German parliament may sue government to access British spy files
June 19, 2015 Leave a comment
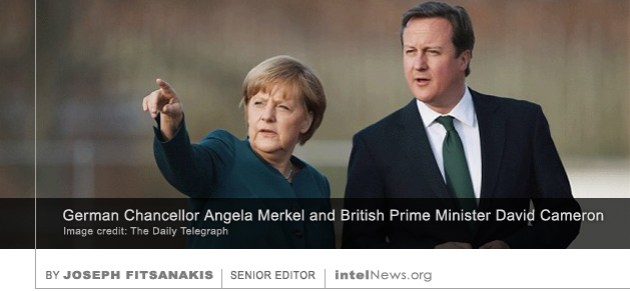 A German parliamentary committee investigating spying operations may take the German government to court in order to force it to give up secret documents on Berlin’s intelligence cooperation with Britain. The Committee of Inquiry into Intelligence Operations was set up in 2014, after files leaked by American defector Edward Snowden revealed 1 that the United States had been spying on the telephone communications of German Chancellor Angela Merkel. But the scope of the committee expanded earlier this year, when it emerged that, while being spied upon by the US and Britain, Germany also collaborated 2 with American and British intelligence agencies in order to spy on France and other European countries.
A German parliamentary committee investigating spying operations may take the German government to court in order to force it to give up secret documents on Berlin’s intelligence cooperation with Britain. The Committee of Inquiry into Intelligence Operations was set up in 2014, after files leaked by American defector Edward Snowden revealed 1 that the United States had been spying on the telephone communications of German Chancellor Angela Merkel. But the scope of the committee expanded earlier this year, when it emerged that, while being spied upon by the US and Britain, Germany also collaborated 2 with American and British intelligence agencies in order to spy on France and other European countries.
Last week, the German Office of the Federal Prosecutor concluded 3 its criminal investigation into alleged espionage operations by the US National Security Agency against Chancellor Merkel. German officials said they had to drop the probe because of the unwillingness of US government officials to share information on the subject. But the parliamentary committee continues the inquiry on the related subject of Germany’s intelligence cooperation with the Britain and the US. The committee’s chairman, Dr. Patrick Sensburg, said on Thursday that his team of investigators would consider “going to court” in order to force the German government to release all relevant documents. Speaking 4 to the British newspaper The Daily Telegraph, Dr. Sensburg said that the parliamentary inquiry had a right to investigate intelligence cooperation between Berlin and London.
However, as intelNews reported 5 in February, the British government is said to have warned Germany that all intelligence cooperation between the two countries will be terminated should classified information about British intelligence operations be shared with an inquiry. Dr. Sensburg was asked by The Telegraph whether reports of the British warnings were true, but he responded that he was unable to comment on the matter.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 19 June 2015 | Permalink: https://intelnews.org/2015/06/18/01-1718/
- J. FITSANAKIS “US surveillance or Merkel’s phone prompts angry German reaction” intelNews [24oct2013] ↩
- J. FITSANAKIS “Airbus to sue Germany for helping US spy on its operations” intelNews [01may2015] ↩
- T. SCHLEIFER “Germany drops probe into U.S. spying on Merkel” cnn [13jun2015] ↩
- J. HUGGLER “German spy inquiry could demand access to British secrets” The Daily Telegraph [18jun2015] ↩
- J. FITSANAKIS “Britain threatens to stop intelligence cooperation with Germany” intelNews [13feb2015] ↩
 A German investigator, who is probing the downing of a civilian airliner over Ukraine nearly a year ago, says that an informant has claimed a multimillion reward for information pointing to those responsible for the attack. The investigator, Josef Resch, of Lübeck, Germany, says that a binding non-disclosure agreement does not allow him to reveal his client, who offered the $47 million reward. But he told German business magazine Capital that he is hopeful his client will soon reveal the details, since “people who pay that kind of money in exchange for information do not keep it for themselves”. However, he also hinted that his client may be an intelligence agency, who may decide to “deal with the matter without fanfare”.
