Western spies used ‘crown jewel’ of espionage tools to hack into Russia’s Google
June 28, 2019 Leave a comment
 Hackers used a malware described by experts as the “crown jewel” of cyber-espionage tools to hack into Russia’s version of Google, in an effort to breach user accounts, according to the Reuters news agency. The hackers targeted Yandex (Яндекс), a Moscow-headquartered company that operates as the Russian version of Google. Yandex is the largest technology venture company in the Russian Federation and the fifth most popular search engine in the world. It also provides services such as mapping and email in Russia and several other countries in Central Asia and the Middle East. It claims that it serves more than 150 million monthly users worldwide.
Hackers used a malware described by experts as the “crown jewel” of cyber-espionage tools to hack into Russia’s version of Google, in an effort to breach user accounts, according to the Reuters news agency. The hackers targeted Yandex (Яндекс), a Moscow-headquartered company that operates as the Russian version of Google. Yandex is the largest technology venture company in the Russian Federation and the fifth most popular search engine in the world. It also provides services such as mapping and email in Russia and several other countries in Central Asia and the Middle East. It claims that it serves more than 150 million monthly users worldwide.
On Thursday, Reuters cited “four people with knowledge on the matter […] in Russia and elsewhere”, who said that Yandex was targeted by a sophisticated hacking operation between October and November of 2018. The news agency said that three of its sources had direct knowledge of the details of the cyber-espionage operation against Yandex. According to the unnamed sources, the hackers appeared to be primarily interested in breaching the accounts of specific employees in Yandex’s research and development unit. Their purpose was to acquire technical information about how Yandex authenticates user accounts. That information could potentially enable them to impersonate Yandex users and access private information, including email messages, geolocation information, and other sensitive private data. Reuters said that the hackers attempted to breach Yandex for purposes of espionage, not sabotage or disruption, or stealing intellectual property for commercial purposes.
Moreover, the hackers used Regin, a highly sophisticated malware that a technical expert from the Symantec Corporation described as “the crown jewel of attack frameworks used for espionage”. Regin was identified as a malware employed by intelligence services of the so-called Five Eyes intelligence alliance between spy agencies of the United Kingdom, Canada, New Zealand, Australia and the United States. It was identified as a Western cyber-espionage tool in 2014, based on revelations made by Edward Snowden, the American former employee of the National Security Agency and the Central Intelligence Agency who defected to Russia. The same malware was used in 2013 to access about a dozen mainframe computers of Belgacom, Belgium’s largest telecommunications service provider, which is partly state-owned. The attack was widely attributed to a consortium of Western intelligence services led by the NSA.
According to Reuters, the hackers were able to penetrate Yandex’s networks for several weeks or longer, without being noticed by the company’s cyber-security monitors. When the penetration was detected, Yandex hired a cyber-security team from the Russian anti-virus firm Kaspersky. The Kaspersky team identified Regin and, according to Reuters, concluded that the hackers behind the cyber-espionage operation were tied to Western intelligence agencies. Kaspersky, the Russian government, and intelligence agencies from the Five Eyes alliance declined requests by Reuters to comment on the story. Yandex confirmed the cyber-espionage attack in a statement to Reuters, but said that its cyber-security experts had been able to detect and “fully neutralize [it] before any damage was done”. Consequently, said Yandex, “no user data was compromised in the attack”.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 28 June 2019 | Permalink
 A group of hackers, allegedly working for the Chinese military, accessed thousands of classified diplomatic cables from the European Union during a protracted cyber-espionage operation, a report has revealed. Over 100 organizations are believed to have been targeted in the multi-year cyber-espionage campaign, including the United Nations, international labor groups, as well as government ministries from dozens of countries. The operation was revealed on Tuesday by Area 1, a cyber-security company founded by former officials of the United States National Security Agency, and
