Islamic State’s online footprint declines drastically, experts say
October 26, 2018 Leave a comment
 The online arm of the Islamic State, which was once one of the organization’s most noticeable trademarks, has declined markedly in 2018, according to expert observers in the United States and elsewhere. This is especially applicable to the militant group’s online propaganda and recruitment campaign, which appears to have effectively ceased, say experts.
The online arm of the Islamic State, which was once one of the organization’s most noticeable trademarks, has declined markedly in 2018, according to expert observers in the United States and elsewhere. This is especially applicable to the militant group’s online propaganda and recruitment campaign, which appears to have effectively ceased, say experts.
According to The Washington Times newspaper, most information warfare experts at the United States Department of Defense believe that very little is left of the Islamic State’s once sizeable Web and social-media presence. The paper said that, according to the US Pentagon, the total media footprint of the group —which is also known as the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS)— has diminished by as much as 83 percent since its peak in 2015. Online activity measured by the US Pentagon includes posts on social media by Islamic State members and commanders, as well as professionally produced pro-ISIS images and videos aired on YouTube and other image- and video-based online platforms. It also includes material from the Islamic State’s press bureau, the Amaq News Agency, which in previous years produced hundreds of pro-ISIS videos.
Experts told The Washington Times that the Islamic State’s online footprint has shrunk as a result of the group’s loss of its territory. The loss of ISIS’ physical bases in the Middle East has resulted in the death of many of the group’s online propagandists. Those who survived are currently hiding or fleeing from the authorities, fearing arrest or death. This has “crushed [the militant Sunni group’s] ability to mount a coordinated Web-based strategy”, said The Washington Times. The military attacks against ISIS continue to take place alongside an “aggressive counterstrategy in cyberspace”, said the paper, which is being led by the US Pentagon and its allies. This has included the successful targeting of thousands of social media accounts belonging to ISIS members and supporters, as well as complex hacking operations. The US Pentagon also coordinates the delivery of online content that counters the Islamic State’s narrative and messages.
But some experts warned the paper that the Islamic State continues to recruit members online and that the group’s online recruitment efforts are not completely a thing of the past. In fact, new ISIS-sponsored content continues to appear online regularly, they said. In September of this year alone, the Islamic State released 12 different videos, mostly aimed at recruiting new members. Additionally, the militant group continues to use Facebook, YouTube, and other popular online social media platforms, experts warned.
► Author: Ian Allen | Date: 26 October 2018 | Permalink
 Officials in the White House are concerned about President Donald Trump’s insistence on using an unsecured iPhone to communicate with friends and associates, despite warnings that foreign spies may be listening in. Prior to being elected president, Trump used an Android phone, made by Google, which the NSA advised him to abandon due to security concerns. That is when he switched to using iPhones. Since his election to the presidency, Trump has routinely used three iPhone cell phones. He uses one of them to access a limited list of authorized applications, including Twitter. He uses the second iPhone for phone calls, but cannot use it to send texts, take pictures, or download and install applications. Both of these iPhones have been vetted and secured by the National Security Agency (NSA).
