Outgoing CIA director acknowledges US killed ‘couple of hundred’ Russians in Syria
April 13, 2018 1 Comment
 The outgoing director of the Central Intelligence Agency, Mike Pompeo, appeared on Thursday to confirm reports from last February that United States troops killed more than 200 Russian soldiers in Syria. According to sources from the US Pentagon, the armed confrontation took place on February 7, when a 500-strong Syrian government force crossed the Euphrates River and entered Kurdish-controlled territory in Syria’s northeastern Deir al-Zour region. US-supported Kurdish forces in the area, which include embedded American troops, responded with artillery fire, while US military aircraft also launched strikes on the Syrian government forces. The latter withdrew across the Euphrates after suffering heavy losses. The US side estimated at the time that over 100 attackers had been left dead, with another 200-300 injured. The toll later rose to several hundred dead.
The outgoing director of the Central Intelligence Agency, Mike Pompeo, appeared on Thursday to confirm reports from last February that United States troops killed more than 200 Russian soldiers in Syria. According to sources from the US Pentagon, the armed confrontation took place on February 7, when a 500-strong Syrian government force crossed the Euphrates River and entered Kurdish-controlled territory in Syria’s northeastern Deir al-Zour region. US-supported Kurdish forces in the area, which include embedded American troops, responded with artillery fire, while US military aircraft also launched strikes on the Syrian government forces. The latter withdrew across the Euphrates after suffering heavy losses. The US side estimated at the time that over 100 attackers had been left dead, with another 200-300 injured. The toll later rose to several hundred dead.
At a press conference held soon after the armed clash, US Secretary of Defense James Mattis refused to discuss the matter, which he referred to as “perplexing”. Bloomberg said at the time that American officials were “in talks” with Russian counterparts “in search of an explanation for what happened”. On Thursday, however, Pompeo appeared to acknowledge that US troops killed hundreds of Russians in Deir al-Zour. The outgoing CIA director was speaking before a committee of the US Senate, during a hearing pertaining to his nomination to serve as the next US secretary of state. He was making the point that the administration of US President Donald Trump had maintained a hardline policy on Russia. After referring to the recent expulsions of 60 Russian diplomats from the US, Pompeo said: “in Syria, now, a handful of weeks ago the Russians met their match. A couple of hundred Russians were killed”.
Pompeo’s comments were seen by the media as an acknowledgement by a senior US government official of the incident in Deir al-Zour, which has remained shrouded in mystery since it happened. Later in his speech, Pompeo said that the Kremlin had “not yet gotten the full message about US determination to block aggression from Moscow. We need to continue to work at that”, he said.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 13 April 2018 | Permalink
 The head of Germany’s domestic intelligence agency has warned of security risks resulting from Chinese direct investment in high-technology German and other European companies. Since 2012, Hans-Georg Maassen has served as director of the Federal Office for the Protection of the Constitution, Germany’s domestic security and counterintelligence agency.
The head of Germany’s domestic intelligence agency has warned of security risks resulting from Chinese direct investment in high-technology German and other European companies. Since 2012, Hans-Georg Maassen has served as director of the Federal Office for the Protection of the Constitution, Germany’s domestic security and counterintelligence agency. 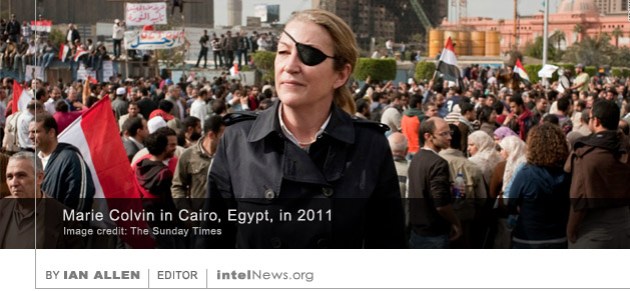 The Syrian government tracked down and killed American journalist Marie Colvin in order to stop her from reporting about the Syrian Civil War, according to a Syrian intelligence officer who has defected to Europe. Colvin was an experienced war correspondent who worked for The Sunday Times. The British newspaper sent her to Syria soon after the outbreak of the war. From there, she gave live interviews to media outlets such as CNN and the BBC. But on the morning of February 22, 2012, Colvin was killed along with French war photographer Remi Ochlik. Their death came when Syrian government forces repeatedly shelled a media center in the city of Homs, which housed the two reporters.