A German investigator, who is probing the downing of a civilian airliner over Ukraine nearly a year ago, says that an informant has claimed a multimillion reward for information pointing to those responsible for the attack. The investigator, Josef Resch, of Lübeck, Germany, says that a binding non-disclosure agreement does not allow him to reveal his client, who offered the $47 million reward. But he told German business magazine Capital that he is hopeful his client will soon reveal the details, since “people who pay that kind of money in exchange for information do not keep it for themselves”. However, he also hinted that his client may be an intelligence agency, who may decide to “deal with the matter without fanfare”. Australian law enforcement and intelligence agencies routinely use paid informants in Indonesia and Pakistan as part of a decade-old covert war against human traffickers in the Indian Ocean. This information has been revealed by The Australian newspaper in response to
Australian law enforcement and intelligence agencies routinely use paid informants in Indonesia and Pakistan as part of a decade-old covert war against human traffickers in the Indian Ocean. This information has been revealed by The Australian newspaper in response to  A Russian former intelligence officer, who is accused by the British government of having killed a former KGB spy in London, has agreed to testify at a public inquiry to be held in the British capital next month. British government prosecutors believe Russian businessman Dmitri Kovtun, who worked for the KGB during the Cold War, poisoned his former colleague in the KGB, Alexander Litvinenko, in 2006. Litvinenko was an officer in the Soviet KGB and one of its successor organizations, the FSB, until 2000, when he defected with his family to the United Kingdom. He soon became known as a vocal critic of the administration of Russian President Vladimir Putin. In 2006, Litvinenko came down with radioactive poisoning soon after meeting Kovtun and another former KGB officer, Andrey Lugovoy, at a London restaurant. He was dead less than two weeks later.
A Russian former intelligence officer, who is accused by the British government of having killed a former KGB spy in London, has agreed to testify at a public inquiry to be held in the British capital next month. British government prosecutors believe Russian businessman Dmitri Kovtun, who worked for the KGB during the Cold War, poisoned his former colleague in the KGB, Alexander Litvinenko, in 2006. Litvinenko was an officer in the Soviet KGB and one of its successor organizations, the FSB, until 2000, when he defected with his family to the United Kingdom. He soon became known as a vocal critic of the administration of Russian President Vladimir Putin. In 2006, Litvinenko came down with radioactive poisoning soon after meeting Kovtun and another former KGB officer, Andrey Lugovoy, at a London restaurant. He was dead less than two weeks later. American Congressional lawmakers have voted to cut funding for the Central Intelligence Agency’s secret operations in Syria, in a surprise move that indicates growing concern on Capitol Hill with Washington’s strategy on the Syrian Civil War. The CIA’s involvement in the Syrian Civil War began in 2012, when US President Barack Obama
American Congressional lawmakers have voted to cut funding for the Central Intelligence Agency’s secret operations in Syria, in a surprise move that indicates growing concern on Capitol Hill with Washington’s strategy on the Syrian Civil War. The CIA’s involvement in the Syrian Civil War began in 2012, when US President Barack Obama 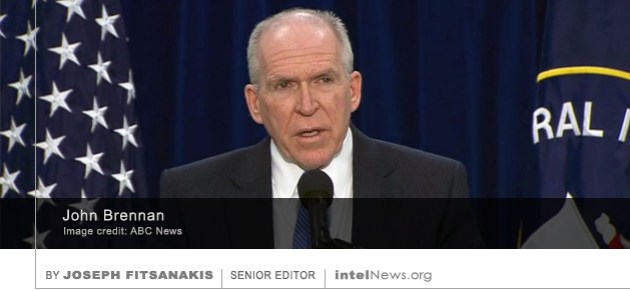 The director of the United States Central Intelligence Agency visited Israel in secret last week to discuss the Jewish state’s refusal to endorse an emerging deal with Iran over its nuclear program. Citing “two senior Israeli officials”, the Tel Aviv-based Israeli newspaper Haaretz said on Tuesday that CIA Director John Brennan arrived in Israel last Thursday. Although he was officially hosted by Tamir Pardo, director of Israeli intelligence agency Mossad, Brennan used the opportunity to hold secret meetings with several senior Israeli officials, said Haaretz. Among them were Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, National Security Adviser Yossi Cohen, as well as Major General Hartzl Halevi, who heads Israel’s Military Intelligence Directorate.