Officials in the White House are concerned about President Donald Trump’s insistence on using an unsecured iPhone to communicate with friends and associates, despite warnings that foreign spies may be listening in. Prior to being elected president, Trump used an Android phone, made by Google, which the NSA advised him to abandon due to security concerns. That is when he switched to using iPhones. Since his election to the presidency, Trump has routinely used three iPhone cell phones. He uses one of them to access a limited list of authorized applications, including Twitter. He uses the second iPhone for phone calls, but cannot use it to send texts, take pictures, or download and install applications. Both of these iPhones have been vetted and secured by the National Security Agency (NSA). A French government report warns of an “unprecedented threat” to security after nearly 4,000 leading French civil servants, scientists and senior executives were found to have been accosted by Chinese spies using the popular social media network LinkedIn. The report was authored by France’s main intelligence agencies, the General Directorate for Internal Security (DGSI) and the General Directorate for External Security (DGSE). According to the Paris-based Le Figaro newspaper, which
A French government report warns of an “unprecedented threat” to security after nearly 4,000 leading French civil servants, scientists and senior executives were found to have been accosted by Chinese spies using the popular social media network LinkedIn. The report was authored by France’s main intelligence agencies, the General Directorate for Internal Security (DGSI) and the General Directorate for External Security (DGSE). According to the Paris-based Le Figaro newspaper, which  Russian espionage activities in Switzerland are increasing and are crossing long-established “red lines”, according to senior Swiss defense and intelligence officials who spoke at a news conference last week. The claims were made by Guy Parmelin, head of Switzerland’s Federal Department of Defense, and Jean-Philippe Gaudin, director of the Swiss Federal Intelligence Service (NDB). The two men spoke on Friday before reporters in Bern. Following the news conference, Gaudin spoke with reporters from the Reuters news agency.
Russian espionage activities in Switzerland are increasing and are crossing long-established “red lines”, according to senior Swiss defense and intelligence officials who spoke at a news conference last week. The claims were made by Guy Parmelin, head of Switzerland’s Federal Department of Defense, and Jean-Philippe Gaudin, director of the Swiss Federal Intelligence Service (NDB). The two men spoke on Friday before reporters in Bern. Following the news conference, Gaudin spoke with reporters from the Reuters news agency. The government of Iran is smuggling parts for ballistic missiles to Lebanon, where they are secretly assembled in clandestine factories operated by the Shiite militant group Hezbollah, according to Israel’s former spy chief. For several months now, the international news agency Reuters has been
The government of Iran is smuggling parts for ballistic missiles to Lebanon, where they are secretly assembled in clandestine factories operated by the Shiite militant group Hezbollah, according to Israel’s former spy chief. For several months now, the international news agency Reuters has been  The hardline former director of Pakistan’s military intelligence agency is preparing to take the helm of the country’s powerful spy agency, the Inter-Services Intelligence directorate (ISI). Lieutenant General Asim Munir, who has spent more than two decades as a career military officer, has been officially appointed as director-general of ISI. In one of his first notable assignments, Munir served as a military attaché in Pakistan’s embassy in Saudi Arabia. After being promoted to a two-star general, he was appointed commander of Force Command Northern Areas in Gilgit-Baltistan, Pakistan’s northernmost region. The area borders Jammu and Kashmir, an autonomous Indian-administered region, which the Pakistanis claim belongs to them. Gilgit-Baltistan is also a strategic geopolitical corridor that connects Pakistan with one of its major regional allies, China.