The Syrian government tracked down and killed American journalist Marie Colvin in order to stop her from reporting about the Syrian Civil War, according to a Syrian intelligence officer who has defected to Europe. Colvin was an experienced war correspondent who worked for The Sunday Times. The British newspaper sent her to Syria soon after the outbreak of the war. From there, she gave live interviews to media outlets such as CNN and the BBC. But on the morning of February 22, 2012, Colvin was killed along with French war photographer Remi Ochlik. Their death came when Syrian government forces repeatedly shelled a media center in the city of Homs, which housed the two reporters. The British government may relocate Sergei Skripal, the Russian double spy who appears to have survived an assassination attempt in England, to the United States, in an effort to protect him from further attacks. The BBC
The British government may relocate Sergei Skripal, the Russian double spy who appears to have survived an assassination attempt in England, to the United States, in an effort to protect him from further attacks. The BBC  The government of Taiwan has acknowledged publicly for the first time that a Chinese major general, who was executed by Beijing in 1999 for espionage, was indeed one of its spies. The military officer was Liu Liankun, a logistician for the Chinese People’s Liberation Army, who headed its Department of General Logistics. However, China arrested Liu for espionage in 1999, and accused him of having spied for Taiwan for five years, in exchange for money. At the time, Taiwan denied that Liu spied on its behalf and refused to acknowledge that it had any role in the major general’s alleged espionage activities.
The government of Taiwan has acknowledged publicly for the first time that a Chinese major general, who was executed by Beijing in 1999 for espionage, was indeed one of its spies. The military officer was Liu Liankun, a logistician for the Chinese People’s Liberation Army, who headed its Department of General Logistics. However, China arrested Liu for espionage in 1999, and accused him of having spied for Taiwan for five years, in exchange for money. At the time, Taiwan denied that Liu spied on its behalf and refused to acknowledge that it had any role in the major general’s alleged espionage activities. The United States government has for the first time admitted publicly that it has detected devices known to be used by foreign intelligence services to spy on cellular communications in the nation’s capital. Known commonly as Stingrays, after a leading hardware brand, these devices are primarily used by government agencies, including law enforcement. But they can be purchased by anyone with anywhere from $1,000 to $200,000 to spare. They work by simulating the activity of legitimate cell towers and tricking cell phones into communicating with them. That allows the users of these cellphone-site simulators to monitor the physical whereabouts of targeted cell phones. Some of the more expensive Stingray models can intercept the actual content of telephone conversations and can even plant Trojans on the compromised phones of unsuspecting users.
The United States government has for the first time admitted publicly that it has detected devices known to be used by foreign intelligence services to spy on cellular communications in the nation’s capital. Known commonly as Stingrays, after a leading hardware brand, these devices are primarily used by government agencies, including law enforcement. But they can be purchased by anyone with anywhere from $1,000 to $200,000 to spare. They work by simulating the activity of legitimate cell towers and tricking cell phones into communicating with them. That allows the users of these cellphone-site simulators to monitor the physical whereabouts of targeted cell phones. Some of the more expensive Stingray models can intercept the actual content of telephone conversations and can even plant Trojans on the compromised phones of unsuspecting users. The collapse of the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria is giving rise to a host of successor groups, which are quickly regrouping, recruiting members and launching increasingly sophisticated attacks against government forces, according to experts. A military victory in the war against ISIS was officially declared by the Iraqi government in December of last year. In recent weeks, United States President Donald Trump has repeated his government’s claim that American forces are “knocking the hell out of ISIS”. The Sunni militant group, which rose to prominence in 2014 after conquering much of Syria and northwestern Iraq, is clearly on the retreat, having lost every major urban center that it used to control. However, the collapse of the organization has led to the emergence of numerous insurgent groups that are quickly forming in Iraq and Syria.