The director of the United States Central Intelligence Agency visited Israel in secret last week to discuss the Jewish state’s refusal to endorse an emerging deal with Iran over its nuclear program. Citing “two senior Israeli officials”, the Tel Aviv-based Israeli newspaper Haaretz said on Tuesday that CIA Director John Brennan arrived in Israel last Thursday. Although he was officially hosted by Tamir Pardo, director of Israeli intelligence agency Mossad, Brennan used the opportunity to hold secret meetings with several senior Israeli officials, said Haaretz. Among them were Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, National Security Adviser Yossi Cohen, as well as Major General Hartzl Halevi, who heads Israel’s Military Intelligence Directorate. The Swiss federal government has rejected a multi-million dollar contract bid by one of the world’s largest broadband Internet service providers, saying it is foreign-owned and could serve as “a gateway for foreign spies”. The company, UPC Cablecom, is headquartered in Zurich, is subject to Swiss law, and is currently the largest broadband cable operator in Switzerland. However, in 2005 it became a subsidiary of the UPC Broadband division of Liberty Global Europe, an international telecommunications and television company based in London, England. It is therefore technically considered a foreign company according to Swiss law. In 2013, UPC Cablecom submitted a bid for a competitive contract to provide broadband Internet services to Swiss government agencies. But in January 2014, the company was informed by Swiss officials that such a contract could not be awarded to a foreign-owned telecommunications service provider such as UPC Cablecom.
The Swiss federal government has rejected a multi-million dollar contract bid by one of the world’s largest broadband Internet service providers, saying it is foreign-owned and could serve as “a gateway for foreign spies”. The company, UPC Cablecom, is headquartered in Zurich, is subject to Swiss law, and is currently the largest broadband cable operator in Switzerland. However, in 2005 it became a subsidiary of the UPC Broadband division of Liberty Global Europe, an international telecommunications and television company based in London, England. It is therefore technically considered a foreign company according to Swiss law. In 2013, UPC Cablecom submitted a bid for a competitive contract to provide broadband Internet services to Swiss government agencies. But in January 2014, the company was informed by Swiss officials that such a contract could not be awarded to a foreign-owned telecommunications service provider such as UPC Cablecom.
 Representatives from Israel and Saudi Arabia have publicly admitted for the first time that they met secretly to discuss their common foe Iran, even though Saudi Arabia does not officially acknowledge Israel’s existence. The admission was made at a symposium held on Thursday at the Council on Foreign Relations, a foreign-policy think tank based in Washington, DC.
Representatives from Israel and Saudi Arabia have publicly admitted for the first time that they met secretly to discuss their common foe Iran, even though Saudi Arabia does not officially acknowledge Israel’s existence. The admission was made at a symposium held on Thursday at the Council on Foreign Relations, a foreign-policy think tank based in Washington, DC. The former director of Colombia’s intelligence service returned to court this week to face charges of complicity in the assassination of a leading presidential hopeful, who was gunned down in 1989 by a powerful drug cartel. Luis Carlos Galán, a senator and former minister, was tipped to win the 1990 presidential election in which he stood on the Liberal Party ticket. His popularity with the electorate is largely attributed to his uncompromising stance against Colombia’s powerful drug cartels. He had vowed to arrest leading drug lords and send them to the United States to face criminal charges. He would do so, he said, after signing a mutual extradition treaty with Washington. However, Galán was assassinated on August 18, 1989, during a campaign rally in Soacha, a working-class suburb of Colombia’s capital, Bogotá. The assassination took place before thousands of spectators who were present at the rally, and is considered one of the highest-profile political killings in the history of Colombia.