The hardline former director of Pakistan’s military intelligence agency is preparing to take the helm of the country’s powerful spy agency, the Inter-Services Intelligence directorate (ISI). Lieutenant General Asim Munir, who has spent more than two decades as a career military officer, has been officially appointed as director-general of ISI. In one of his first notable assignments, Munir served as a military attaché in Pakistan’s embassy in Saudi Arabia. After being promoted to a two-star general, he was appointed commander of Force Command Northern Areas in Gilgit-Baltistan, Pakistan’s northernmost region. The area borders Jammu and Kashmir, an autonomous Indian-administered region, which the Pakistanis claim belongs to them. Gilgit-Baltistan is also a strategic geopolitical corridor that connects Pakistan with one of its major regional allies, China. Officials in the Czech Republic have announced that the country’s spy agency headed an operation in several countries, aimed at neutralizing a cyberespionage network operated by the Lebanese militant group Hezbollah. Early last week, the Security Information Service (BIS), the primary domestic national intelligence agency of the Czech Republic, issued a short
Officials in the Czech Republic have announced that the country’s spy agency headed an operation in several countries, aimed at neutralizing a cyberespionage network operated by the Lebanese militant group Hezbollah. Early last week, the Security Information Service (BIS), the primary domestic national intelligence agency of the Czech Republic, issued a short  There were conflicting reports yesterday in Ankara of an alleged evacuation of Iran’s ambassador to Turkey, following credible reports of a suicide bomb attack, possibly by the Islamic State. Several Turkish media outlets reported on Monday afternoon that authorities in Ankara had communicated an urgent intelligence warning to the Iranian embassy there of a possible suicide bomb attack. According to the
There were conflicting reports yesterday in Ankara of an alleged evacuation of Iran’s ambassador to Turkey, following credible reports of a suicide bomb attack, possibly by the Islamic State. Several Turkish media outlets reported on Monday afternoon that authorities in Ankara had communicated an urgent intelligence warning to the Iranian embassy there of a possible suicide bomb attack. According to the  The government of Pakistan has dismissed a High Court judge who accused the country’s powerful intelligence agency of interfering with the judicial process in order to rig the outcome of last July’s general election. On July 25, the governing center-right Pakistan Muslim League – Nawaz (PML-N) was unseated by the conservative-centrist Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf, headed by former cricket star Imran Khan. The elections took place amidst a corruption scandal that saw Nawaz Sharif, former prime minister of Pakistan and leading member of PML-N, arrested on charges of fraud. Sharif was charged following the release of the so-called
The government of Pakistan has dismissed a High Court judge who accused the country’s powerful intelligence agency of interfering with the judicial process in order to rig the outcome of last July’s general election. On July 25, the governing center-right Pakistan Muslim League – Nawaz (PML-N) was unseated by the conservative-centrist Pakistan Tehreek-e-Insaf, headed by former cricket star Imran Khan. The elections took place amidst a corruption scandal that saw Nawaz Sharif, former prime minister of Pakistan and leading member of PML-N, arrested on charges of fraud. Sharif was charged following the release of the so-called 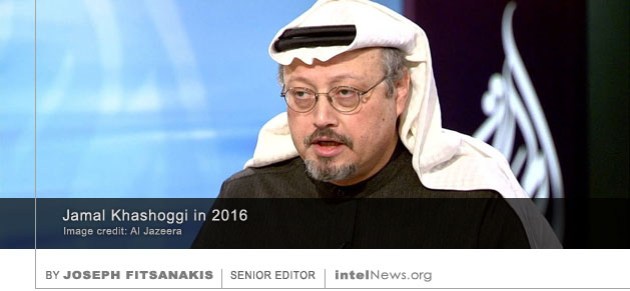 American intelligence agencies have evidence that the Saudi royal family tried to lure The Washington Post journalist Jamal Khashoggi back to Saudi Arabia, in order to capture him, according to sources. Khashoggi, 59, is a Saudi government adviser who in 2015 became a critic of the kingdom’s style of governance. He moved to the United States, from where he began to criticize Saudi Arabia’s involvement in the civil war in Yemen, its support for the repression of political freedoms in Egypt, and other issues. He also joined the staff of The Washington Post and penned columns in which he criticized Saudi policies. He has been missing since Tuesday, when he visited the Saudi consulate in Istanbul. He went there for a scheduled appointment in order to be issued a document certifying his divorce from his former wife in Saudi Arabia.