The collapse of the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria is giving rise to a host of successor groups, which are quickly regrouping, recruiting members and launching increasingly sophisticated attacks against government forces, according to experts. A military victory in the war against ISIS was officially declared by the Iraqi government in December of last year. In recent weeks, United States President Donald Trump has repeated his government’s claim that American forces are “knocking the hell out of ISIS”. The Sunni militant group, which rose to prominence in 2014 after conquering much of Syria and northwestern Iraq, is clearly on the retreat, having lost every major urban center that it used to control. However, the collapse of the organization has led to the emergence of numerous insurgent groups that are quickly forming in Iraq and Syria. A surge in the activity of Russian intelligence personnel on United States soil has caused American spy agencies to rehire retired Russia specialists,
A surge in the activity of Russian intelligence personnel on United States soil has caused American spy agencies to rehire retired Russia specialists,  Though unprecedented in size, the recent expulsions of over 150 diplomats by nearly 30 countries and organizations around the world have hardly made a dent on Russia’s huge diplomatic footprint. The
Though unprecedented in size, the recent expulsions of over 150 diplomats by nearly 30 countries and organizations around the world have hardly made a dent on Russia’s huge diplomatic footprint. The  Britain secured the largest expulsion of Russian diplomats in history by sharing “unprecedented degrees of intelligence” with dozens of foreign countries about the attempted killing of former spy Sergei Skripal. Nearly 30 countries and international organizations, including the European Union and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, have expelled or refused to accredit over
Britain secured the largest expulsion of Russian diplomats in history by sharing “unprecedented degrees of intelligence” with dozens of foreign countries about the attempted killing of former spy Sergei Skripal. Nearly 30 countries and international organizations, including the European Union and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, have expelled or refused to accredit over  Relations between Russia and much of the West reached a new low on Monday, with the expulsion of over 100 Russian diplomats from two dozen countries around the world. The unprecedented expulsions were publicized on Monday with a series of coordinated announcements issued from nearly every European capital, as well as from Washington, Ottawa and Canberra. By the early hours of Tuesday, the number of Russian diplomatic expulsions had reached 118 —not counting the 23 Russian so-called “undeclared intelligence officers” that were expelled from Britain last week. Further expulsions of Russian diplomats are expected in the coming days.
Relations between Russia and much of the West reached a new low on Monday, with the expulsion of over 100 Russian diplomats from two dozen countries around the world. The unprecedented expulsions were publicized on Monday with a series of coordinated announcements issued from nearly every European capital, as well as from Washington, Ottawa and Canberra. By the early hours of Tuesday, the number of Russian diplomatic expulsions had reached 118 —not counting the 23 Russian so-called “undeclared intelligence officers” that were expelled from Britain last week. Further expulsions of Russian diplomats are expected in the coming days. predecessor, Barack Obama, and his Secretary of State Hillary Clinton, who is known for her hardline anti-Russian stance. In Europe, the move to expel dozens of Russian envoys from 23 different countries —most of them European Union members— was a rare act of unity that surprised European observers as much as it did the Russians.
predecessor, Barack Obama, and his Secretary of State Hillary Clinton, who is known for her hardline anti-Russian stance. In Europe, the move to expel dozens of Russian envoys from 23 different countries —most of them European Union members— was a rare act of unity that surprised European observers as much as it did the Russians. Sergei Skripal, the Russian double agent who was poisoned with a military-grade nerve agent in England earlier this month, wrote to the Kremlin asking to return to Russia, according to one of his old school friends. Skripal, 66, and his daughter Yulia, 33, remain in critical condition in hospital, three weeks after being
Sergei Skripal, the Russian double agent who was poisoned with a military-grade nerve agent in England earlier this month, wrote to the Kremlin asking to return to Russia, according to one of his old school friends. Skripal, 66, and his daughter Yulia, 33, remain in critical condition in hospital, three weeks after being  For the past year, the Netherlands has had a new law governing its two secret services, the AIVD and the MIVD. The new Intelligence and Security Services Act (Wet op de inlichtingen- en veiligheidsdiensten or Wiv) was and still is heavily criticized, especially because it allows untargeted access to cable-bound telephone and internet traffic. Under the previous law, which dates from 2002, the intelligence services were only allowed to conduct bulk interception of wireless transmissions, like satellite and radio communications —besides of course the traditional targeted telephone and internet taps aimed at individual targets.