A group of hackers, allegedly working for the Chinese military, accessed thousands of classified diplomatic cables from the European Union during a protracted cyber-espionage operation, a report has revealed. Over 100 organizations are believed to have been targeted in the multi-year cyber-espionage campaign, including the United Nations, international labor groups, as well as government ministries from dozens of countries. The operation was revealed on Tuesday by Area 1, a cyber-security company founded by former officials of the United States National Security Agency, and  The main domestic intelligence agency of the Czech Republic has accused Russia of “the most serious wave of cyberespionage” to target the country in recent years. The claim was made on Monday in Prague by the Security Information Service (BIS), the primary domestic national intelligence agency of the Czech Republic. Details of the alleged cyberespionage plot are included in the BIS’
The main domestic intelligence agency of the Czech Republic has accused Russia of “the most serious wave of cyberespionage” to target the country in recent years. The claim was made on Monday in Prague by the Security Information Service (BIS), the primary domestic national intelligence agency of the Czech Republic. Details of the alleged cyberespionage plot are included in the BIS’  Russia’s minister of foreign affairs has downplayed the arrest and expulsion of four Russian military intelligence officers in Holland last April, saying that the incident was caused by a “misunderstanding”. Last Thursday, the US government named and indicted seven officers of the Main Directorate of the General Staff of Russia’s Armed Forces, known as GRU. The seven are
Russia’s minister of foreign affairs has downplayed the arrest and expulsion of four Russian military intelligence officers in Holland last April, saying that the incident was caused by a “misunderstanding”. Last Thursday, the US government named and indicted seven officers of the Main Directorate of the General Staff of Russia’s Armed Forces, known as GRU. The seven are  Supporters of the Islamic State, most of them Persian speakers, were spied on by the government of Iran after they downloaded a fake smartphone application with wallpaper images, according to an online security firm. Iran is a major adversary of the radical Sunni group Islamic State. The latter considers Shiism (Iran’s state religion) as an abomination. Not surprisingly, therefore, the Islamic State, which is also known as the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS), relies largely on supporters from the Arabic-speaking regions of the Levant. But according to estimates, Sunnis constitute about 10 percent of Iran’s population, and ISIS has found some fertile ground among Iran’s 8 million-strong Sunni minority. As a result, the government in Tehran is highly mistrustful of Iranian Sunnis, many of whom are ethnic Kurds, Baluchis, Azeris or Turkomans, and systematically spies on them.
Supporters of the Islamic State, most of them Persian speakers, were spied on by the government of Iran after they downloaded a fake smartphone application with wallpaper images, according to an online security firm. Iran is a major adversary of the radical Sunni group Islamic State. The latter considers Shiism (Iran’s state religion) as an abomination. Not surprisingly, therefore, the Islamic State, which is also known as the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS), relies largely on supporters from the Arabic-speaking regions of the Levant. But according to estimates, Sunnis constitute about 10 percent of Iran’s population, and ISIS has found some fertile ground among Iran’s 8 million-strong Sunni minority. As a result, the government in Tehran is highly mistrustful of Iranian Sunnis, many of whom are ethnic Kurds, Baluchis, Azeris or Turkomans, and systematically spies on them. An American cyber security firm has reported the discovery of a previously undetected, “highly active” Iranian cyber espionage group, whose extensive target list consists mainly of large organizations and companies in the Middle East. The cyber security firm Symantec, makers of Norton antivirus software, which uncovered the cyber espionage group’s existence, has dubbed it “Leafminer”. It said the group has been active since the beginning of 2017, but has “significantly ramped up its activities” in 2018 and is currently involved in dozens of ongoing attacks.
An American cyber security firm has reported the discovery of a previously undetected, “highly active” Iranian cyber espionage group, whose extensive target list consists mainly of large organizations and companies in the Middle East. The cyber security firm Symantec, makers of Norton antivirus software, which uncovered the cyber espionage group’s existence, has dubbed it “Leafminer”. It said the group has been active since the beginning of 2017, but has “significantly ramped up its activities” in 2018 and is currently involved in dozens of ongoing attacks. The head of Germany’s domestic intelligence agency has warned of security risks resulting from Chinese direct investment in high-technology German and other European companies. Since 2012, Hans-Georg Maassen has served as director of the Federal Office for the Protection of the Constitution, Germany’s domestic security and counterintelligence agency.