American intelligence agencies have evidence that the Saudi royal family tried to lure The Washington Post journalist Jamal Khashoggi back to Saudi Arabia, in order to capture him, according to sources. Khashoggi, 59, is a Saudi government adviser who in 2015 became a critic of the kingdom’s style of governance. He moved to the United States, from where he began to criticize Saudi Arabia’s involvement in the civil war in Yemen, its support for the repression of political freedoms in Egypt, and other issues. He also joined the staff of The Washington Post and penned columns in which he criticized Saudi policies. He has been missing since Tuesday, when he visited the Saudi consulate in Istanbul. He went there for a scheduled appointment in order to be issued a document certifying his divorce from his former wife in Saudi Arabia. A leading suspect in a failed attempt to kill Venezuelan President Nicolas Maduro using drones, has died in mysterious circumstances while being held by the country’s intelligence agency. The
A leading suspect in a failed attempt to kill Venezuelan President Nicolas Maduro using drones, has died in mysterious circumstances while being held by the country’s intelligence agency. The  Russia’s minister of foreign affairs has downplayed the arrest and expulsion of four Russian military intelligence officers in Holland last April, saying that the incident was caused by a “misunderstanding”. Last Thursday, the US government named and indicted seven officers of the Main Directorate of the General Staff of Russia’s Armed Forces, known as GRU. The seven are
Russia’s minister of foreign affairs has downplayed the arrest and expulsion of four Russian military intelligence officers in Holland last April, saying that the incident was caused by a “misunderstanding”. Last Thursday, the US government named and indicted seven officers of the Main Directorate of the General Staff of Russia’s Armed Forces, known as GRU. The seven are  A new report by the British government alleges that the so-called ‘Cyber Caliphate’, the online hacker wing of the Islamic State, is one of several supposedly non-state groups that are in fact operated by the Russian state. The group calling itself Cyber Caliphate first appeared in early 2014, purporting to operate as the online wing of the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS), which was later renamed Islamic State. Today the Cyber Caliphate boasts a virtual army of hackers from dozens of countries, who are ostensibly operating as the online arm of the Islamic State. Their known activities include a strong and often concentrated social media presence, as well as computer hacking, primarily in the form of cyber espionage and cyber sabotage.
A new report by the British government alleges that the so-called ‘Cyber Caliphate’, the online hacker wing of the Islamic State, is one of several supposedly non-state groups that are in fact operated by the Russian state. The group calling itself Cyber Caliphate first appeared in early 2014, purporting to operate as the online wing of the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS), which was later renamed Islamic State. Today the Cyber Caliphate boasts a virtual army of hackers from dozens of countries, who are ostensibly operating as the online arm of the Islamic State. Their known activities include a strong and often concentrated social media presence, as well as computer hacking, primarily in the form of cyber espionage and cyber sabotage.






Britain knew of Saudi plan to target journalist, warned Saudis against it
October 29, 2018 by Joseph Fitsanakis 9 Comments
Now a new report claims that Britain’s external intelligence agency, the Secret Intelligence Service (MI6), was aware of a plot by the Saudi government to kidnap Khashoggi in order to silence him. British newspaper The Sunday Express says it has evidence from “high ranking intelligence sources” that MI6 was in possession of communications intercepts containing conversations about Khashoggi. The conversations were between Saudi government officials and officers of the General Intelligence Directorate (GID), the Kingdom’s primary spy agency. In the intercepts, a member of the Saudi royal family is allegedly heard giving orders for the GID to kidnap Khashoggi from Turkey sometime in early September. He also instructs the GID to secretly transport the dissident journalist to Saudi soil where he could be interrogated. During the conversation, a discussion took place about the possibility that Khashoggi would physically resist his abductors. At that point in the conversation, the high ranking intelligence source told The Express, the royal family member “left the door open for alternative remedies […] should Khashoggi be troublesome”.
The paper reports that MI6 “became aware” of the arrival of a 15-member Saudi hit squad in Istanbul on October 1, a day before Khashoggi went missing. According to the paper’s source “it was pretty clear what their aim was”, so MI6 contacted the GID directly and warned the Saudi spy agency to “cancel the mission”, said the source. However, the source added, “this request was ignored”. On October 10, The Washington Post, the newspaper that employed Khashoggi, said that American intelligence agencies had evidence that the Saudi royal family tried to lure The Washington Post journalist Jamal Khashoggi back to Saudi Arabia, in order to capture him.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 29 October 2018 | Permalink
Filed under Expert news and commentary on intelligence, espionage, spies and spying Tagged with disappearances, human rights, Istanbul, Jamal Khashoggi, MI6, News, Saudi Arabia, Saudi Arabian consulate in Istanbul, suspicious deaths