 1953 of Julius and Ethel Rosenberg, an American couple who were convicted of spying for the Soviet Union. The Rosenbergs were arrested in 1950 for being members of a larger Soviet-handled spy ring, which included Ethel’s brother, David Greenglass. Greenglass agreed to testify for the US government in order to save his life, as well as the life of his wife, Ruth, who was also involved in the spy ring. He subsequently fingered Julius Rosenberg as a courier and recruiter for the Soviets, and Ethel as the person who retyped the content of classified documents before they were surrendered to their handlers. That piece of testimony from Greenglass the primary evidence used to convict and execute the Rosenbergs. A leaked document from an American intelligence agency appears to confirm that Israeli commandos were behind the assassination of a top Syrian government official, who was shot dead outside his luxury villa on the Syrian coast in 2008. Muhammad Suleiman had been a close aide of current Syrian President Bashar al-Assad even before the latter rose to power in 2000. Once al-Assad became ruler of Syria, Suleiman was appointed special presidential advisor in the areas of arms procurement and strategic weapons. He handled intelligence affairs for the Assad regime and he was involved in weapons transfers from Iran to the Lebanese militant group Hezbollah, while also helping train Hezbollah operatives. He was also rumored to have a senior administrative role in the Syrian nuclear weapons program.
A leaked document from an American intelligence agency appears to confirm that Israeli commandos were behind the assassination of a top Syrian government official, who was shot dead outside his luxury villa on the Syrian coast in 2008. Muhammad Suleiman had been a close aide of current Syrian President Bashar al-Assad even before the latter rose to power in 2000. Once al-Assad became ruler of Syria, Suleiman was appointed special presidential advisor in the areas of arms procurement and strategic weapons. He handled intelligence affairs for the Assad regime and he was involved in weapons transfers from Iran to the Lebanese militant group Hezbollah, while also helping train Hezbollah operatives. He was also rumored to have a senior administrative role in the Syrian nuclear weapons program. A lawsuit against Britain’s Security Service (MI5) by a former spy, who in the 1980s infiltrated the Provisional Irish Republican Army, commonly known as IRA, is to be judged in secret, a court in London has decided. The spy, Martin McGartland, of Belfast, Northern Ireland, was recruited by the Special Branch of the Royal Ulster Constabulary in the mid-1980s. The information he supplied to the security agencies over several years is widely credited with having saved the lives of at least 50 British police officers and soldiers. His autobiographical experiences formed the basis of the 2008 motion picture 50 Dead Men Walking.
A lawsuit against Britain’s Security Service (MI5) by a former spy, who in the 1980s infiltrated the Provisional Irish Republican Army, commonly known as IRA, is to be judged in secret, a court in London has decided. The spy, Martin McGartland, of Belfast, Northern Ireland, was recruited by the Special Branch of the Royal Ulster Constabulary in the mid-1980s. The information he supplied to the security agencies over several years is widely credited with having saved the lives of at least 50 British police officers and soldiers. His autobiographical experiences formed the basis of the 2008 motion picture 50 Dead Men Walking.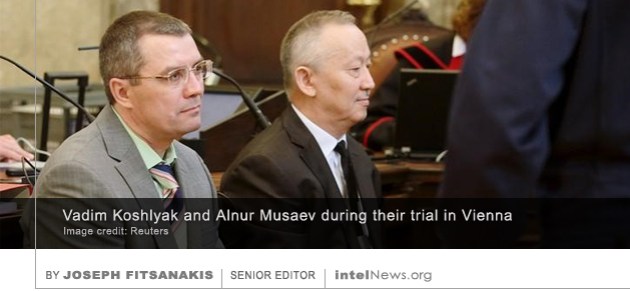 Kazakhstan’s former spy chief and a former presidential bodyguard have been acquitted by an Austrian jury, five months after a co-defendant in their double-murder trial, who was also the Kazakh president’s former son-in-law, was found dead in his Vienna cell. As intelNews has written
Kazakhstan’s former spy chief and a former presidential bodyguard have been acquitted by an Austrian jury, five months after a co-defendant in their double-murder trial, who was also the Kazakh president’s former son-in-law, was found dead in his Vienna cell. As intelNews has written  The head of the main intelligence agency of the island state of Cyprus has resigned after an invoice leaked online showed that the agency made several purchases of controversial surveillance software. Andreas Pentaras, who has led the Cyprus Intelligence Service (KYP) since 2013,
The head of the main intelligence agency of the island state of Cyprus has resigned after an invoice leaked online showed that the agency made several purchases of controversial surveillance software. Andreas Pentaras, who has led the Cyprus Intelligence Service (KYP) since 2013,  A Patriot missile system stationed in Turkey by the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) was allegedly hacked by a remote source, according to reports. German magazine Behörden Spiegel
A Patriot missile system stationed in Turkey by the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) was allegedly hacked by a remote source, according to reports. German magazine Behörden Spiegel  A fortnight ago, I gave an
A fortnight ago, I gave an  On July 2, 2015, the Dutch government released for public consultation a long-awaited bill that overhauls the Dutch Intelligence and Security Act of 2002. Known also as Wiv2002, the Act is the legal framework for the operations of the General Intelligence and Security Service (AIVD) and the Military Intelligence and Security Service (MIVD). The bill is a complete rewrite of the present law, and includes expansions of power, as well as changes to the approval regime and oversight. The below provides a brief overview focused on the interception and hacking powers.