The head of Germany’s domestic intelligence agency has warned of security risks resulting from Chinese direct investment in high-technology German and other European companies. Since 2012, Hans-Georg Maassen has served as director of the Federal Office for the Protection of the Constitution, Germany’s domestic security and counterintelligence agency. 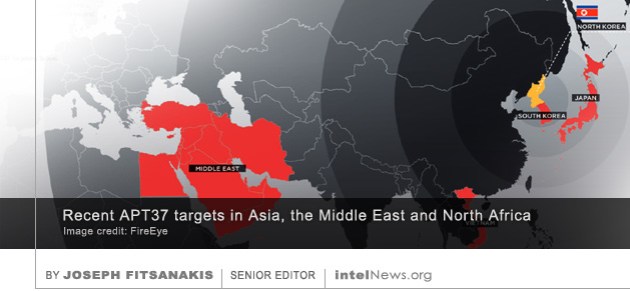 A little-known North Korean cyber espionage group has widened its scope and increased its sophistication in the past year, and now threatens targets worldwide, according to a new report by a leading cyber security firm. Since 2010, most cyber-attacks by North Korean hackers have been attributed to a group dubbed “Lazarus” by cyber security specialists. The Lazarus Group is thought to have perpetrated the infamous Sony Pictures attacks in 2014, and the worldwide wave or ransomware attacks dubbed WannaCry by experts in 2017. It is widely believed that the Lazarus Group operates on behalf of the government of North Korea. Most of its operations constitute destructive attacks —mostly cyber sabotage— and financial criminal activity.
A little-known North Korean cyber espionage group has widened its scope and increased its sophistication in the past year, and now threatens targets worldwide, according to a new report by a leading cyber security firm. Since 2010, most cyber-attacks by North Korean hackers have been attributed to a group dubbed “Lazarus” by cyber security specialists. The Lazarus Group is thought to have perpetrated the infamous Sony Pictures attacks in 2014, and the worldwide wave or ransomware attacks dubbed WannaCry by experts in 2017. It is widely believed that the Lazarus Group operates on behalf of the government of North Korea. Most of its operations constitute destructive attacks —mostly cyber sabotage— and financial criminal activity.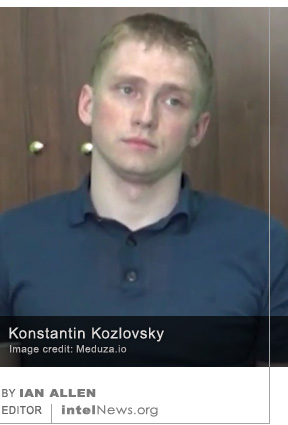 A member of a prolific Russian hacker group reportedly stated in court that he was hired by the Russian government to break into the computer systems of the Democratic Party in the United States. The hacker, Konstantin Kozlovsky, operated online as a member of Lurk, a notorious hacker group whose members are believed to have stolen in excess of $45 million from hundreds of companies since 2011. Most of the group’s members were apprehended in a
A member of a prolific Russian hacker group reportedly stated in court that he was hired by the Russian government to break into the computer systems of the Democratic Party in the United States. The hacker, Konstantin Kozlovsky, operated online as a member of Lurk, a notorious hacker group whose members are believed to have stolen in excess of $45 million from hundreds of companies since 2011. Most of the group’s members were apprehended in a  A cyber espionage group that has alarmed security researchers by its careful targeting of government agencies has links to the Iranian state, according to a new report. The existence of the group calling itself CopyKittens was first confirmed publicly in November of 2015. Since that time, forensic analyses of cyber attacks against various targets have indicated that the group has been active since at least early 2013. During that time, CopyKittens has carefully targeted agencies or officials working for Jordan, Saudi Arabia, Turkey, Israel, the United States, and Germany, among other countries. It has also targeted specific offices and officials working for the United Nations.