The former director of Colombia’s intelligence service returned to court this week to face charges of complicity in the assassination of a leading presidential hopeful, who was gunned down in 1989 by a powerful drug cartel. Luis Carlos Galán, a senator and former minister, was tipped to win the 1990 presidential election in which he stood on the Liberal Party ticket. His popularity with the electorate is largely attributed to his uncompromising stance against Colombia’s powerful drug cartels. He had vowed to arrest leading drug lords and send them to the United States to face criminal charges. He would do so, he said, after signing a mutual extradition treaty with Washington. However, Galán was assassinated on August 18, 1989, during a campaign rally in Soacha, a working-class suburb of Colombia’s capital, Bogotá. The assassination took place before thousands of spectators who were present at the rally, and is considered one of the highest-profile political killings in the history of Colombia. A team of officers from Israel’s Mossad intelligence agency were heading to Cyprus late yesterday to be briefed on the arrest of a dual Lebanese-Canadian citizen, who was found to be in possession of 67 thousand packages of ammonium nitrate. It is not yet clear whether the passports held by the 26-year-old man are genuine. Cypriot police said he used his Canadian passport to enter the Mediterranean island about a week ago. But he was
A team of officers from Israel’s Mossad intelligence agency were heading to Cyprus late yesterday to be briefed on the arrest of a dual Lebanese-Canadian citizen, who was found to be in possession of 67 thousand packages of ammonium nitrate. It is not yet clear whether the passports held by the 26-year-old man are genuine. Cypriot police said he used his Canadian passport to enter the Mediterranean island about a week ago. But he was 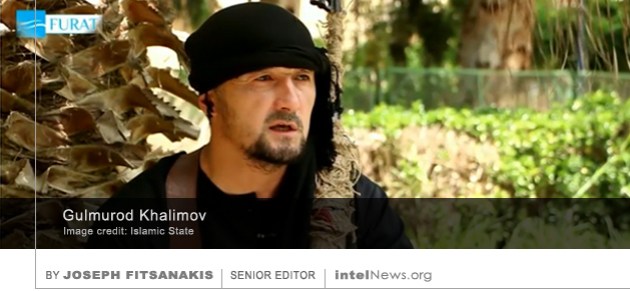 A former army colonel and police commander in Tajikistan, who features in a new Islamic State propaganda video, was trained in counterterrorism by the United States government, according to officials. Until earlier this year, Colonel Gulmurod Khalimov was a commander in Tajikistan’s Special Purpose Mobile Units. Known commonly as OMON, these elite units are a cross between anti-riot corps and counterterrorism forces. They date from the Soviet era and are common features of the law enforcement architecture of most former Soviet republics, including Tajikistan, whose population is 98 percent Muslim.
A former army colonel and police commander in Tajikistan, who features in a new Islamic State propaganda video, was trained in counterterrorism by the United States government, according to officials. Until earlier this year, Colonel Gulmurod Khalimov was a commander in Tajikistan’s Special Purpose Mobile Units. Known commonly as OMON, these elite units are a cross between anti-riot corps and counterterrorism forces. They date from the Soviet era and are common features of the law enforcement architecture of most former Soviet republics, including Tajikistan, whose population is 98 percent Muslim. The office of the Swiss Federal Prosecutor has launched an investigation into claims that the country’s largest telecommunications provider was spied on by a consortium of German and American intelligence agencies. The spy project was
The office of the Swiss Federal Prosecutor has launched an investigation into claims that the country’s largest telecommunications provider was spied on by a consortium of German and American intelligence agencies. The spy project was  A United States district judge has ordered the release of the last major piece of sealed evidence in one of the most important espionage cases of the Cold War. The case led to the execution in 1953 of an American couple, Julius and Ethel Rosenberg, who were convicted of conspiring to spy for the Soviet Union. The Rosenbergs were arrested in 1950 for being members of a larger Soviet-handled spy ring, which included Ethel’s brother, David Greenglass. Greenglass later told a US court that he firmly believed the USSR should have access to nuclear technology and actively tried to give Moscow information on the Manhattan Project. Greenglass agreed to testify for the US government in order to save his life, as well as the life of his wife, Ruth, who was also involved in the spy ring. He subsequently fingered Julius Rosenberg as a courier and recruiter for the Soviets, and Ethel as the person who retyped the content of classified documents before they were surrendered to their handlers. This piece of testimony from Greenglass was used as the primary evidence to convict and execute the Rosenbergs.