On July 2, 2015, the Dutch government released for public consultation a long-awaited bill that overhauls the Dutch Intelligence and Security Act of 2002. Known also as Wiv2002, the Act is the legal framework for the operations of the General Intelligence and Security Service (AIVD) and the Military Intelligence and Security Service (MIVD). The bill is a complete rewrite of the present law, and includes expansions of power, as well as changes to the approval regime and oversight. The below provides a brief overview focused on the interception and hacking powers. A Soviet double spy, who secretly defected to Britain 30 years ago this month, has revealed for the first time the details of his exfiltration by British intelligence in 1985. Oleg Gordievsky was one of the highest Soviet intelligence defectors to the West in the closing stages of the Cold War. He joined the Soviet KGB in 1963, eventually reaching the rank of colonel. But in the 1960s, while serving in the Soviet embassy in Copenhagen, Denmark, Gordievsky began feeling disillusioned about the Soviet system. His doubts were reinforced by the Soviet invasion of Czechoslovakia in 1968. It was soon afterwards that he made the decision to contact British intelligence.
A Soviet double spy, who secretly defected to Britain 30 years ago this month, has revealed for the first time the details of his exfiltration by British intelligence in 1985. Oleg Gordievsky was one of the highest Soviet intelligence defectors to the West in the closing stages of the Cold War. He joined the Soviet KGB in 1963, eventually reaching the rank of colonel. But in the 1960s, while serving in the Soviet embassy in Copenhagen, Denmark, Gordievsky began feeling disillusioned about the Soviet system. His doubts were reinforced by the Soviet invasion of Czechoslovakia in 1968. It was soon afterwards that he made the decision to contact British intelligence.






US spy for Israel ‘may be released’ as part of Iran nuclear deal
July 27, 2015 by Joseph Fitsanakis Leave a comment
The Wall Street Journal published an article on Friday suggesting that the Obama administration was “preparing to release” Pollard. Citing unnamed US officials, the paper said Washington hoped that the move would “smooth [America’s] relations with Israel in the wake of the Iran nuclear deal”. The latter was signed earlier this month between Tehran and the so-called P5+1 nations, namely the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council plus Germany. The New York Times added to the speculation on Saturday with a detailed front-page article, which confirmed that “some in Washington appear to be highlighting” Pollard’s upcoming 30-year parole hearing, which is set to take place in November. It added that the White House was contemplating using Pollard’s release to appease, not only Tel Aviv, but also pro-Israel supporters in Congress, many of whom have campaigned for years in favor of Pollard’s release.
But the paper also cautioned that linking a possible release of the jailed American spy with the Iranian nuclear deal was risky and could in fact provoke a serious backlash. It quoted Israeli and American analysts who said that, although Israel was in the past prepared to accept Pollard’s release in exchange for minor concessions in its conflict with the Palestinians, the coalition government of Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu considers the nuclear agreement with Iran to be “too serious a threat” to concede to, no matter what the trade-off is from Washington. Some Israeli commentators used strong words to describe Washington’s alleged plan to release Pollard as a way of appeasing Israel, describing it as “cynical, cheap and misguided”.
The Times said it contacted the US National Security Council on Friday and was told by a spokesman that there was “absolutely zero linkage between Mr. Pollard’s status and foreign policy considerations”.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 27 July 2015 | Permalink: https://intelnews.org/2015/07/27/01-1743/
Filed under Expert news and commentary on intelligence, espionage, spies and spying Tagged with double agents, Iranian nuclear program, Israel, Jonathan Jay Pollard, News, United States