A cyber espionage group that has alarmed security researchers by its careful targeting of government agencies has links to the Iranian state, according to a new report. The existence of the group calling itself CopyKittens was first confirmed publicly in November of 2015. Since that time, forensic analyses of cyber attacks against various targets have indicated that the group has been active since at least early 2013. During that time, CopyKittens has carefully targeted agencies or officials working for Jordan, Saudi Arabia, Turkey, Israel, the United States, and Germany, among other countries. It has also targeted specific offices and officials working for the United Nations. The same group cyber-spies that attacked the campaign of French presidential candidate Emmanuel Macron is now attacking German institutions that are connected to the country’s ruling coalition parties, according to a report by a leading cyber-security firm. The Tokyo-based security software company Trend Micro published a 41-page report on Tuesday, in which it tracks and traces the attacks against French and German political targets over the past two years. The report, entitled
The same group cyber-spies that attacked the campaign of French presidential candidate Emmanuel Macron is now attacking German institutions that are connected to the country’s ruling coalition parties, according to a report by a leading cyber-security firm. The Tokyo-based security software company Trend Micro published a 41-page report on Tuesday, in which it tracks and traces the attacks against French and German political targets over the past two years. The report, entitled  A new report authored by a consortium of government and private organizations in Britain has revealed the existence of a computer hacking operation, allegedly based in China, that is said to be “one of the largest ever” such campaigns globally. The operation is believed to have compromised sensitive information from an inestimable number of private companies in Southeast Asia, Europe and the United States. The
A new report authored by a consortium of government and private organizations in Britain has revealed the existence of a computer hacking operation, allegedly based in China, that is said to be “one of the largest ever” such campaigns globally. The operation is believed to have compromised sensitive information from an inestimable number of private companies in Southeast Asia, Europe and the United States. The  A United States federal contractor, who remains in detention following his arrest last summer for stealing classified documents, may have worked for an elite cyber espionage unit of the National Security Agency. The man was
A United States federal contractor, who remains in detention following his arrest last summer for stealing classified documents, may have worked for an elite cyber espionage unit of the National Security Agency. The man was 






Attack by Chinese hacker group targeted high-profile individuals around the world
July 9, 2019 by Joseph Fitsanakis 2 Comments
The operation is thought to have compromised close to a dozen major global telecommunications carriers in four continents —the Middle East, Europe, Asia and Africa. According to Cybereason, the hackers launched persistent multi-wave attacks on their targets, which gave them “complete takeover” of the networks. However, they did not appear to be interested in financial gain, but instead focused their attention on the call detail records (CDRs) of just 20 network users. With the help of the CDRs, the hackers were able to track their targets’ movements around the world and map their contacts based on their telephone activity. According to The Wall Street Journal, which reported on Cybereason’s findings, the 20 targets consisted of senior business executives and government officials. Others were Chinese dissidents, military leaders, as well as law enforcement and intelligence officials.
An especially impressive feature of SOFTCELL was that the hackers attacked new telecommunications carriers as their targets moved around the world and made use of new service providers. The attacks thus followed the movements of specific targets around the world. Although this is not a new phenomenon in the world of cyberespionage, the geographical scope and persistence of the attacks are unprecedented, said The Wall Street Journal. Speaking last week at the 9th Annual International Cybersecurity Conference in Tel Aviv, Israel, Lior Div, Cybereason’s chief executive officer and co-founder, said SOFTCELL attacks occurred in waves over the course of several months. The hackers used a collection of techniques that are commonly associated with identified Chinese hacker groups. If detected and repelled, the hackers would retreat for a few weeks or months before returning and employing new methods. The Cybereason security experts said that they were unable to name the targeted telecommunications carriers and users “due to multiple and various limitations”.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 09 July 2019 | Permalink
Filed under Expert news and commentary on intelligence, espionage, spies and spying Tagged with APT10, China, Cybereason, cyberespionage, cybersecurity, News, Operation SOFTCELL, telecommunication service providers