A United States district judge has ordered the release of the last major piece of sealed evidence in one of the most important espionage cases of the Cold War. The case led to the execution in 1953 of an American couple, Julius and Ethel Rosenberg, who were convicted of conspiring to spy for the Soviet Union. The Rosenbergs were arrested in 1950 for being members of a larger Soviet-handled spy ring, which included Ethel’s brother, David Greenglass. Greenglass later told a US court that he firmly believed the USSR should have access to nuclear technology and actively tried to give Moscow information on the Manhattan Project. Greenglass agreed to testify for the US government in order to save his life, as well as the life of his wife, Ruth, who was also involved in the spy ring. He subsequently fingered Julius Rosenberg as a courier and recruiter for the Soviets, and Ethel as the person who retyped the content of classified documents before they were surrendered to their handlers. This piece of testimony from Greenglass was used as the primary evidence to convict and execute the Rosenbergs.






Panel to present findings on mysterious death of UN secretary general
June 22, 2015 by Joseph Fitsanakis Leave a comment
On September 17, 1961, a Douglas DC-6 transport aircraft carrying United Nations Secretary General Dag Hammarskjöld crashed in the British-administered territory of Northern Rhodesia (now Zambia). The crash killed everyone onboard. Three successive investigations into the crash, conducted by the Rhodesian Board of Investigation, the Rhodesian Commission of Inquiry, and the United Nations Commission of Investigation, viewed “pilot error” as the most likely cause of the tragedy. However, the latter probe, which was closed in 1962, opined that deliberate sabotage could not be ruled out as a likely cause of the tragedy.
Since that time, numerous scholars and independent investigators, such as Swedish development expert Göran Björkdahl and British academic Susan Williams, have raised the possibility that the plane carrying Secretary General Hammarskjöld may have been “shot down by an unidentified second plane”. Several commentators have also pointed to what seemed like eagerness by British colonial administrators in Northern Rhodesia to obscure the details of the incident. One argument is that Hammarskjöld, described as the most independent-minded secretary general in the history of the UN, had angered many world powers due to this fierce support for anti-colonial movements that were sweeping the African continent. Indeed, at the time of his death, Hammarskjöld was flying to the Congo’s mineral-rich Katanga region to meet European-supported chieftains who in 1960 had seceded from the nationalist government of Congolese Prime Minister Patrice Lumumba. Ironically, Lumumba had been assassinated in a Western-backed coup exactly eight months before Hammarskjöld’s own death.
In 2012, the independently funded Hammarskjöld Inquiry Trust appointed an international team of jurists to study all available evidence on the plane crash. The team, called the Hammarskjöld Commission, was composed of a diplomat and three judges from the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, South Africa, and Sweden. The Commission reported in 2013 that “significant new evidence” had emerged, which suggested that American intelligence agencies, notably the National Security Agency and the Central Intelligence Agency, held “crucial evidence” that could help clarify the causes of the crash.
The report by the Hammarskjöld Commission prompted the UN’s current Secretary General, Ban Ki-moon, to appoint a UN-sponsored panel of experts to examine the new evidence and present it before the UN General Assembly. The three-member panel traveled to several countries, including Zambia, the US, Britain and Belgium, to access government, as well as private archives. Its report is expected to be delivered to the UN General Assembly this week. It is said to include written testimony by a Belgian pilot who says he shot down the plane carrying Hammarskjöld by error, while trying to divert it on orders by a government entity. Another witness, a former intelligence officer with the US National Security Agency, is believed to have told the UN experts that he listened to a recording of a pilot who said he shot down the UN Secretary General’s plane.
Once this new evidence is presented, the UN General Assembly will have to vote on whether the UN should hold an official probe into the plane crash. It would mark the first such inquiry since 1962.
► Author: Joseph Fitsanakis | Date: 22 June 2015 | Permalink: https://intelnews.org/2015/06/21/01-1719/
Filed under Expert news and commentary on intelligence, espionage, spies and spying Tagged with Africa, assassinations, Cold War, Congo, Dag Hammarskjöld, history, News, Northern Rhodesia, suspicious deaths, United Nations