For the past year, the Netherlands has had a new law governing its two secret services, the AIVD and the MIVD. The new Intelligence and Security Services Act (Wet op de inlichtingen- en veiligheidsdiensten or Wiv) was and still is heavily criticized, especially because it allows untargeted access to cable-bound telephone and internet traffic. Under the previous law, which dates from 2002, the intelligence services were only allowed to conduct bulk interception of wireless transmissions, like satellite and radio communications —besides of course the traditional targeted telephone and internet taps aimed at individual targets.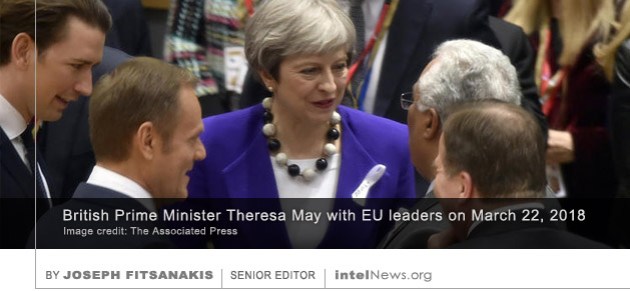 The European Union has recalled its ambassador to Moscow in an apparent response to the poisoning of Sergei Skripal, a Russian double agent, who was attacked with a nerve agent in England earlier this month. Skripal, 66, and his daughter Yulia, 33, remain in critical condition in hospital, nearly three weeks after being poisoned with a nerve agent that British scientists say belongs to Russia’s Cold-War-era chemical stockpiles. Moscow has angrily rejected claims that Skripal, who spied for Britain in the early 2000s, was on a Kremlin-approved hit-list of defectors. But British Prime Minister Theresa May traveled to Brussels on Thursday to brief European Union heads of state about the attack on Skripal.
The European Union has recalled its ambassador to Moscow in an apparent response to the poisoning of Sergei Skripal, a Russian double agent, who was attacked with a nerve agent in England earlier this month. Skripal, 66, and his daughter Yulia, 33, remain in critical condition in hospital, nearly three weeks after being poisoned with a nerve agent that British scientists say belongs to Russia’s Cold-War-era chemical stockpiles. Moscow has angrily rejected claims that Skripal, who spied for Britain in the early 2000s, was on a Kremlin-approved hit-list of defectors. But British Prime Minister Theresa May traveled to Brussels on Thursday to brief European Union heads of state about the attack on Skripal.






Russian ex-spy sees link between Skripal and GCHQ officer found dead in 2010
April 16, 2018 by Joseph Fitsanakis 3 Comments
But eight years ago, another mysterious attack on a spy in Britain drew the attention of the world’s media. Gareth Williams, a mathematician in the employment of Britain’s signals intelligence agency, GCHQ, had been seconded to the Secret Intelligence Service (MI6), Britain’s external intelligence agency, to help automate intelligence collection. He had also worked with United States agencies, including the Federal Bureau of Investigation and the National Security Agency. But his career came to an abrupt end in August 2010, when he was found dead inside a padlocked sports bag at his home in Pimlico, London. It remains unknown whether his death resulted from an attack by assailants.
Last weekend, however, Boris Karpichkov, a former intelligence officer in the Soviet KGB and its post-Soviet successor, the FSB, said that Williams was killed by the Russian state. Karpichkov, 59, joined the KGB in 1984, but became a defector-in-place for Latvian intelligence in 1991, when the Soviet Union disintegrated. He claims to have also spied on Russia for French and American intelligence. In 1998, carrying two suitcases filled with top-secret Russian government documents, and using forged passports, he arrived with his family in Britain, where he has lived ever since. In an interview with the British tabloid newspaper The Sunday People, Karpichkov said that Williams was killed by Russian intelligence operatives with an untraceable poison substance, because he had discovered the identity of a Russian agent within his agency, the GCHQ. According to Karpichkov, Williams had befriended the mole, codenamed ORION by the Russians, and had realized that he was working for the Russians. The mole then allegedly told his Russian handler, a non-official-cover officer with an Eastern European passport, codenamed LUKAS, that Williams had grown suspicious. Read more of this post
Filed under Expert news and commentary on intelligence, espionage, spies and spying Tagged with assassinations, Boris Karpichkov, Gareth Williams, News, Pimlico (London), Russia, Sergei Skripal, suspicious deaths, UK